Head & Neck II Flashcards
What are the 3 regions that the nasal cavity is divided into?
- olfactory region
- respiratory region
- nasal vestibule
What is the nose split by?
- nasal septum (cartilage)
What are choanae?
- openings at the back of the nose
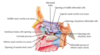
Label this image


What is the spheno-ethmoidal recess?
- connection between the sphenoid bone and the ethmoid bone
What is the cell type found in the meatuses?
- pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Label this image
+ find sphenoethmoidal recess


Label this image


What are the 4 cartilages of the nose?
- nasal septal (lateral and septal processes)
- Major alar (medial and lateral crus)
- Minor alar
- Alar fibrofatty tissue
Which structures open into the three meatuses?
- superior : posterior ethmoidal sinus
- middle : frontal, maxillary and anterior ethmoidal sinuses
- inferior : nasolacrimal duct, eustachian tube
What are the paired and unpaired bones that make up the nasal septum?
- Paired bones: Nasal, maxillary and palatine bones.
- Unpaired bones: Ethmoid and vomer bones.
What is the frontonasal duct?
- connection between the frontal bone and nasal cavity
What does the frontonasal duct drain via?
- the infundibulum between the superior and middle nasal concha
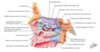
Label 1-25


What are the 6 ethmoidal structures?
- Crista galli (attachment of the falx cerebri)
- Cribriform plate (has all the olfactory nerves)
- Perpendicular plate
- Superior nasal concha
- Middle nasal concha
- Uncinate process
What is found on the lower part of the uncinate process?
- opening into the maxillary sinus
Label this image

Where does the nasolacrimal canal open into?
- inferior concha
Label this image


Label this image


Where does the frontal sinus drain into?
- ethmoidal
What is the only way in and out of the maxillary sinus?
- uncinate process
If the maxillary sinus is inflamed then where can it caused pain?
- referred pain along alveolar nerve
What is the cell type of the lining of the sinuses?
- pseudo stratified columnar epithelium