Exam 1 Histology Flashcards
The primitive streak forms in the embryonic disc during prenatal development, causing:
a. initiation of palatal development.
b. bilateral symmetry.
c. fusion of the mandibular processes.
d. disintegration of the oropharyngeal membrane.
b. bilateral symmetry.
* During the beginning of the third week of prenatal development within the embryonic period, the primitive streak forms within the bilaminar disc. The primitive streak causes the disc to have bilateral symmetry,*
* with a right half and left half.*
What is cleavage and when does it occur?
Cleavage – the process during prenatal development when mitosis converts a zygote to a blastocyst
After fertilization, the zygote then undergoes mitosis, or individual cell division, that splits it into more and more cells due to cleavage. After initial cleavage, the solid ball of cells becomes a morula. Because of the ongoing process of mitosis and secretion of fluid by the cells within the morula, the zygote now becomes a blastocyst (or blastula). The rest of the first week is characterized by further mitotic cleavage, in which the blastocyst splits into smaller and more numerous cells as it undergoes successive cell division by mitosis.

When does the maxillary and nasal processes form?
4th week
The migratory cells located in the middle between the epiblast and hypoblast layers become mesoderm, an embryonic connective tissue, as well as embryonic ______.
endoderm
Neuroectoderm
specialized group of cells that differentiates from ectoderm. Gives rise to the respiratory epithelium and cells of glands

The neural crest cells migrate from the crests of the neural folds and then join the _______ to form mesenchyme.
mesoderm
By the end of the ______ week, the mesoderm additionally differentiates and begins to divide on each side of the tube into 38 paired cuboidal segments of mesoderm, forming the _____.
third; somites
Hypoblast
inferior layer from the bilaminar embryonic disc composed of small cuboidal cells.
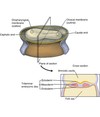
After a morula cleaves through additional mitotic divisions it is now called a __________
blastocyst
How many processes are included in facial development?
Facial development depends on the five major facial processes that form during the fourth week and surround the primitive mouth of the embryo:
1. frontonasal process.
2/3. mandibular process (paired)
4/5. maxillary process (paired)
- The line of demarcation between the attached gingiva and the alveolar mucosa is the:
a. mucogingival junction.
b. interdental gingiva.
c. mucobuccal fold.
d. marginal gingiva.
a.mucogingival junction.
Junctional epithelium
the epithelial attachment provides a seal at the base of the sulcus
non keratinized separates the periodontal ligament from the oral environment

- The development of the neck parallels the development of the face over time, beginning during the fourth week of prenatal development within the embryonic period and completed during the _____ period.
a. preimplantation
b. embryonic
c. fetal
d. both the embryonic and fetal
c.fetal
______ is the superior layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc
Epiblast
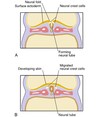
Where do the neural crest cells migrate from?
These cells migrate from the crests of the neural folds and then join the mesoderm to form mesenchyme.
The line of demarcation between the firmer and pinker attached gingiva and the movable and redder alveolar mucosa is the scallopp-shaped ________
Mucogingival junction
There are 4 muscles of mastication:
- Masseter
- Temporalis
- Medial pterygoid
- Lateral pterygoid
All attach to the mandible and are innervated by V3
Form in the tenth week of development
First arches (mandibular arches)
Which of the following muscles is involved in the lateral deviation of the mandible?
a. masseter muscle
b. medial pterygoid muscle
c. lateral pterygoid muscle
d. temporalis muscle
e. digastric muscle
c. lateral pterygoid muscle
What are the 3 stages of pregnancy?
Preimplantation period – first week (zygote, blastocyst)
Embryonic period – weeks 2-8 (disc, embryo, folded embryo)
Fetal period – months 3-9 (embryo, fetus)
- In which week of prenatal development does facial development begin in the embryo?
a. Second
b. Fourth
c. Fifth
d. Eighth
b.Fourth
The ______ of the hyoid arches helps form the muscles of facial expression, the middle ear muscles, and a suprahyoid muscle.
mesoderm
in week 3 (embryonic period), the Neural Crest Cells develop into what?
- ) components of nervous system pigment cells, connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, certain dental tissue
- ) Histologic Features- Varies
- ) Origin- Migrating neuroectoderm
- What does the maxillary process form from during the fourth week of prenatal development?
a. Lateral nasal processes
b. Mandibular arch
c. Intermaxillary segment
d. Medial nasal processes
b.Mandibular arch
What exact cells or structures develop from neuroectoderm and migrate from the neural folds to then join mesoderm to form mesenchyme during the third week of prenatal development?
a. Somites
b. Neural crest cells
c. Mesoderm
d. Yolk sac
b.Neural crest cells
- In which of the following do the final stages of meiosis occur during prenatal development?
a. Placenta
b. Ovum
c. Sperm
d. Yolk sac
b.Ovum
Which specific muscle can become clinically enlarged in patients who habitually clench or grind (with bruxism) their teeth and in those who constantly chew gum?
a. Masseter muscle
b. Lateral pterygoid muscle
c. Medial pterygoid muscle
d. Temporalis muscle
a. Masseter muscle
Gingival margin
.
the edge of the gingiva nearest to the incised surface of the tooth

