Integumentary System Flashcards
(40 cards)
What are the 4 Skin Derivatives
- Sweat Glands
- Oil Glands
- Hairs and hair follicles
- Nails
What are the 6 functions of skin?
- Chemical, physical & biological protection
- Body Temperature Regulation
- Cutaneous Sensation
- Metabolic functions
- Blood reservoir
- Excretion
How much skin can hold the body’s total blood volume?
5%
What’s the 6 types of damage the skin protects from
- Mechanical Damage
- Chemical Damage
- Baterial Damage
- Thermal Damage
- Ultraviolet Radiation
- Desiccation
What type of skin tissue is the epidermis made of?
Stratified Squamous Epithelium with Keratin

What are the 5 epidermis layers?
- Stratum Basale
- Stratum Spinosum
- Stratum Granulosum
- Stratum Lucidum
- Stratum Corneum
What stratum layer is letter A?
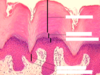
Stratum Corneum

What stratum layer is letter B?

Stratum Lucidum
What Stratum layer is letter D?

Stratum Spinosum
What Stratum Layer is letter E?

Stratum Basale
What Stratum Layer is letter C?

Stratum Granulosum

Where do calluses develop?
Palms of hands and soles of feet
What is the type of protein that provides waterproofing and preserves permeability characteristics such as Nicotine Patches
Glycolipids
What is the upper layer of skin called?
Epidermis
What is the lower, strong, flexible connnective tissue of the skin called?
Dermis
What are the two layers of the Dermis called?
- Papillary Layer
- Reticular Layer
The layer of the dermis that has pain receptors, is a thin, superficial layer of areolar connective tissue and has projections that are for friction ridges and fingerprints
Papillary Layer
The layer of the dermis that makes up 80% of the dermis, has blood vessels, sweat glands
Reticular Layer
What does the reticular layer of the dermis have?
Blood vessels, glands, nerve receptors and eleastic fibers
What is the gland that produces oil, softens and lubricates hair and skin and are activated at puberty
Subaceous Glands

What is the type of sweat gland that dissipates excess heat through evaporative cooling?
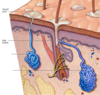
Eccrine Gland

What is the sweat gland that is in the armpits & pubic area that ducts emptu into hair follicles and is activated by strees, pain & sexual excitement and NOT by temperture

Apocrine Gland

What is the modified sweat gland that is found in the lining of the external ear canal
Ceruminous gland
Where on the skin is hair not on?
Soles, Lips, & Nipples



