Histology: Glands and secretion Flashcards
Organs in the human body that would be made up of epithelial cells that function mainly to produce and secrete various macromolecules.
Glands
___can be used in the body or they can be discharged into the surroundings
Macromolecules
Macromolecules that are useful
secretions from pancreatic gland
salivary gland
Macromolecules that can be discharged
secretions from the sweat glands
Functions of glands
Synthesize, store and release proteins, lipids, complexes of carbohydrates and proteins
secretes substances mainly made up of proteins
Pancreas
secretes lipids
Adrenal and Sebaceous glands
secretes complexes of carbohydrates and proteins
Salivary gland
secretes milk which is actually composed of all of the above substances (proteins, lipids, complexes of carbohydrates and proteins)
Mammary gland
Some glands have ____ activity and secrete mostly ___ and ____
little synthetic
water and electrolytes
Elaboration or release or discharge of fluids by epithelial cells containing various substances usually mucin, enzymes or hormones needed by the body
Secretion
Secretion does not require expenditure of energy (ATP) thus work is performed, T/F
False- requires
Elaboration or release of waste products not
needed by the body
Excretion
T/f, Excretion doesn’t require energy therefore no work is
Performed
true
Epithelial linings of internal body surfaces
lubricated by mucin
Mucous membranes
___is a product of combination of water and glycoprotein (mucin
Mucus
a.k.a. scattered secretory cells
UNICELLULAR GLANDS
T/F, Secretory cells are not distributed among non-secretory cells
False- distributed
Class of glands common in columnar, cuboidal and pseudostratified epithelium
UNICELLULAR GLANDS
Example of Unicellular glands
Goblet cells
important component in the lining of the intestines (columnar epithelium) and respiratory tract (pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)
Goblet cells
Secretes lubricating mucus that aids in the function of the intestines and respiratory tract
Goblet cells
Developed from the covering epithelia in the fetus by self-proliferation and growth in the underlying connective tissue followed by further differentiation
MULTICELLULAR GLANDS
Formed by invagination of epithelial layers in deeper tissue to form a diverticulum
MULTICELLULAR GLANDS
Parts of MULTICELLULAR GLANDS
o Proximal part
o Distal part
Part of MULTICELLULAR GLANDS that forms duct
Proximal part
Parts of MULTICELLULAR GLANDS
o Distal part
MULTICELLULAR GLANDS differentiate into?
exocrine and endocrine glands.
TYPES OF MULTICELLULAR GLAND
EXOCRINE GLAND
ENDOCRINE GLAND
Glands will remain connected with the surface epithelium through the duct and deliver the secreted material where it is going to be used.
EXOCRINE GLAND
Example of Exocrine glands
Lacrimal gland (in the eyes),
Salivary gland,
Urethral gland,
Intestinal glands
Releases hormones which will exert their effect at a distant target organ and loose their connection to their original epithelium
ENDOCRINE GLAND
ENDOCRINE GLAND do not have ducts, T/F
True
They have thin walled vessels (capillaries) that are going to be adjacent to the endocrine cells
ENDOCRINE GLAND
secrete products directly into the bloodstream
endocrine glands
Examples of endocrine glands
Pituitary gland, Pineal Gland, Thyroid, Parathyroid, Adrenal, Ovaries
___ have both endocrine and exocrine components
Testis, Pancreas
pancreatic gland that discharge pancreatic juice into small intestine
EXOCRINE GLAND
pancreatic gland that discharge various hormones such as insulin from beta cells
endocrine
pour their secretions onto an epithelial surface directly or through ducts
EXOCRINE GLAND
Organ that secretes erythropoietin (EPO)
kidney
hormone that stimulates blood cell production
Erythropoietin
Target organ of Erythropoietin
Target organ: Bone Marrow
organized as a continuous system of many small secretory portions and ducts that transport the secretion out of the gland
Epithelia of exocrine glands
small secretory systems that transport secretions out of the gland
Secretory acini
both endocrine and exocrine gland, units are supported by a ___.
stroma of connective tissue
layers of tissue are surrounding the larger ducts to form ____ separating the glands into lobes and lobules.
partitions or septa
CLASSIFICATION OF EXOCRINE GLANDS ACCORDING TO BRANCH FEATURE
SIMPLE GLANDS
COMPOUND GLANDS
Type of exocrine glands in which DUCTS do not branch, open directly to surfaces
SIMPLE GLANDS
Type of exocrine glands in which DUCTS branch out into several secretory units