By the end of the _____ week of the preimplantation period, the blastocyst stops traveling and undergoes ______ and thus becomes embedded in the prepared endometrium, the innermost lining of the uterus on its back wall.
first; implantation
Which local anesthetic block anesthetizes the largest intraoral area?
A. Buccal block
B. Inferior alveolar block
C. Mental block
D. Incisive block
B. Inferior alveolar block
- Implantation of the zygote may also occur outside the uterus during prenatal development with a(n):
a. infection with rubella.
b. infection with syphilis.
c. ectopic pregnancy.
d. case of ectodermal dysplasia.
c.ectopic pregnancy.
_____ is the process of joining embryonic tissue of two separate surfaces, elimination of a furrow between two adjacent swellings, or development disturbances in which adjacent tooth germs unite to form large tooth
Fusion
Mesoderm
embryonic layer located between ectoderm and endoderm. Gives rise to CT such as skin dermis, cartilage, bone, blood, muscle, and associated other tissue
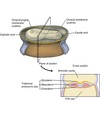
_____ is the embryonic layer located between ectoderm and endoderm.
Mesoderm
- Which of the following are considered cervical muscles?
a. Masseter and medial pterygoid muscles
b. Medial and lateral pterygoid muscles
c. Sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
d. Buccinator and epicranial muscles
c.Sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
Bilateral symmetry
Bilateral symmetry is when each half of an embryo mirrors the other half.

The ______ _____ provides anesthesia for the mandibular anteriors and premolars but only for the associated facial periodontium, and it can be used bilaterally without complications.
mental block
- On what structure do BOTH heads of the masseter muscle originate?
a. Zygomatic process of the maxilla
b. Coronoid process
c. Zygomatic process of the frontal bone
d. Zygomatic arch
d.Zygomatic arch
- When does the blastocyte stop traveling and undergo implantation during prenatal development?
a. First week
b. Second week
c. Third week
d. Fourth week
a.First week
- By the end of the first week of prenatal development, the blastula stops traveling and undergoes:
a. implantation.
b. migration.
c. disintegration.
d. amniocentesis.
a.implantation.
Lateral pterygoid
The superior head originates from the greater wing of the sphenoid. The inferior head originates from the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid. The two heads converge into a tendon, which attaches to the neck of the mandible.

short thick almost conical muscle of mastication superior to the medial pterygoid. Two separate heads (superior an inferior). They are separated anteriorly by a slight interval but fuse together posteriorly.
The entire muscle lies within the infratemporal fossa deep to the temporalis muscle.
The only muscle of mastication that ASSISTS in depressing the mandible, lowering the lower jaw! Depression of the mandible occurs during the opening of the jaws. Protrusion also occurs when the jaws are opened
The muscle is innervated by the lateral pterygoid nerve, a branch of the mandibular nerve (V3)
Pterygomandibular space is formed by the lateral pterygoid muscle (roof), medial pterygoid muscle (medial wall), and the mandibular ramus (lateral wall). It is the injection site for the inferior alveolar block.

