EXAM III Flashcards
What is the most important opsonin? Why?
C3b
Has the highest binding affinity
Primary or secondary lymph follicles/nodules contain a germinal center? What does this germinal center consist of?
Secondary
B lymphocytes memory B cells, plasma cells, dendritic reticular cells
What is the difference between lymph nodules and lymph nodes?
Nodules are apart of lymph nodes and other lymphatic vessels/organs (primary & seconday)
Lymph nodes are enclosed by a capsule
What are the primary and secondary lymphoid organs?
Primary - bone marrow and thymus (precursor cells mature into immunocompetent cells programmed to recognize a specific Ag)
Seconday - spleen, tonsils, lymph nodes (trapped Ag stimulate clonal expansions of mature T and B cells)
Distinguish between primary and secondary lymph nodules
Primary follicles - virgin B cells and dendritic reticular cells that haven’t been exposed to Ag
Secondary - been exposed to foreign Ag; not present at birth
What are the 3 propria-associated lymphoid tissues?
MALT
BALT (bronchial)
GALT
Which T cells does MHC I and MHC II express their Ag peptide fragment to?
MHC I = CD8+
MHC II = CD4+ helper
What are CD16/56+ T cells? What are they activated by and what do they release?
NK cells
Activated by tumor cells Ags and release cytokines
What are HEVs? Where are they found? Whats it used for
High Endothelial Vessels are found in the deep cortex of lymph which allows entry point for circulating differentiated lymphocytes to leave the bone marrow and enter lymph node by easily leaving the venules
Define Hassall’s corpuscle. What do they produce and stimulate?
Whorls of highly keratinized medullary epithelial cells in the medulla of the lobules of the thymus
Produce cytokine thymic stromal lymphopoietin
Stimulates thymic dendritic cells needed for single (+) T cell maturation
Describe characteristics of the red pulp of the spleen. Function? What does it surround? Explain Billroth cords
Surrounds white pulp
Filters blood
Contains Billroth cords which form red pulp parenchyma = blood cells, plasma cells, APCs
Terminal capillaries open directly into the substance of cords = open circulation
What type of epithelium is the respiratory epithelium?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
What part of the kidney is the most important in generating the countercurrent osmol gradient?
Loop of Henle
What type of epithelium is located within the olfactory?
Pseudostratified columnar without goblet cells, without basement membrane
What are the specialized cell types of the pulmonary system? (
Type I Alveolar/Pneumocytes - covers large surface area
Type II Alveolar/Penumocytes - secrete surfactant, contains lamellar bodies w/ lecithin, phagocytize old surfactant (combine w/ proteins from Clara cells)
Clara Cells - secrete surfactant preventing collapse of terminal bronchioles during exhalation
Dust Cells
Characteristics of clara cells? Location? Function?
Found only in bronchioles
Secrete surfactant preventing collapse of terminal bronchioles during exhalation
Define Type I alveolar cells/Type I Pneumocytes, where are they located?
Less numerous than Type II
Cover largest suface area (more thinner)
Walls of Alveoli
Define Type II Alveolar Cells/Pneumocytes
Produce surfactant
Cuboidal/rounded
Stem cells for Type I and Type II
What two cells secrete surfactant?
Clara and Type II Alveolar/Pneumocytes
Characteristics of Type II Alveolar cells
Lamellar bodies = Distinctive under EM; contain lecithin
Phagocytize old surfactant; more round
Can divide and replace Type I
Secreted from apical domain of cells
Combine w/ proteins from Clara cells
Produce phospholipid-protein surfactant that coats alveolar walls
Define Clara cells, where are they found, which cell do they work with in the pulmonary system?
Secrete surfactant & lipoprotein that prevents collapse of terminal bronchioles during exhalation
Bronchioles
Identified by apical surface that bulges into lumen of airway
Abundant SER; greater # with less ciliated columnar cells
Work with Type II Pneumocytes
What are dust cells and what are their roles? Where are they located?
Macrophages; derived from monocytes
Phagocytize pollutants, bacteria, surfactant
Walls of alveoli
Where are intercalated cells found? What is their function in terms of ion concentration and its relationship with angiotensin-aldosterone pathway?