COMPOUND GLANDS
Secretory units drain into smaller ducts that converge into one large duct
COMPOUND GLANDS
CLASSIFICATION OF EXOCRINE GLANDS ACCORDING TO MECHANISM OF EXOCRINE GLAND SECRETION
I. MEROCRINE SECRETION
II. HOLOCRINE SECRETION
III. APOCRINE SECRETION
Most common method of protein or glycoprotein secretion
MEROCRINE SECRETION
Involves exocytosis from membrane bound vesicles or secretory granules
MEROCRINE SECRETION
MEROCRINE SECRETION release their secretion either by ___ or ____ with the glandular cell remaining intact;
diffusion or exocytosis
most common manner of secretion
MEROCRINE SECRETION
Manner at which Salivary glands and pancreatic glands are secreted
MEROCRINE SECRETION
T/f, Most exocrine glands are merocrine
true
Releases product and debris into the gland’s lumen as cells disintegrate
HOLOCRINE SECRETION
Seen in sebaceous glands producing lipids rich materials in the skin.
HOLOCRINE SECRETION
As the cell grows larger, it accumulates more and more products and eventually, this cell will disintegrate and would release their secretion into the lumen of the duct
HOLOCRINE SECRETION
Meibomian gland of the eyelid undergoes what type of secretion
HOLOCRINE SECRETION
Best example of Holocrine glands
Sebaceous glands of hair follicles
Products accumulate in the apical ends where a portion of cell will be extruded to release products with small amounts of cytoplasm and cell membrane
APOCRINE SECRETION
lipid droplets by mammary glands undergoes what type of secretion
APOCRINE SECRETION
Part of the glandular cell usually the ___ is discharged with the secretion which causes damage to the part of cell/loss of cytoplasm
apical portion
Example of apocrine secretion
Mammary glands
CLASSIFICATION OF EXOCRINE GLANDS ACCORDING TO NATURE OF SECRETORY PRODUCTS
I. MUCOUS GLANDS
II. SEROUS GLANDS
SECRETORY PRODUCTS WILL HAVE DISTINCT STAINING PROPERTIES
secretions of mucous and serous glands
Contain mucous cells
MUCOUS GLANDS
Goblet cells are what type of exocrine
MUCOUS GLANDS
The Cytoplasm of MUCOUS GLANDS is filled with secretory granules containing ___
mucinogen
MUCOUS GLANDS stain ___ with H&E and therefore gives ___
very lightly
empty look
In Mucous glands, the Nuclei is basally placed and rounded, T/F
F- flattened
___pushes the nuclei of Mucous glands
mucoid
Mucous glands have___ and ___that are filled apically with secretory granules
RER
Golgi complexes
heavily glycosylated proteins in mucous glands
mucin
Mucin has ___binding properties
water
Mucin is ___when released from the cell
hydrated
Water + Mucin =
Mucus layer
____ is usually washed from cells during routine histological preparation
Hydrophilic mucus
Hydrophilic mucus stain ___with eosin; therefore looks ___
poorly
empty
What should be present in a developing mucinogen granules to allow the mucous cells to be stained by the Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) Method
sufficient oligosaccharides
Mucous gland secretions contain ___which collects in the ___ part of cell
mucopolysaccharides
apical
Contain serous cells
SEROUS GLANDS
In SEROUS GLANDS, the cells have well developed RER and Golgi complex. T/F
true
Serous cells are filled apically with ___ in different stages of maturation
secretory granules
Serous cells stain intensely with ___ and ____
basophilic and acidophilic stains
Secretions of SEROUS GLANDS are
thin, watery, rich in enzymes, protein in nature
The cytoplasm of SEROUS GLANDS are
granular & rich in RER
The cytoplasm of SEROUS GLANDS stains
darkly from pink to dark purple with H&E
The nuclei of SEROUS GLANDS are
Rounded and basally placed
SEROUS GLANDS synthesize proteins that are mostly ____
not glycosylated
Example of serous gland secretion
Digestive Enzymes
E.g. of serous cells
Acini of Pancreas and
Parotid Salivary glands
Contain both serous and mucous secretory units
MIXED GLANDS
They have serous acini and mucous tubules with clustered serous cells
MIXED GLANDS
Product of MIXED GLANDS are a mixture of ___ and ____
digestive enzymes and watery mucous
Serous cells form crescentic caps on mucous acini called ____
serous demilunes
Contractile cells that are rich in actin filaments and myosin
MYOEPITHELIAL CELLS
MYOEPITHELIAL CELLS are found at _____
basal ends of secretory units
Have long processes that will embrace an acinus as an octopus might embrace a rounded boulder
MYOEPITHELIAL CELLS
MYOEPITHELIAL CELLS are bound to basal lamina by ____
hemidesmosomes
MYOEPITHELIAL CELLS are connected to epithelial cell by ___ and ____
