Histology Flashcards
Which epithelium is in the oral cavity, oropharynx and laryngopahrynx?
Stratified squamous
Which epithelium is in the nasal cavity and nasopharynx?
Respiratory epithelium
Which epithelium and features are found on the anterior 2/3rds of the tongue?
Stratified squamous epithelium and papillae
Which epithelium is posterior 1/3rd of the tongue?
Smooth stratified squamous (no papillae)
What are the 4 kinds of papillae and their functions?
1) Filiform - for gripping with no tast buds (majority) 2) Fungiform - taste buds 3) Foliate (laterally) 4) Circumvallate (large papillae at the back) - taste buds

What are the 4 layers of the digestive tract (lumen outwards)?
1) Muscosa (made up of epithelium, lamina propria and muscular mucosal) 2) Submucosa (loose CT) 3) Muscular externa/propria (inner circular and obture longitudinal m. layers) 4) Serosa or adventitia (Ct for attaching to stuff)

What are the muscle types in different parts of the oesophagus?
Upper third- skeletal Middle third - mixture of skeletal and smooth Lower third - smooth muscle
Histologically, what is the gasto-oeosphageal junction?
Abrupt change from stratified squamous of oesophagus to columnar epithelium of the stomach (Z line)

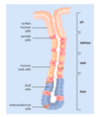
What are unique features to the stomach epithelium?
Flat mucosa but containing gastric pits, with 1-7 gastric glands at the bottom

Which cells are mostly at in the isthmus of the gastric pits of the stomach?
Parietal cells
What is the function of parietal cells in the stomach?
Produce HCL and intrinsic factor
Which cells are found on the surface of the stomach?
Surface mucous cells

What is the function of surface mucous cells in the stomach?
Secrete mucous into the lumen
Which cells are found at the neck of the gastric pits?
Mucous neck cells and stem cells

What is the function of mucous neck cells in the stomach?
Secrete mucous only on vagal stimulation
What is the function of gastric stem cells?
This epithelium is being renewed at a vast rate, so need stem cells to replace these
Which cells are found at the base of the gastric glands?
Chief cells and enteroendocrine cells

What is the function of chief cells in the stomach?
Produce pepsinogen and gastric lipase
What is the function of enteroendocrine cells?
Release signals to control lots of GI motility, secreting serotonin an other hormones
How do the gastric pits/glands differ between stomach regions?
• Cardia: Deep gastric pits that branch into loosely packed, tortuous glands. • Body: Shallow gastric pits with long straight gastric glands. • Pylorus: Deep gastric pits with branched, coiled gastric glands at a higher density than in the cardia.

What cells are subtypes of enteroendocrine cells in the stomach?
G cells and enterochromaffin-like cells
What is the function of G cells in the stomach and duodenum?
Secrete gastrin
What is the function of enterochromaffin-like cells?
Secrete histamine
What is a unique feature of the muscularis external in the stomach and what is it for?
Additional oblique layer of muscle internal to the circular layer. It aids the churning action of the stomach.
What are the unique histological features of the small intestine?
The surface view is one of finger-like projections, the villi, and between the bases of adjacent villi are pits ‘drilling’ downwards, the crypts of Lieberkuhn.

Where are Brunner’s glands located?
Duodenum
**What structures are the hallmark of the jejunum?
Plicae circularis

What structures are the hallmark of the ileum??
Peter’s patches - aggregations of lymphoid tissue of the GALT

What are the cells of the small intestine?
Enterocytes, goblet cells, paneth cells, stem cells ad neuroendocrine cells (K, L, I, G, N, S and enterochromaffin-like cells)
What are the cells of the stomach?
Surface mucous cells, parietal cell, mucous neck cells, stem cells, chief cells and enteroendocrine cells (G cells, D cells and enterochromaffin-like cells)
What is the function of Delta cells in the stomach and SI?
Secrete somatostatin
What is the function and characteristic of enterocytes in the SI?
Tall columnar cells with a brush border and are the principle absorptive cell.
What is the function of goblet cells in the stomach/SI?
Produce mucin to protect epithelium and lubricate passage of material.
What is the function of paneth cells in the SI and where are they found?
Found at the base of the crypts of Lieberkuhn, they have a defensive function and have a role in regulating bacterial flora (secrete lysozyme and definsins).
What is the function of stem cells in the SI and where are they found?
Found at the base of the crypts of Lieberkuhn, they divide to replenish epithelium.
What is the function of I cells in the SI?
Secrete CCK and GLP-1
What is the function of L cells in the SI?
Secrete Peptide YY
What is the function of L cells in the stomach and SI?
Secrete gherkin
**What is unique about the duodenum?
Contains glands in the submucosa: Brunner’s glands

What is the function of Brunner’s glands?
When stimulated by the presence of chyme they produce a thin, alkaline mucous to neutralise the chyme.
What is the histology of the large intestine like?
The large intestine is now again like a flat surface with holes drilled into them: colonic glands • Like test-tubes of mucosal tissue being held in a rack

What are the 2 main types of cells of the large intestine?
Goblet cells and absorptive cells
What is unique about the walls of the large intestine?
The outer longitudinal muscle is collected in 3 large bands running longitudinally along the intestines: teniae coli

What occurs at the rectoanal junction?
Abrupt junction (J) between the mucosa of the rectum (RM) and the stratified squamous epithelium (SS) of the anal canal. •Becomes keratonised to blend with the exterior facing skin
What is the name of the 2 network of fibres which control gut motility?
Myenteric plexus between the fibres of the muscularis externa, and the submucosal plexus in the submucosa
What are the origins of mucosal epithelium and associated glands and ducts?
Endoderm
What are the origins of the liver?
Has both both endoderm and septum transversum components
Endoderm: liver cells & lining of the biliary tree
Septum transversum: Hematopioetic cells, Kupffer cells and connective tissue
What does the liver develop as?
An outsprouting of the duodenum
What 2 main components does the pancreas and common bile duct come from?
- ventral pancreatic bud – smaller and below the gallbladder
- dorsal pancreatic bud by the duodenum

Annular pancreas
Sometimes the ventral pancreatic bud can form a bi-lobe structure. If this happens then the two lobes go around opposite sides of the duodeunum and eventually wrap the tube as solid tissue
Pancreas works fine still, but causes duodenal stenosis

Which germ layer does the spleen originate from?
Mesoderm
Foregut
oesophagus to part 2 of the duodenum (of 4)
Midgut
Part 3 of duodenum to proximal 2/3 of transverse colon
Hind gut
Distal 3/3 of transverse colon to anus
Which germ layer does the gut tube originate from?
Endoderm


