GIT L1: Overview of GIT Flashcards
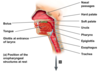
The GIT is an _______ muscular tube - about _____ m in an adult living human - called also digestive tract / gut / alimentary canal
open-ended; 4.5
Why does the mucus change in areas?
To stop infection..etc (different bacteria) due to the open-ended structures
What are the 6 major functions of the GIT (6 steps; 4 basic processes)?
- Ingestion
- Motility / propulsion
- Digestion
- Secretion
- Glands which secrete juices
- Absorption Get nutrients from
- Elimination (defecation)
What are the 4 layers of the GIT?
EXAM QUESTION
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Muscularis externa
- Serosa

The GIT is _____ within open ended structure.
homogenous

What are 2 characteristics of mucosa?
- Has different layers
- Where secretion produced and absorption occur

What are 2 characteristics of submucosa?
- Maintain mucosa in a particular shape
- Bring blood from vessels and nutrients to the mucosa

What are 2 characteristics of muscularis externa?
- Muscles used to push food forward
- Help stomach to have a mechanical breakdown (digestion)
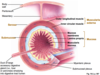
What is a characteristic of serosa?
Overs the whole tube

What are 4 functional types of epithelium?
- Protective
- Secretory
- Absorptive
- Absorptive/Protective

What are 4 examples of protective epithelium in the GIT wall?
- oral cavity
- pharynx
- oesophagus
- anal canal

What is an example of secretory epithelium in the GIT wall?
stomach

What is an example of absorptive epithelium in the GIT wall?
small intestine

What is an example of absorptive/protective epithelium in the GIT wall?
large intestine

What are 2 types of digestive motility?
- Peristalsis
- Segmentation
What is peristalsis?
EXAM QUESTION
Adjacent segments of the alimentary canal organs alternately contract and relax.
- Food is push FORWARD through the digestive tract (no digestion occurs)
- Very strong (hang upside down –> can still each against gravity)

What is segmentation?
EXAM QUESTION
Nonadjacent segments of the alimentary canal organs contract and relax.
- Food is moved FORWARD THAN BACKWARD
- MIX food with DIGESTIVE JUICES and help with ABSORPTION
What are 2 ways to regulate GIT functions?
EXAM QUESTION
- Involuntary
- Voluntary

What are long reflexes in the GIT triggered by? EXAM QUESTION
External stimuli (sight, smell, taste, thought of food) system needs to prepare food by producing gastric juices
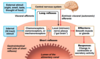
What are short reflexes in the GIT triggered by? EXAM QUESTION
Internal stimuli (food inside month) –> chemoreceptors, osmoreceptors or mechanoreceptors
Pressure receptors activated when food is in the mouth

What are 2 examples of salivation regulation?
EXAM QUESTION
- Simple reflex (pressure receptors activated when food is in the mouth)
- Conditioned reflex (think about food)

What are 4 functions of the oral cavity?
- Ingestion
- Mastication
- Lubrication
- Limited digestion

What is ingestion function in the oral cavity?
and sensory analysis of material (before swallowing)
What is mastication function in the oral cavity?
(mechanical processing) – through actions of teeth, tongue, and palatal surfaces
Food in smaller pieces to aid the breakdown