gap junction and desmosomes
Contraction of MYOEPITHELIAL CELLS propel secretory products from the ____ to the ___
acini to the duct system
Includes sweat glands, lacrimal glands, salivary glands and mammary glands
MYOEPITHELIAL CELLS
Lack myoepithelial cells
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
Specialized for protein or steroid hormone synthesis
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
Proteins of ENDOCRINE GLANDS are released by ___
exocytosis
Lipophilic steroids are released by ___through ____ for uptake by binding proteins outside the cell
diffusion
cell membrane
ENDOCRINE GLANDS targets _____
cells throughout the body
__ glands in which secreted substances are hormones carried throughout the body by the interstitial fluid and blood, with specificity produced by the hormone receptors of target cells.
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
ENDOCRINE GLANDS lack ducts, T/F
true
Substance Action of ENDOCRINE GLANDS
Autocrine action
Paracrine action
Endocrine action
substance produced will act on itself
Autocrine action
substances produced will act on
Paracrine action
substance produced is transferred to distant cell through circulatory system
Endocrine action
The liver’s endocrine gland produces and secrete ____, ____, and ___ into the bloodstream.
plasma proteins, clotting factors and insulin-like growth factors
The liver’s exocrine gland secretes___ into the digestive system for chemical digestion of lipids.
bile
endocrine cells of pancreas is called
Islet of Langerhans
exocrine cells of pancreas is/are called
cells surrounding the Islet
Adrenal Cortex of the Adrenal Gland only has (endocrine or exocrine) Function???
endocrine
layer of adrenal gland that secretes Aldosterone
Zona Glomerulosa
layer of adrenal gland that secretes cortisol
Zona Fasciculata
layer of adrenal gland that secretes androgens
Zona Reticularis
Layers of adrenal cortex
Zona Glomerulosa
Zona Fasciculata
Zona Reticularis
Capsule
Simple branched acinar exocrine glands within the skin
SEBACEOUS GLANDS
SEBACEOUS GLANDS release a fatty substance known as___ in follicular ducts
sebum
Sebum helps the skin to be ___ and ___.
flexible and prevents water loss.
SEBACEOUS GLANDS is a what type of secretion
holocrine
The sebum in SEBACEOUS GLANDS is going to be released when these secretory cells _____
degenerate or disintegrate
Entire sebaceous cell is filled up with ____- rich product as they differentiate
lipid
separate and disintegrate to release lipid that serves to protect and lubricate adjacent skin and hair
Mature cells (a.k.a. Terminally differentiated cell)
SEBACEOUS GLANDS is filled with myoepithelial cells, T/F
false, lacks
____ in SEBACEOUS GLANDS inside a dense, inelastic consecutive tissue capsule continuously forces product into the duct
Cell proliferation
T/F. MAMMARY GLANDS demonstrate apocrine secretion
true
Products of MAMMARY GLANDS are lack cell membrane
false- enclosed
Only Apocrine secretion can occur in MAMMARY GLANDS, T/F
False- both Apocrine and Merocrine secretion can occur
Contractile cells
Myoepithelial cells
Light stained cells
Mucous Cell
Heavily stained cells
Serous Cell
Crescentic caps on mucous acini
Serous demilunes
Process in which protein is release in endocrine glands
Exocytosis
Action when substances produced will act on nearby cells
Paracrine Action
Lipophilic steroids are released through cell membrane by
Diffusion
Type of secretion seen in sebaceous glands associated with hair follicles.
Holocrine secretion
Most common type of gland that release secretory products via exocytosis.
Merocrine glands
Contractile cells that are absent in sebaceous glands.
Myoeopithelial cells
Secretes lubricating substance that aid stomach
Goblet cells
Identify

Respiratory epithelium with goblet cells (top) and intestinal epithelium with goblet cells (bottom)
Identify all parts

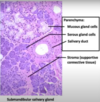
Identify

Simple tubular
Identify

Branched tubular
Features of simple tubular


Branched tubular
Example of simple tubular

Example of branched tubular

Identify

Coiled tubular
Identify

Acinar or alveolar
Identify

Branched acinar

Coiled tubular

Acinar/ Alveolar

Branched acinar
sweat gland structure
Coiled tubular
small mucous glands along urethra structure
acinar/alveolar
sebaceous glands on skin structure
branched acinar
identify

acinar/alveolar
identify

tubuloacinar

acinar/alveolar

tubuloacinar
submucosal glands of brunner in the duodenum structure
tubular

Merocrine

holocrine

aprocrine


