GI & Hepatology: Decompensated Chronic Liver Disease Flashcards
Outline the pathophysiology of Decompensated Chronic Liver Disease
Decompensated cirrhosis is defined by the development of jaundice, ascites, variceal hemorrhage, or hepatic encephalopathy
Cirrhosis implies irreversible liver damage - stage 3/4 cirrhosis
Loss of normal hepatic architecture with bridging fibrosis and nodular regeneration
Outline the aetiology of Decompensated Chronic Liver Disease
Alcohol abuse
HBV
HCV
Hemochromatosis
Alpha 1 anti-trypsin deficiency
Autoimmune hepititis
Non-alcholic fatty liver disease
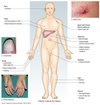
What are the signs and symptoms of Decompensated Chronic Liver Disease
Leukonychia
Terry’s nail - ground glass opacification
Clubbing
Palmar erythema
Dupuytren’s contracture
Spider naevi
Xanthelasma
Gynaecomastia
Atrophic testis
Loss of body hair
Parotid enlargement
Hepatomegaly
Jaundice
Caput medusa
Ascities
How would you investigate Decompensated Chronic Liver Disease
Bilirubin = raised
AST = raised
ALT = raised
Alk phos = raised
GGT = raised
Albumin = reduced
PT/INR = reduced
Clotting factors = reduced
Liver US + duplex
MRI
Ascitic tap = MC+S
Liver biopsy
Upper endoscopy - screen for varices
How would you manage Decompensated Chronic Liver Disease
Good nutrition - high protein
Alcohol abstinence
Avoid NSAIDs, sedatives, opiates
Colestyramine = pruritus
Penicillamine = wilsons disease (excess copper)
Ascites = bed rest, fluid restriction, low-salt diet, spironolactone + furosemide, theraputic drain, IV albumin
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis = cefotaxime, tazocin
Liver transplantation
What are the common differential diagnoses for an individual presenting with jaundice?
Haemolysis = malaria, DIC, AHA
Hepatocyte damage = hepatitis A B C, CMV, EBV, alcohol
Impaired hepatic excretion = primary biliary cirrhosis, gallstones, pancreatic cancer

What are the key investigations for patients with jaundice?
US = are bile ducts dilated, gallstones, metastasis, pancreatic mass
Liver biopsy
Haematology = FBC, bilirubin, clotting, film, reticulocyte count, coombs, malaria parasites
Why might a patient with chronic liver disease be malnourished and what can you do about each potential cause?
Cause may be alcoholism, who tend to be malnourished due to poor diet = rehabilitation for addiction
Cancer/metastasis = chemotherapy, radiotherapy, resection
Result of reduced intake, absorption, processing and storage of nutrients = higher calorie diets, IV nutrition
How should alcohol withdrawal be managed in patients being admitted to hospital?
BP + TPR (temp, pulse, RR) every 4h
1st 3 days give chlordiazepoxide or diazepam
Vitamins may be needed
What services and treatments are available to help patients with alcohol addiction?
AA = group therapy
Acamprosate = may help intense anxiety, insomnia and craving
What long-term complications of cirrhosis should the patient be monitored for?
Varices
Ascites
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE)
Hepatopulmonary hypertension
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatorenal syndrome
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
Coagulation disorders
What is NASH?
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
Inflammation and liver cell damage, along with fat in the liver
What investigations are performed in a liver screen?
Hep B + C serology
Iron studies - ferritin, transferrin saturation
AutoAbs (antimitochondrial Abs + Smooth Muscle Abs) and Igs
Caeuruloplasmin if <30yrs (protein made in liver, carries copper)
Alpha-a-antitrypsin
Coeliac serology
TFTs, lipids, glucose
What questions are important to ask when taking a Hx from a pt with liver disease?
Blood transfusions prior to 1990 in UK
IV drug use
Operations/vaccinations
Sexual exposure
Medications
FH - liver disease, DM, IBD
Obesity
Alcohol
Foreign travel


