Infectious and Skin Diseases Flashcards
What type of inflammation is depicted here?

Fibrinous inflammation (deposit from extudate due to large vascular leakage)
F = fibrin
P = pericardium

What cell produces Immunoglobulin A (IgA)?
Plasma cells associated with mucosa
True or false
Bacterial exotoxins are highly toxic and can be fatal in microgram quantities.
True
What type of inflammation is depicted here? What are the arrows, triangles, and stars indicating?

Chronic inflammation
Triangle = tissue destruction
Arrow = attempted repair
Star = granuloma (chronic inflammatory cells)

Pemphigus is an autoimmune disorder that causes blisters. Where do autoantibodies attack?
Intercellular junctions in the epidermis and mucosa
(Desmoglein, BPAG2, and anchoring filaments)
What type of blister is depicted here?

Subcorneal
What type of blister is depicted here?

Subepidermal
What disease is depicted here? What are its hallmark characteristics?

Psoriasis
Thickened epidermis (elongated rete ridges)
Neutrophil infiltration
Excessive epidermal proliferation
Accumulation of nucleated cells in stratum corneum (parakeratosis)
What type of inflammation is depicted here? Is it acute or chronic?

Granuloma
Chronic
What organism causes trichinosis? How is it usually obtained?
Trichinella Spiralis (nematode)
Ingestion of undercooked meat (typically pork)
Is this initial or late acute inflammation?
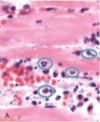
Initial
(congested blood vessels and neutrophil infiltration)

Describe the enteric and muscle phases of trichinosis in regard to Trichinella spiralis’s life cycle.
Enteric:
- Adult in intestines and produce larva
- Larva infiltrate blood
- Exit blood vessels
Muscle:
- Infect skeletal muscle fibers
- Adults die and muscle fiber calcifies

True or false
Bacterial exotoxins do not bind to specific receptors.
False.
They DO bind to specific receptors.
What type of blister is depicted here?

Suprabasal
What type of inflammation is depicted here? Is it acute or chronic?

Purulent inflammation
Acute

Describe the cytology of verrucae
Cytoplasmic vacuolization (halos)
Increased keratohyalin granules
Eosinophilic keratin aggregates in cells

What type of blister is a Vulgaris pemphigus?
Suprabasal
What is the clinical presentation of muscle stage trichinosis?
Myalgia and paralysis
Fever, headache, skin rash
Edema and conjunctivitis
(typical of infection/muscle damage)
Is this initial or late acute inflammation?

Late
(mononuclear WBCs - lymphocytes, macrophages, and plasma cells)

What tissue does trichinosis infect? What are the symptoms?
Infects skeletal muscle
Symptoms: fever, myalgia, and periorbital edema
What type of inflammation is pictured here? Is it acute or chronic?

Serous inflammation (blister)
Acute

What type of blister is a Bullous pemphigoid?
Subepidermal
(or nonacantholytic)
What causes verrucae?
Human papillomaviruses (HPV)
What structure is depicted here?
Hint: trichinosis

Nurse cell-larva complex
What are some histologic indicators of acute inflammation?
Dilation of small blood vessels
Increased microvasculature permeability
Migration and activation of immune cells
How does IgA prevent degradation against viral/bacterial proteases?
Extensive glycosylation
True or false
Bacterial endotoxins are excreted by the cell.
False.
They are part of the cell way and are released when bacteria are destroyed
What is the clinical presentation of enteric stage trichinosis?
Diarrhea
Nausea
Vomiting
Pain
Low-grade fever
(all typical of enteric diseases)
True or false
bacterial endotoxins don’t typically induce fever?
False.
They always induce fever.
What are some histologic indicators of chronic inflammation?
Infiltration by macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells
Tissue destruction
Attempts at healing
True or false
Bacterial exotoxins are highly antigenic and can be neutralized by antitoxins.
True
What is a consequence of such a strong immune response against Trichinella spiralis larvae?
Inflammatory response can cause widespread tissue damage
What type of blister is a Foliaceus pemphigus?
Subcorneal
What is depicted here?

Verruca (wart)
What is acantholysis?
Dissolution of intercellular bridges
At what dose are endotoxins actually toxic?
10-100 micrograms
What are the symptoms of viral and bacterial meningitis?
Acute onset fever
Headache
Stiff neck
Photophobia
Confusion
What causes the most damage to neuronal tissue in meningitis?
Pressure
Describe ciliostasis
Attachment of bacteria to impede cilia movements, which prevents movement of bacteria out of the tissue


