Imaging-Fractures Flashcards
(29 cards)
What are the areas of bone indicated?

Physis, medulla and cortex

How many views are necessary for radiological diagnosis?
2 othogonal (perpendicular) views. You can’t see a fracture unless the x-ray beam is tangential to the fracture.

Why is it important to get a view of distal and proximal structures of a deltoid ligament rupture as seen below?

The force needed to break the ligament is also transmitted up the interosseous membrane. Notice the fracture that concurrently occurred in the top of the fibula.

What is soft tissue swelling typically related to in a child? In an adult?
Child = bone injury (weakest part of their bodies). Adult = ligament or tendon injury
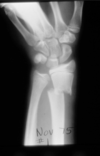
What is dislocated in this patient?

Lunate. It should be lined up parallel with the capitate and the scaphoid.

What are important things to look for when trying to find fractures in radiographs?
Breaks in the cortex, abnormal densities (dislocations), soft tissue swelling and hemarthrosis.
What is the sail sign in the elbow?
The anterior fat pad that surrounds the joint capsule of the elbow gets pushed out due to joint effusion. Joint effusion can hint towards a fracture because a fracture can cause blood to fill the joint space.

What fracture is common in a FOOSH injury in children and elderly? Adults? Really young children?
Colles fracture (distal radius). scaphoid. Distal humerus fracture.
An elderly woman falls on an outstretched hand. Radiographs are shown below. What is your diagnosis?

Colles fracture (distal radius)
What bone could you examine better for a fracture if you have the patient ulnar deviate?

Scaphoid

What lingo do you use when describing a fracture to an orthopedic surgeon?
*

When might you have to treat this patient with antibiotics?

If it is a tuft fracture (the nailbed is not in tact and it is an open fracture)
Where is this humeral head displaced?

Anteriorly, this is the most common direction for dislocations because ligaments are weak there.
What type of fracture is this?
Transverse. It is transverse to the bone.
What type of fracture is this?

Oblique. The fracture is oblique to the bone.
What type of fracture is this?

Spiral fracture. It goes 360 degrees around the bone.
How would you describe the angulation of this femoral fracture?

The apex of angulation is medial or the apex of the distal fragment is lateral.
How would you describe the displacement of this radial fracture?

The distal fragment is displaced laterally half the bone width.
How can you tell if a fracture has rotated?
Look for changes in density around the cortex of the fracture.
Which of these breaks is more common?

The over-ride. Muscle often pulls the broken bone back so they over-ride each other. Distraction is much less common.
What modality is more sensitive in diagnosing stress fractures?
Bone scan (bottom picture) or MRI (top picture)

What do you see here?

A little stress fracture. Note the little line of sclerosis that breaks the lines of trebeculae that go in the weight bearing direction.
A hurdler comes to see you with this condition. What is your diagnosis?

An avulsion fracture of the ischial tuberosity from the hamstrings pulling on it.
What makes your wheels start spinning when you see this? What additional view do you need to do to confirm you diagnosis?

There is a lot soft tissue swelling beneath the patella so you start thinking about joint effusion. Doing a cross-table lateral view will allow you to see elevation of fat caused by fat leaking out of the marrow of a broken bone.





