Immune and Soft Tissue Diseases Flashcards
What are two potential therapies for osteoporosis?
Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)
Bisphosphonates (induce osteoclast apoptosis)
Where are Rheumatoid nodules typically found?
Regions subjected to pressure
Ex: elbows and lumbosacral region
What are Rheumatic diseases? Are they autoimmune?
Connective tissue disorders, mainly bone/cartilage
Not all are autoimmune
True or false. In chronic autoimmune diseases, relapses are typically milder.
False. Immune memory makes it so relapses have a more robust response
(In a normal immune system, amplification mechanisms are beneficial to eliminated pathogens)
Describe a type I hypersensitivity
Immediate hypersensitivity
Production of IgE and later recruitment of inflammatory cells
What are some profibrotic cytokines? (3)
Transforming Growth Factor (TGF-β)
IL-13
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
Excessive fibrosis throughout the body is known as?
Systemic sclerosis
Glomerular Lupus Nephritis results in?
Compromised kidney function

Describe mast cell-dependent/IgE-independent Urticaria.
Direct degranulation of mast cells
Induced by opioids, antibiotics, curare, contrast media
What is allergic rhinitis? Cause?
Immediate hypersensitivity to inhaled antigens
Sustained IgE release in response to antigen
Secondary immunodeficiency syndromes are?
An effect of another disease like cancer, infection, or malnutrition
What is osteomyelitis?
Inflammation of bone and/or marrow
Are autoimmune diseases typically monogenic or complex multigenic disorders?
Complex multigenic disorders
Increased production of IgE leads to?
Immediate release of vasoactive amines and other mediators from mast cells
What are the clinical characteristics of Bruton agammaglobulinemia?
Absent/decreased circulatory B-cells
Low Ig levels of all types
Germinal centers underdeveloped (lymph nodes, tonsils, etc.)
Plasma cells absent throughout
What type of autoimmune disease is Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
Type III hypersensitivity
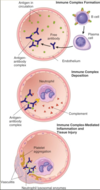
Describe the etiology acute necrotizing vasculitis
Type III hypersensitivity
Inflammation induced at the site of immune complex deposition
What are some consequences of fibrosis in regard to the GI tract?
Progressive atrophy/fibrous replacement of muscularis (especially in esophagus)
Weakens esophageal sphincter (causes GERD)
Malabsorption due to loss of villi/microvilli in small intestine
Describe the progression of joint damage?
- Lymphatic infiltration of synovium
- Vasodilation and angiogenesis
- Fibrin aggregates overlying synovium and free floating in fluid
- Surface synovial neutrophil accumulation
- Pannus formation
- Osteoclastic destruction

Describe the pathology of erythematosus
Degeneration of stratum basale
Edema in epidermis and dermis
Vasculitis
Immune complex deposition at epi:dermis junction

