Gluteal Region, Posterior Compartment of Thigh and Popliteal Fossa Flashcards
What forms the greater and lesser sciatic foramina? What does the sciatic foramina provide?


Greater sciatic foramina and lesser sciatic foramina

What do the sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments prevent?





Also, what are all these lines attachment sites for?

Big muscles in the gluteal area, gluteus minimus, gluteus maximus, and gluteus medius





Where do gluteus medius and gluteus minimus attach?
The greater trochanter










Also whats its action?

Correct movement and distortion but also medially rotate the thigh

Constriction of what two muscles on stance side prevents excessive pelvic tilt during swing phase on opposite side?

What is the purpose of the Trendelenberg test?
What is the patient asked to do?
What is a positive result?
Purpose is to test strenght of gluteus medius and or gluteus minimus.

What is the Trendelenberg gait? (gluteus medius limp)




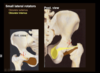






What are the small lateral rotator muscles?
Obturator externus, obturator internus, Superior gemellus, inferior gemellus, quadratus femoris, piriformis













































