Imaging of the abdominal viscera Flashcards
What are the different imaging modalaties for abdomen?
▶X-ray (plain film) / Fluoroscopy
▶Ultrasound (US)
▶Computed Tomography (CT)
▶Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
What are the 2 types of MRI images?
▶Many types of image sequences, but T1 & T2 weighted are the most important
◦T1 : fluid is black
◦T2 : fluid is white
How are these MRI images weighted?


What is contrast?
▶Used to increase contrast resolution (ie. highlight specific areas/organs)
▶Is given intravenously (IV), or enteral (oral/PR) before a scan
▶Is either more or less dense than surrounding tissues (for XR/CT), or paramagnetic (for MRI)
Complete the table on imaging modalities


What is Intra-peritoneal vs Retro-peritoneal?

What are the solid abdominal viscera and what is a good first line test for them?
liver, spleen, pancreas
US – a good first line test for solid viscera
What are hepatic segements divided by?
◦Divided by portal vein (horizontally) & hepatic (vertically) veins
Label the diagram


























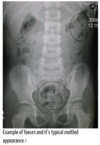
What is the pathology?

CT :gallstones

What is the pathology?

CT : metastases

What is the intervention?

Intervention: ERCP