Late DCT and Collecting Tubule
Reabsorb K+ during depletion, secrete H+ or Bicarbonate
Affected by angiotensin (increases Na+ reabsorption)
What are the types of T cells involved during T cell differentiation?
Double (-) T cells - lack cell surface molecules, enter cortex from blood vessels, proliferate in subscapular area
Double (+) T cells - move to outer cortex, express CD4 & CD8 & TCR, interact w/ epithelial cells w/ MHC I & II for clonal selection,
Single (+) T cells - move to inner cortex, express TCR and EITHER CD4 or CD8
Medulla = clonal deletion completed (copies of T cells)
List the layers of the epidermis from deep to outermost
Thick Skin
vs
Thin Skin
Thick: Remember, Please Bring Some Good Chapstick
Thin: Remember, Please Bring Some Good Lip Chap
Stratum basale/germinativum
Stratum spinosum
Stratum granulosum
Stratum lucidum - absent in thin skin
Stratum corneum
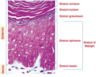
What are the steps necessary during differentiation of T cells? (4)
Double negative
Double positive
Single positive
Clonal deletion
What are the characteristics of double negative T cells? Where are they located?
Lack cell surface molecules (in mature T cells)
Proliferate in subcapsular area (outside cortex)
Enter cortex from blood vessels
What are the characteristics of double positive T cells and what do they express?
Express both CD4 & CD8 coreceptors and TCR receptors
Are deeper in cortex
Confronted with epithelial cells w/ cell surface MHC classes I and II for clonal selection
What do single positive T cells express?
Either CD4 or CD8 and TCR receptors
Mature T cells
Where does clonal deletion of T cells occur?
Medulla
What occurs in the white pulp of the spleen?
Clonal expansion of Ag-stimulated lymphocytes
What is the function of the marginal zone of the spleen?
Forms sinusoidal interface between red pulp and white pulp
The site of initial Ag exposure to lymphocytes
What are the 4 arteries of the spleen?
Splenic artery - enters hilus
Trabecular artery - branches off
Central artery - where adventitia loosens and becomes mesh-like reticulum infiltrated with lymphocytes. A penicillus is formed when capillaries enter red pulp
Penicullar arterioles –> Terminal Capillaries
Veins: Venous Sinuses, Pulp Vein, Trabecular Vein, Splenic veins, Hilus
What are Meissner’s Corpuscle? What is their function?
(Tactile corpuscle)
Type of mechanoreceptor
Type of nerve ending in the skin responsible for sensitivity to light touch
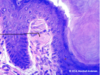
What are Pacini Corpuscles
One of the 4 major types of mechanoreceptors
Nerve endings in skin responsible for sensitivity to vibration and pressure
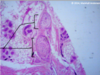
Where are intercalated cells found? What is their function in terms of ion concentration and its relationship with angiotensin-aldosterone pathway?
Late Distal Tubule and Medullary CT
Reabsorb K+
Secrete H+ or bicarbonate
Affected by Angiotensin II
Where are principal cells found? What is their function in terms of ion concentration and its relationship with angiotensin-aldosterone pathway?
Late DCT and Collecting Duct
Reabsorb Na+ and Water
Secrete K+
Affected by Aldosterone
Define space of Disse and describe its location
Separates hepatic cells from endothelial cells (between hepatocytes and sinusoids; separates basolateral domain of the hepatocytes from blood circulating in the hepatic sinusoid
Active in transfer between blood and parenchyma
Function of sinusoids in the liver; explain both hepatic lobules
Canal area that feeds into the central venule which is within the Classic lobule
Portal triads are at an angle (hepatic artery, portal vein, bile duct)
Portal lobules - contain 3 central venules of adjacent lobules that form a triangle

For CCK hormone, state the site of secretion, targets, and effects
Duodenum (upper intestinal mucosa) in response to gastric contents
Targets pyloric sphinctor to slow stomach emptying
Stimulates bile release from gall bladder
Stimulates secretion of pancreatic enzymes
Competitive inhibitor of gastrins
For gastrin hormone, state the site of secretion, targets, and effects
Duodenum
Targets Pancreas
Insulin release by pancreatic beta cells
Bicarbonate secretion by pancreas
For secretin hormone, state the site of secretion, targets, and effects
Pyloric-antral portion of stomach
Targets stomach
Stimulates HCl production by gastric parietal cells
gastric motility
Insulin release by pancreatic beta cells
Which taste bud is only found on along the sulcus terminalis?
