Brain 2: Primer for Somatosensory pathways Flashcards
Somatic sensation is what? What are the 4 things you can have perceptionof?

What are the two types of proprioception? What are they?
Conscious: limb or joint position
Non-conscious: maintenance of normal muscle tone, posture, cordination (cerebellum)
Describe local reflexes
These somatic neurons can enter the spinal cord, synapse in gray matter and result in a local reflex at the same level OR it may ascend (move up) in the CNS, which means travel through white matter tract from the spinal cord to the brainstem to the thalamus and then cortex

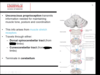
Whats going on here?

Somatic sensory neuron is acending throug CNS


In somatosensory neurons, how many neurons link the target to the cortex?
3, first order (primary) sensory neuron, second order (secondary) seonsory neuron, and third order (tertiary) sensory neuron
Where is the cell body of a first order sensory neuron?
Cell body in dorsal root ganglion. Has both a peripheral process and central process
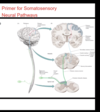
Where does a secondary sensory neuron project it project?
projects to thalamus

Where does a third order sensory neuron project?
Projects to somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus

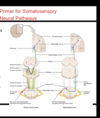
What are the 2 main pathways in the spinal cord for conscious somatic sensation?

What information does the dorsal column medial lemniscal pathway carry?
Conscious proprioception, vibration, fine discriminative touch
What information does the spinothalamic tract (anterolateral system) carry?
Pain, temperature
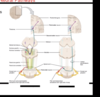
Describe the fine touch test: 2 point discrimination.
What is a positive finding on this test?

Explain what happens to the first order sensory neuron of fine touch, conscious proprioception, and vibratory sense
Central process of first order neuron ascends in dorsal (posterior) columns of spinal cord to medulla. Then synapses on 2nd order neuron cell body in nucleus gracilis (lower limb) or nucleus cuneatus (upper limb)



What happens to the secondary sensory neurons? For fine touch, vibratory touch and conscious proprioception
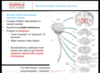


What does decussate mean?
Crosses midline
All of the thousands of second order somatosensory axons from DCML pathway that are ascending together through spinal cord and brain stem are called?
Medial lemniscus
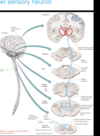
The nuclei in the thalamus that receive somatosensory information are called what?
ventral posterior lateral (VPL) nuclei of thalamus. One on each side of thalamus
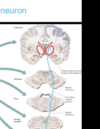
Explain what happens to the first order primary sensory neuron for pain and temperature (anterolateral or spinothalamic)
Cell body starts in dorsal root ganglion, and central process will extend into the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, and it will synapse there (different from the somatosensory neuron, which ascended). Can synapse in substantia gelatinosa or nucleus proprius
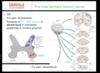
Explain what happens to the seconday spinothalamic sensory neuron
Crosses midline (decussates) at anterior commissure, then ascends in white matter via spinothalamic tract. Projects to thalamus, specifically the ventral posterior lateral (VPL) nuclei of thalamus.
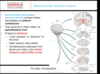
Where do DCML neurons decussate?
In the medulla
Where do spinothamalic neurons decussate?
In the spinal cord
Where do both 3rd order neurons (spinothalamic and DCML) project?
Somatosensory cortex in postcentral gyryus

How are sensory pathways organized in the cortex?
Where are regions representing the hand next to?
Whats the somatotopic map on cortex called?

Unconcsious proprioception transmits information needed for maintaining what?
Muscle tone, posture and coordination
Info for unconscious proprioception arises from what? What are the two tracts they travel through? Where do they terminate?

Do unsconsious proprioception neurons have 1st order, 2nd order, 3rd order neurons ect?
No, there usually is like 2 neurons, and they are not really named. They start in stretch receptors.

Describe what happens to the first neuron in unconcious proprioception pathway, from lower part of body. Where does it synapse?
First neuron travels with DCML path for a short distance. Goes through fasiculus gracilis (because it’s coming through lower part of the body). BUt will synapse in different nucleus ,dorsal nucleus of Clarke (C8-L3 SC levels).

What are the spinal cord levels for the dorsal nucleus of Clarke?
C8-L3

What is the tract called that unconcsious proprioception, second order neurons travel through? What does it travel through on its way to the cerebellum?
Dorsal (posterior) spinocerebellar tract, travels thorugh the inferior cerebellar peduncle

What do we call it when the neuron stays on the same side as it travels? Which type of neuron does this?
ipsilateral. Unconcsious proprioception
If the unconscious proprioception neuron was arising from muscle stretch receptors in the upper extremities, where would we find the first order axons?
Where will it synapse?
After that, what is the tract that it will ascend in called?
Finally, what wil it travel through to reach cerebellum?
fasiculus cuneatus
synapse in external cuneate nucleus in medulla (lateral to cuneate nucleus)
Ascend in cuneocerebellar tract
travel through inferior cerebellar peduncle to reach cerebellum
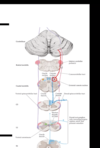
What is the difference in the location of the 1st order neuron cell bodies between the DCML Gracilis and Cuneatus pathways?
Cuneatus: dorsal Root Ganglion above T6 and Gracilis is dorsal root ganglion below T6


