gas exchange in humans Flashcards
Features of Gas Exchange Surfaces
Large surface area to allow faster diffusion of gases across the surface
Thin walls to ensure diffusion distances remain short
Good ventilation with air so that diffusion gradients can be maintained
Good blood supply to maintain a high concentration gradient so diffusion occurs faster
gas exchange surface in humans is
The alveolus



Several of the features of alveoli that make them suited to their function are the same as those that make
because all of these structures are involved in
villi suited to their function; or root hair cells suited to their function.
-transporting substances across their surfaces – by diffusion, active transport, osmosis or a combination.




The Intercostal Muscles
Muscles are only able to pull on bones, not push on them
This means that there must be two sets of intercostal muscles; one to pull the rib cage up and another set to pull it down
One set of intercostal muscles is found on the outside of the ribcage (the external intercostal muscles)
The other set is found on the inside of the rib cage (the internal intercostal muscles)
here are two sets of intercostal muscles: the external, on the outside of the rib cage, and the internal, on the inside of the rib cage
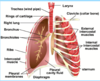


The Trachea
Rings of cartilage surround the trachea (and bronchi)
The function of the cartilage is to support the airways and keep them open during breathing
If they were not present then the sides may collapse inwards when the air pressure inside the tubes drops
The Function of Cilia & Mucus
he passages down to the lungs are lined with ciliated epithelial cells
Cilia comes from the Latin for eyelash, so unsurprisingly these cells have tiny hairs on the end of them that beat and push mucus up the passages towards the nose and throat where it can be removed
The mucus is made by special mucus-producing cells called goblet cells because they are shaped like a goblet, or cup
The mucus traps particles, pathogens like bacteria or viruses, and dust and prevents them getting into the lungs and damaging the cells there

The function of cilia and mucus
- The mucus is produced by goblet cells and traps bacteria, dust, particles
- The cilia beat
and push the mucus away from the lungs towards the throat
inhalation
During inhalation the external set of intercostal muscles contract to pull the ribs up and out
The external and internal intercostal muscles work as antagonistic pairs
The external and internal intercostal muscles work as antagonistic pairs

exhalation
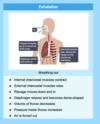
Inhalation & Exhalation basics
The external and internal intercostal muscles work as antagonistic pairs (meaning they work in different directions to each other)
During inhalation the external set of intercostal muscles contract to pull the ribs up and out
During exhalation the internal set of intercostal muscles contract to pull the ribs down and in
The point of this is to increase or decrease the volume of the chest cavity (thorax) so that the lungs can follow and increase or decrease in size
The muscle surrounding the diaphragm also helps to increase and decrease the volume of the thorax
This means that when we are doing ‘quiet breathing’ there may be no noticeable chest movement as the lungs are ventilated mainly by changes in the shape of the diaphragm
When we need to increase the rate of gas exchange (for example during strenuous activity) the intercostal muscles will also work to pull the ribs up and out and increase the volume of the thorax more
This is because we now require a greater volume of gases to be exchanged, so we need to inflate the lungs quicker and almost to their maximum
As the volume of the thorax increases, the pressure inside the lungs decreases
Once it drops below the air pressure outside the lungs, air will be forced in
During exhalation, the reverse occurs; volume decreases, pressure in the thorax increases and air is forced out
be able to explain in detail what is happening when breathing in and out to:
the external and internal intercostal muscles
the rib cage
the diaphragm
the volume and the pressure of the lungs
inhalation OR …(breathing in)
exhalation OR ..(breathing out)
- inspiration
- expiration
Differences between Inhaled & Exhaled Air


Reasons for Differences in Inhaled & Exhaled Air


Using Limewater to Test for CO2 in Exhaled Air
We can use the apparatus below to investigate the difference between the amount of carbon dioxide in inhaled air and exhaled air
When we breathe in, the air is drawn through boiling tube A
When we breathe out, the air is blown into boiling tube B
Lime water is clear but becomes cloudy (or milky) when carbon dioxide is bubbled through it
The lime water in boiling tube A will remain clear, but the limewater in boiling tube B will become cloudy
This shows us that the percentage of carbon dioxide in exhaled air is higher than in inhaled air

Investigating the Effect of Exercise on Breathing
Exercise increases the frequency and depth of breathing
This can be investigated by counting the breaths taken during one minute at rest and measuring average chest expansion over 5 breaths using a tape measure held around the chest
Exercise for a set time (at least 3 minutes)
Immediately after exercising, count the breaths taken in one minute and measure the average chest expansion over 5 breaths
Following exercise, the number of breaths per minute will have increased and the chest expansion will also have increased
Explaining the Effect of Exercise on Breathing
Frequency and depth of breathing increase when exercising
This is because muscles are working harder and aerobically respiring more and they need more oxygen to be delivered to them (and carbon dioxide removed) to keep up with the energy demand
If they cannot meet the energy demand they will also respire anaerobically, producing lactic acid
After exercise has finished, the lactic acid that has built up in muscles needs to be removed as it lowers the pH of cells and can denature enzymes catalysing cell reactions
It can only be removed by combining it with oxygen – this is known as ‘repaying the oxygen debt’
This can be tested by seeing how long it takes after exercise for the breathing rate and depth to return to normal – the longer it takes, the more lactic acid produced during exercise and the greater the oxygen debt that needs to be repaid
Carbon Dioxide Concentration & the Brain
As respiration rates increase, more carbon dioxide is produced and enters the blood
Carbon dioxide is an acidic gas in solution and so it can affect the working of enzymes in the cells and needs to be removed as quickly as possible
As blood flows through the brain, the increase in carbon dioxide concentration stimulates receptor cells
These send impulses to the muscles of the lungs, causing them to contract faster and more strongly
This causes the frequency and depth of breathing to increase until the carbon dioxide concentration of the blood has lowered sufficiently