Circumvallate papillae
Filiform papillae
Foliate papillae
Fungiform papillae
Circumvallate papillae; projections along sulcus terminalis
Along the lateral walls
Which taste bud is found on the oral surface of epithelium of the tongue?
Circumvallate papillae
Filiform papillae
Foliate papillae
Fungiform papillae
Fungiform papillae
mushroom appearance
What are the 4 layers of the digestive gut tube?
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis externa
Serosa & Adventitia
Type of epithelium in the mucosal layer of the digestive gut tube? What are the 2 layers?
Stratified squamous transitioning to simple columnar
Lamina propria - loose areolar CT
Muscularis mucosa - 1-3 layers of smooth muscle
Type of epithelium in submucosa of the digestive tube? Is it vascularized? What special item is within it
Dense, irregular CT
Vascularized
Meissner’s plexus (nerve/submucosa plexus)
Type of epithelium in the muscularis externa layer of the digestive tube? What are the 2 layers and what special item does it hold
Inner circular layer of SM (regulates lumen size)
Outer longitudinal layer (regulates rhythmic movement of GI tract)
Myenteric/Auerbach’s nerve plexus - between the two muscle layers
What type of epithelium or CT is within the Serosa and Adventitia of the digestive gut tube?
Serosa
Dense, irregular CT; forms visceral peritoneum, covers intraperitoneal portions of abdominal organs
Adventitia
Dense, irregular CT with adipose tissue
Covers retroperitoneal portions of digestive system

Where does carbohydrate digestion begin?
Mouth
via amylase
Which of the following best describes the olfactory mucosa?
Stratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells and a distinct basement membrane
Simple ciliated columnar epi with goblet cells and a distinct basement membrane
Stratified, non-keratinized epi lacking goblet cells with thick basement membrane
Pseudostratified columnar epi lacking goblet cells w/ no distinct basement membrane
Pseudostratified columnar epi lacking goblet cells with no distinct basement membrane
Which of the following is NOT a necessary part of the respiratory membrane?
Pneumocyte I
Basal lamina of pneumocyte I
Dust cells
Basal lamina of endothelial cell
Endothelial cell
Dust cells
Which of the following is characteristic of an arteriole?
Thick tunica adventitia and large lumen
Thick tunica media in relation to size of lumen
Thin tunica media and relatively large lumen
Large blood-filled lumen
Large amounts of elastic fibers in the tunica media
Thick tunica media in relation to size of lumen
Where in the body of a normal, healthy individual would you expect most erythrophagocytosis to be occurring?
Marginal zone of spleen
Hematopoietic cord in bone marrow
Cord of Billroth in spleen
Paratrabecular sinus in lymph node
Cord of Billroth in spleen
Which of the following sequences best describes the flow of red blood cells through the spleen?
Trabecular arteries, central arteries, splenic arteries, penicullus, venous sinuses
Splenic artery, central arteries, trabecular arteries, venous sinuses, penicillus
Splenic artery, central arteries, trabecular arteries, venous sinuses, penicillus
Trabecular arteries, splenic arteries, central arteries, penicullus, venous sinuses
Splenic artery, trabecular arteries, central arteries, penicullus, venous sinuses
Splenic artery, trabecular arteries, central arteries, penicillus, venous sinuses
The simple cuboidal epithelium of this portion of the kidney tubule is composed of cells in the form of truncated pyramids which are characterized by basal striations that mark the location of mitochondria
PCT
Descending thin segment of LOH
Ascending thick segment of LOH
DCT
Collecting Duct
PCT
Renin is secreted by which of the following?
Liver
Macula densa cells
Atrial cells of the heart
Mesangial cells
Juxtaglomerular cells
Juxtaglomerular cells


