Anatomy-Final Cram Sesh Flashcards
What is indicated by the white arrow?

Vertebral prominens
Where are the breaks located in this bone?

Pars interarticularis
What is coming out of the vertebral body in this image?

Nucleus pulposus
What causes this?

This is winged scapula caused by loss of innervation to the serratus anterior (long thoracic nerve)
What comes from the paraxial mesoderm?
Somites. These then differentiate into skeletal muscle, cartilage, tendons, endothelia and skin.
Where does CSF reside?
Subarachnoid space
Where does 50% of cervical spine motion come from?
The atlanto-axial joint. The axis has the dens and the atlas sits on top of it, holding the dens in place with the transverse ligament

What provides blood supply to the ventral 2/3 of the spinal cord?
Anterior spinal arteries, to include the Great Anterior Segmental Medullary Artery of Adamkiewicz
What are all of these structures of the lateral neck?

Posterior scalene, Middle scalene, Phrenic nerve, Internal Jugular, Anterior Scalene, and Subclavian Artery/Vein

What are the different branches that come off the axillary artery?

1.) Superior thoracic 2.) Thoracoacromial, Lateral Thoracic 3.) Subscapular, Anterior and Posterior Circumflex Humeral

What muscles of the rotator cuff are seen here?

Supraspinatous, infraspinatous and teres minor

What muscles of the rotator cuff are seen here?

Supraspinatous, biceps long head tendon and infraspinatous

What are the different parts of the breast?

Lobule, fat, retromammary space and suspensory ligaments

How can you detect if the phrenic nerve was lacerated?
The paralyzed side will ascend on inspiration due to increased pressure from the gut as the non-paralyzed side descends on inspiration.

What are the branches of the brachial plexus?

*

What are the different components of the arm?

*

What is the pathway of lymph node drainage from the breast?

*

What is causing skin dimpling in this breast?

An aggressive breast tumor that has invaded the suspensory ligaments of Cooper

What is causing the signs seen in this breast?

Obstruction of lymphatics by advancer cancer cells.
What percent of breast cancers metastasize to the parasternal lymph nodes? What is the greatest risk factor for breast cancer?
5%. Age
What muscles attatch to the medial epicondyle of the humerus?
Pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris

What is the pathway of the radial artery through the forearm and into the hand? The ulnar?
*

What goes around Lister’s tubercle?
Extensor pollicus longus
Where does the anterior interosseous nerve branch from? Posterior interosseous nerve?
Median. Radial
What muscles of the hand are supplied by the median nerve?
Abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis and the first two lumbricals
What muscles of the forearm are supplied by the radial nerve and deep branch of the radial nerve?

Brachioradialis, ECRL, ECRB (deep branch), supinator (deep branch)

What muscles of the forearm are supplied by the posterior interosseous branch of the radial nerve?

extensor digitorum, extensor digit minimi, extensor carpi ulnaris, APL, EPB, EPL and extensor indicis

What are the bones of the hand?

*

What muscles do the nerves indicated innervate?

Median = 1st and 2nd lumbricals. Recurrent Median = APB, FPB and opponens pollicis. Ulnar deep branch = 3rd and 4th lumbricals, dorsal interossei, palmar interossei, digiti minimi (flexor, abductor and opponens) and adductor pollicis.

What is the most common type of shoulder dislocation?
Anterior
What actions do the interossei of the hand do?
Flexion of MPJs and extension of IPJs.
What are the primary flexors of the MPJ of the thumb?
Thenar muscles
What are the primary extensors of the MPJ of the thumb?
EPB
What is the primary flexor of the IPJ of the thumb?
FPL
What is the primary extensor of the IPJ of the thumb?
EPL
What flexes the MPJs of the phalanges? What extends them?
Interossei = flex. EDC = extend
What flexes the PIPs of the phalanges? What extends them?
FDS = flex. Interossei = extend
What flexes the DIPs of the phalanges? What extends them?
FDP = flex. Interossei = extend
What are the extensor compartments of the wrist?

*

What muscles flex the joints of the fingers when making a fist? What about in extension?
Flexion = DIP: FDP, PIP: FDS, MPJ:IO Extension = DIP: IO, PIP: IO/EDC, MPJ: EDC
What is meant by PAD and DAB? How can you use this to test for ulnar nerve function?
Dorsal interossei abduct, palmar interossei adduct. Someone with an intact ulnar nerve will still be able to abduct their fingers.
What nerve is injured if you can’t oppose your thumb?
Median nerve
Which artery supplies the superficial palmar arch? Deep palmar arch?
Superficial = ulnar artery. Deep = radial artery
Radial nerve palsy presentation?
Numbness of 1st interosseous webbed space. Wrist drop because they cannot extend their wrist.
Median nerve palsy presentation?
Thenar atrophy. Weakness in thumb opposition and abduction.
Ulnar nerve palsy presentation?
1st dorsal interosseous atrophy. Cannot abduct fingers and claw hand.
Why are bursa sacs located over the ischial tuberosity, greater trochanter and elbow?
They protect bony prominences that are not covered by muscle and have a high potential for friction.
What muscles allow the opposite foot to clear the ground with each step? What innervates these structures? What positive test will they have?
Gluteus medius, minimus and tensor fascia lata. Superior gluteal nerve. Trendelenberg’s test.
What innervates the short head of the biceps? The other hamstrings?
Common fibular division of sciatic nerve. Tibial division of sciatic nerve.
How does a patient present with a posterior dislocation of the hip?
Internally rotated and short limb than cannot be extended.
How does a patient present with an anterior dislocation of the hip?
Laterally rotated thigh that is lengthened. The femoral head will also be palpable under the inguinal ligament.
What inverts the foot
Tibialis anterior and posterior
What everts the foot
Fibularis longus, brevis and extensors
If a patient wakes up from laying on their side for a number of hours and wakes up with a foot drop, what nerve was likely compressed?
The anterior and lateral compartments are affected because the common fibular nerve was compressed.
Where can you find the dorsalis pedis pulse?
Lateral to the extensor hallicis longus
*

*

What are the sensory nerves that innervate the different portions of the leg?

*

What muscles fire during gait?
*

What aspects of the urogenital and anal triangles are shared? What are unique?
Urogenital and anal triangles share base borders with points at the ischial tuberosities. The peak of the urogenital triangle is the pubic symphysis and the coccyx for the anal triangle.

What are the landmarks indicated in this femur?

*

What vascular structure runs with the pudendal nerve?
Internal pudendal artery
What muscle in the anterior compartment receives some blood supply from the lateral circumflex femoral artery?
Vastus lateralis
What is the main arterial supply of all the gluteal muscles?
Superior gluteal artery
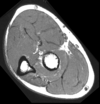
Label the muscles seen in this image.

*

What muscle does the obturator nerve sit on top of?
Adductor brevis
What two bones are joined together by the spring ligament?
Calcaneus and navicular
What tendons support the cuneiforms like a stirrup?
Tibialis posterior and fibularis longus tendons
Where are diabetics most likely to get sores on their feet?
Weight bearing areas: Heads of metatarsals, sesamoid bones and calcaneus
At what joint does most inversion and eversion of the foot take place?
Subtalar
What bones of the hand articulate with the bones of the arm?
The scaphoid and lunate articulate with the radius. Nothing articulates with the ulna.
Label the muscles seen in this image.


Label the muscles in this image.