final exam knee joint Flashcards
which joint is the largest and most superficial in the body?
the knee joint
how is the knee joint formed?
the articulation of the femur, tibia and patella
during development what are the 3 separate joints that become continuous with each other and form a single large knee joint cavity?
1 between the patella and femur 2 btw the lateral condyles of the femur and tibia 3 btw the medial condyles and tibia
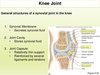
the articulating surfaces of the tibial condyles are often referred to as?
lateral and medial tibial plateaus
the joint between the femur and tibia is classified as?
ginglymus (hinge) with some degrees of rotation
the joints between the patella and femur are classified as?
plane gliding
what nerves supply the knee joint?
femoral, obturator, common fibular and tibial
what are the 4 openings in the anterior capsular ligament which allow synovial membrane to pass through and form bursae?
1 subcutaneous prepatellar
2 subcutaneous infrapatellar
3 deep infrapatellar
4 suprapatellar
what are the 4 extrinsic ligaments of the knee?
1 ligamentum patella
2,3 collateral ligament- lateral and medial
4 oblique and arcuate popliteal
which extrinsic ligament is anterior and is the distal common tendon of insertion of the quadriceps?
ligamentum patella
which ligament plays an important role in alignment of patella relative to the articular surface of the femur?
ligamentum patella
which ligaments are taut when knee joint is fully extended and thus contribute to stability while standing?
collateral ligaments
where does the lateral (fibular) collateral ligament attach?
it is superficial and separate from the articular capsule of the joint and attaches from the lateral epicondyle of the femur proximally to the head of the fibula distally

what is the function of the lateral collateral ligament?
it functions as a wall and prevents lateral movement (abduction) at the joint
where does the medial collateral ligament attach?
it blends with the articular capsule and is directly attached to the medial meniscus;
medial epicondyle of the femur proximally to medial side of tibia distally, just below the condyle

what is the function of the medial collateral ligament?
acts as a wall and prevents medial movement (adduction) at the joint
where are the oblique and arcuate popliteal ligaments found?
posterior aspect of the joint

what is the function of the oblique and arcuate popliteal ligaments?
act as wall to prevent hyperextension of the joint and stabilize posterior aspect
what are the 6 intrinsic ligaments of the knee?
1 cruciate ligaments- anterior and posterior
2 menisci- medial and lateral
3 coronary ligaments
4 transverse ligament

what are the main bonds between the femur and tibia and cross eachother like an X in the center of the joint?
the cruciate ligaments
where does the anterior cruciate ligament run?
it is the weaker of the 2 and runs from the lateral condyle of the femur to the anterior intercondylar area of the tibia distally

what is the function of the anterior cruciate ligament?
prevents anterior displacement of the tibia and functions like a rope
where does the posterior cruciate ligament attach?
it is the stronger of the 2 and runs from the medial condyle of the femur proximally to the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia proximally

the mensci of semilunar cartilages have a well developed blood supply until when?
from time of birth to 18 months of age; once infant begins to walk it loses about 75% of vascular supply
what are the main functions of the menisci? 3
1 deepen articulating surface
2 act as shock absorber
3 act as a mechanoreceptor to increase positional sense of knee joint
which ligament is C shaped and adheres to the tibial collateral ligament?
medial meniscus
which ligament is nearly circular in shape and smaller than the medial meniscus?
lateral meniscus- more freely movable on tibia
which ligaments are associated with the menisci and attach to the edge of the menisci to help hold them in place?
coronary ligaments
which ligament joins the anterior edges of the medial and lateral menisci and allows them to work together?
transverse ligament of the knee
what are the possible movements of the knee joint?
mainly flexion and extension but some rotation occurs when joint is flexed
how can you “unlock” the knee?
the popliteus muscle must contract to rotate the tibia medially and thus cause flexion at the knee joint
what causes prepatellar bursitis? (housemaids)
1 friction between skin and patella
2 direct blow
3 falling on flexed knee
what causes subcutaneous infrapatellar bursitis?
excessive friction between skin and tibial tubercle- also known as clergyman’s knee
what causes suprapatellar bursitis?
bacteria from an abrasion or penetrating wound
unhappy triad is a term used for a blow to the lateral aspect of the joint while its weight bearing, what does it damage?
medial collateral, anterior cruciate, medial meniscus
what are 2 causes of damage to the medial collateral ligament?
most commonly injured ligament- a lateral blow and rotational forces during trauma
which ligament is damaged when a patient complains of knee “clicking”, locking up or has pain going up stairs?
medial meniscus
if menisci are removed, forces are transmitted to the condyles of the tibia and can lead to?
damage of articular cartilage and eventually osteoarthritis
which ligament is damaged when a patient complains of a “pop” or says their knee “gives out”? damaged in sports that require twisting or jumping
anterior cruciate (ACL)
what is it called when damage to the ACL causes the tibia to be pulled forward excessively under the femur?
positive anterior drawer test
injury to the PCL (posterior cruciate) leads to tibia being pulled excessively backward under femur and is referred to as?
positive posterior drawer test
what portions of knee are replaced in a knee replacement surgery?
total or partial- both femoral and tibial portions
what materials are used with a knee replacement and why?
metal and plastic which provides a smoothness similar to cartilage
what is the lifespan of a prosthetic knee on average?
15 to 20 years


