Histology Exam 1 Flashcards
Which of the following are molecular complexes that primarily serve to prevent paracellular transport?
Zonula adherens
Zonula occludens
Hemidesmosomes
Connexons
Zonula occludens
The cleaving of the non-helical terminal ends of pro-collagen converting it into tropocollagen occurs where? In the RER prior to enclosure into secretory vesicles
In the cytoplasm prior to secretion Immediately after secretion
After the tropocollagen has been polymerized into collage fibrils but before the fibrils have been assembled into fibers
After the collagen fibrils have been assembled into fibers
Immediately after secretion
Simple, non-ciliated columnar epithelium is most likely to be found associated with which of the following?
Urinary tract
Digestive tract
Respiratory tract
Integument
Digestive tract
Junctional complexes are associated with which cellular domains?
Apical
Basolateral
Basal only
Lateral only
Basolateral
Transitional epithelium is associated with which of the following systems?
Respiratory
Lymphatic
Cardiovascular
Urinary
Urinary
Although not common, stratified cuboidal epithelium may be found in which of the following areas?
Vaginal epithelium
Part of male urethra
Urinary bladder
Kidney tubules
Part of male urethra
The basal lamina is associated with which type of collagen? Type I Type II Type IV Type VII
Type IV
Which of the following types of cell adhesion molecules is associated with zonula occludens and desmosomes? Cadherins
Integrins
Selectins
Immunoglobulin superfamily
Cadherins
Desmocollins and desmogleins belong to which of the following groups of CAMs?
Cadherins
Integrins
Selectins
Immunoglobulin Superfamily
Cadherins
Which of the following serve as a major interface between the cadherins that hold adjacent cells together and their actin cytoskeletons?
Proteoglycans
Catenins
Laminins
Keratins
Catenins
The extracellular domains of which of the following bind to molecules in the extracellular matrix such as fibronectin and laminin?
Cadherins
Integrins
Selectins
Immunoglobulin Superfamily
Integrins
Which of the following are only associated with the basal domains?
Zonula adherens
Zonula occludens
Hemidesmosomes
Desmosomes
Hemidesmosomes
Lightly keratinzed stratified squamous epithelium is characteristic of which of the following locations?
Vaginal epithelium
Part of male urethra
Urinary bladder
Kidney tubules
Vaginal epithelium
Which of the following molecular complexes that anchor cells together and reinforce the physical integrity of tissues and the cells that make up the tissues?
Zonula adherens
Zonula occludens
Hemidesmosomes
Connexons
Zonula adherens
Which of the following types of epithelium is found in the striated ducts of compound glands?
Squamous
Squamous transitioning to cuboidal
Cuboidal transitioning to columnar
Pseudostratified Columnar
Stratified Columnar
Cuboidal transitioning to columnar
What would be the refractive power of a lens with a focal length of 25 cm?
1 Diopter
2
4
- 25
- 5
4 diopters
ID the type of epithelium. Transitional Stratified Cuboidal Stratified Squamous keratinized Stratified squamous non-keratinized

Stratified squamous non-keratinized
ID the type of epithelium Simple Columnar Simple Cuboidal Simple Squamous Stratified Cuboidal Stratified Squamous

Simple Cuboidal
ID the type of epithelium. Transitional Stratified Cuboidal Stratified Squamous keratinized Stratified squamous non-keratinized

Stratified squamous non-keratinized
ID the type of epithelium. Transitional Stratified Cuboidal Simple Columnar Stratified Squamous keratinized Stratified squamous non-keratinized

Simple Columnar
ID the type of epithelium. Transitional Stratified Cuboidal Simple Columnar Stratified Squamous keratinized Stratified squamous non-keratinized

Simple Columnar
ID the type of epithelium. Transitional Stratified Cuboidal Simple Columnar Stratified Squamous keratinized Stratified squamous non-keratinized

Transitional
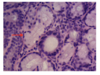
ID Type of Cells (Arrows) Simple Columnar Cells Paneth Cells Goblet Cells Mucous Acini Chief Cells

Goblet Cells
ID type of epithelium. Stratified cuboidal Simple Columnar Pseudostratified Columnar Transitional Stratified Squamous Keratinized

Transitional