Describe the environmental etiology of SLE
UV irradiation (altered DNA becomes immunogenic)
Hormones and drugs
Of the five patterns of Lupus Nephritis, how many involve deposition of immune complexes into the glomerulus and how many involve deposition into the mesanginum
2 in glomerulus
3 in mesanginum
Antibody:antigen complexes form in the presence of?
excess antigen after antibody production
Uric acid levels increase in the body due to? (4)
Excess purine catabolism
Defects in purine salvage
Diuretic administration
Reduced glomerular filtration in the kidneys
How can Glomerular Lupus Nephritis be detected?
Detected as hematuria and proteinuria
Urticaria (aka Hives) is described as?
Acute inflammatory dermatosis
What are the consequences of chronic gout?
Joint damage and eventual joint deformity
Crystal deposition in subcutaneous areas (tophus)
What is the normal function of PDGF?
Regulates proliferation and differentiation of stromal cells during embryogenesis
May promote differentiation of adult stem cells or stimulate existing stromal cells
Still not fully understood
Autoimmune pathogenesis can be caused by?
Failure of self-tolerance
Defective regulation
Abnormal presentation of self-antigens
Inflammation
What is the mechanism by which IgE functions? In what cell type does this happen
Binds to dimer-receptor complex –> activates tyrosine kinase –> degranulation by the release of cytoplasmic vesicles (histamines)
Mast cells
What are the clinicopathologic manifestations of SLE?
Nephritis
Skin lesions
Arthritis
What are some of the clinical presentations of an immediate hypersensitivity? (4)
Anaphylaxis
Bronchial asthma
Allergic rhinitis or sinusitis
Food allergies
An immune response ends when?
Phagocytes clear all antigen
Lack of T-cell stimulation results in apoptosis
Persistent hives may indicate?
Hodgkin lymphoma
How can SLE be diagnosed?
Test for anti-nuclear antibodies to dsDNA
In children with osteomyelitis, how do bacteria typically reach bone?
Bloodstream
Pyogenic osteomyelitis is commonly caused by what bacteria?
S. Aureus
Describe diffuse scleroderma. Is it more or less severe
Onset - widespread skin involvement
Rapid progression
Early visceral involvement
MORE SEVERE
What is Gout? Is it autoimmune?
Inflammation of synovial joints induced by presence of uric acid crystals
Compare and contrast acute vs. chronic rheumatic diseases
Acute:
External initiation, stops after exposure (self-limiting), flares on re-exposure
Chronic:
Remote initiation, autoimmune (self-propagating), frequent flares due to immune memory
What enzyme is responsible for the production of uric acid in purine catabolism? What drug can inhibit it?
Xanthine oxidase
Allopurinol
Primary immunodeficiency syndromes are?
Genetic
What is erythematosus?
Rash of the malar area (bridge of nose and cheeks)
Ankylosis of joints refers to?
Abnormal stiffness and rigidity due to adhesion and fibrosis
Antibody:Antigen complexes are normally cleared by macrophages, but become pathogenic when?
Deposited beneath the epithelium (oftentimes endothelium)
What structures do anti-nuclear antibodies typically recognize?
DNA (native/dsDNA)
Histones
Non-histone RNA-bound proteins
Nucleolar antigens
What occurs after the immediate hypersensitivity reaction (pathologically speaking)?
Infiltration of eosinophils, T-cells, and neutrophils
Patients with BTK have ______ T-cell immunity
Normal
What is the mechanism by which histamine functions?
Diffuses through bloodstream –> binds to G protein-coupled receptor H1-3 on endothelial, nerve, and smooth muscle cells –> increases vascular permeability by dilation blood vessels
What gene is mutated in Bruton agammaglobulinemia? How is it inherited?
Mutation in Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK)
X-linked
What occurs during the early stage of an allergic response?
Release of histamine, leukotrienes, and prostaglandin D2 –> induces sneezing, nasal secretion, and mucosal swelling
(all in ~5 minutes)
Describe a type III hypersensitivity
Immune complex-mediated
deposition of antigen-antibody complexes –> recruitment of leukocytes –> release enzymes and toxic molecules
Describe the neutrophil, protein, and mucin counts in the synovial fluid of someone with Rheumatoid Arthritis
High neutrophil count
High protein count
Low mucin count
What is the normal function of IL-13?
Activates TGF-β
Why should patients with BTK never be given an immunization with a live virus?
Without any functional Ig, the virus can invade the bloodstream and cause the actual infection
What is the primary cause of hives?
Localized mast cell degranulation
Although it is not diagnostic, erythematosus could be an indicator of?
SLE
What gene is typically associated with the etiology of SLE?
Major histocompatibility complex
What is the normal function of BTK?
Part of the signaling pathway within maturing B-cells for quality control checkpoints
What are some consequences of fibrosis in regard to skin?
Loss of elasticity/flexibility
Thinning of epidermis, loss of associated structures (hair and nails)
Development of calcifications and ulcerations
In adults with osteomyelitis, how do bacteria typically reach bone?
Fractures
Surgery
Diabetic infections of the feet
What is the normal function of TGF-β
Activates myofibroblasts to produce extracellular matrix leading to scar formation
What is the most frequent site for systemic sclerosis?
Skin (Scleroderma)
Describe mast cell-dependent/IgE-dependent Urticaria
Localized immediate hypersensitivity
Associated with exposure to pollen, food, drugs, insect venom
What antigens are typically involved in SLE?
Nuclear antigens (circulating or “planted” in the kidney)
Describe a type IV hypersensitivity
Cell-mediated
Activated T-lymphocytes release cytokines –> macrophage activation or T-cell mediated toxicity
Describe limited scleroderma. Is it more or less severe?
Skin involvement is limited to fingers, forearms, and face
Visceral involvement is late (“benign”)
Slow progression
LESS SEVERE
What occurs during the first hour of a hypersensitivity response (pathologically speaking)?
Vasodilation
Congestion
Edema
A hypersensitivity is caused by?
An imbalance between effectors and limiters (failure of normal regulation)
Describe a type II hypersensitivity
Antibody-mediated
Production of IgG and IgM –> opsonization –> phagocytosis or lysis
Patients with BTK are at risk for? Specifically?
Recurrent respiratory tract infections
- H. influenzae*
- S. pneumoniae*
- S. aureus*
What occurs during the late stage of an allergic response? Chronic exposure?
Within 2-4 hours influx of eosinophils and monocytes
Chronic exposure changes tissue structure
What are some consequences of fibrosis in regard to the lungs?
Interstitial fibrosis
Pulmonary hypertension
Mast cell-independent/IgE-independent Urticaria is caused by
Chemicals or drugs that inhibit COX and arachidonic acid production
or
Hereditary disorder
Describe the immunological etiology of SLE
Failure to eliminate self-reactive B-cells
Cytokines promoting unregulated B-cell activity


