Female Flashcards
-Why is the ovaries BOTH exocrine and Endocrine
Because it produces and secretes oocytes (gametes)- exocrine
Produce hormones- endocrine !
What ae the primary and seconday female sex organs
Primary sex organs: the Gonads (ovaries)
Secondary sex organs 2 groups
- Interal genitial- oviduct , uterus , vagiina
- External -vestibule , labia minora, labia major , clitoris

What type of epithelium is on the surface of the ovary?
germinal epithelium = simple cuboidal
What are the parts of the ovary and what are their fxn?
Surface = germinal epithelium -> simple cuboidal epithelium
- Cortex = ovarian follicles in different stages of development
- Medulla - connective tissue and blood vessels
What are the primordial follicles and what stage of meiosis does it occur?
what is outside of the follicular cells?
- oocyte, stromal cells, follicular cell
- Arrested in prophase I (dictyotene) - starts in uterus of baby
stromal cells

When do the granulosa cells form?
At puberty FSH is produced causing flat follicular cells to become cuboidal = granulosa cells
What are the unilaminar primary follicles?
Have one layer of granulosa cells

What are the multilaminar primary follicles and what structure is present?
- Has more than one layer of granulosa cells and has theca interna
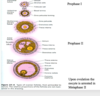
Stromal cell differentiate to form?
why is this important
differentiate to form theca INTERNA this is important because theca interna produces ANDROSTENEDIONE which diffuses into the primary follicle and metabolizes estrogen!
What is the secondary (antral) follicle, what new structure is present? What stage of meiosis does it first appear?
- Has antral space
- Theca externa (connective tissue)
- Prophase II (dictyate)
What causes the secondary antral follicle to become arrested in prophase II?
Oocyte Meiosis Inhibitory (OMI)
inhibitory protein
What is the graafian or tertiary follicle?
the 1 follicle out of 10 follicles that enters differentiation process and ovulates mid cycle
What is the cumulus oophorus and when does it become prominent?
What is the cumulus oophorus and when does it become prominent?
- accumulations of granulosa cells continuous with the pedicle (region where the culmulus oophorus attaches to the other granulosa cells)
- Mature (graafian) follicle

What happens during ovulation?
Oocyte Meiosis Inhibitory substance in antral space is disperses so mature follicle (oocyte) is released into fallopian tubes and can now progress from Prophase II to Metaphase II
What is the tunica albuginea?
Connective tissue in the reproductive system
What is the zona pellucida?
thick layer of proteins (Connective tissue layer) that surrounds oocyte unless fertilization occurs
granulosa cells and oocyte together depositextracellular coat on primary oocyte

What is the corona radiata and when does it first appear?

- Tightly packed layer of granulosa cells around zona pellucida
- Mature
(graafian) follicle
At what stage is the oocyte in prohase 1?
primordial , primary oocyte is arrested in prophase one
1/10 secondary follicle become ____. The granulosa around this oocyte is called
Mature (graafian follicle) granulosa around mature follicle is call culmulus ophorus!
When the graafian follicle ovulates what happens to OMI ? what phase will the oocyte progress to?
OMI is the antral space, when ovulation of mature follicle occurs the OMI disperses so it can no longer arrest the oocyte( which has to leave since ovulating is occurring!)
OOcytes progresses to METHAPHASE II in fallopian tube and remains there unless fertilization occurs
Meiosis is complete when
fertilization occurs , when ferilization doesnt occur that is when the oocyte goes into oviduct , FALLOPIAN TUBE!( metaphase II)