Which of the following is the BEST term used for the embryonic layer located between the ectoderm and the endoderm?
a. Mesenchyme
b. Ectomesenchyme
c. Mesoderm
d. Mesiodens
c. Mesoderm
After folding of the disc, the _____ lies inside the _____, with mesoderm filling in the areas between these two layers. This movement of the embryonic cell layers forms one long, hollow tube lined by endoderm from the cephalic end to the caudal end of the embryo
endoderm; ectoderm
Embryonic layers (germ layers)
increased number of embryonic cells within the blastocyst.
_____ is a layer in trilaminar embryonic disc derived from epiblast layer and lining stomodeum
Ectoderm
- The folding of the embryo during prenatal development causes _____ to be on the _____.
a. endoderm; inside of the embryo
b. ectoderm; inside of endoderm
c. endoderm; outside of the mesoderm
d. mesoderm; outside of the ectoderm
a.endoderm; inside of the embryo
What does the mandibular arch form from?
The fusion of the two mandibular processes
Gingival sulcus
The crevice between the free gingiva and the tooth.
- A type of cleft lip can result during prenatal development from the lack of fusion between _____ processes.
a. mandibular and maxillary
b. medial nasal and maxillary
c. lateral nasal and medial nasal
d. two lateral nasal
e. lateral nasal and maxillary
b.medial nasal and maxillary
How does cleft lip form?
Failure of fusion of the maxillary process
with the medial nasal process
The maxillary first molar is usually NOT a landmark for any maxillary nerve anesthesia, but the ______ _____ _____ is a landmark for the administration of the posterior superior alveolar nerve block.
maxillary second molar
Alveolar mucosa
The thin, moveable, loosely attached tissue covering the alveolar bone.
non keratinized

in week 3 (embryonic period), the trilaminar embryonic disc develops two ends called?
- ) Cephalic end (Head end)
- ) Caudal end (Tail end)
- The neural crest cells migrate from which embryonic structures during prenatal development?
a. Stomodeum
b. First branchial arch
c. Neural folds
d. Frontonasal process
c.Neural folds
After a zygote cleaves through mitosis it is now called a ________
morula
- The developmental disturbance of cleft lip is more commonly found:
a. in males.
b. bilaterally.
c. on the right side.
d. on the lower lip.
a.in males.
_______ means that each half of embryo mirrors the other half
Bilateral symmetry
At the cephalic end, the oropharyngeal membrane forms, which consists of only ______ externally and endoderm internally, without any intermediate mesoderm.
ectoderm
- On which of the following orofacial tissue is the linea alba located?
a. Attached gingiva
b. Marginal gingiva
c. Labial mucosa
d. Buccal mucosa
d.Buccal mucosa
Medial pterygoid

Rectangular form has 2 heads due to differing depth (deep and superficial, smaller head).
The superficial head originates from the maxillary tuberosity and the pyramidal process of palatine bone. The deep head originates from the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone. Both parts attach to the ramus of the mandible, near the angle of mandible.
DEEPEST MUSCLE OF MASTICATION
Elevates the mandible during the closing of the jaws
Innervated by V3

What’s the diff b/w meiosis and mitosis
Meiosis – The process of reproductive cell production that ensures the correct number of chromosomes; meiosis that takes place during fertilization.
Mitosis – cell division that occurs in phases and results in two daughter cells; Mitosis is a process that takes place during tissue growth or regeneration
- Which of the following tissues listed will develop from the ectoderm layer of the embryo during prenatal development?
a. Epidermis
b. Liver
c. Muscle
d. Dermis
a.Epidermis
Masseter

Most superficial and strongest. Thick flat rectangular muscle on each side of the face, anterior to the parotid gland.
2 heads (superficial and deep)
Origin- Both heads originate from the zygomatic arch. Superficial =angle of the mandible. Deep = ramus
When the patient clenches their teeth is when the elevation of the mandible is taking place (closing of the jaws)
Innervated by the Masseteric nerve (V3)

- Which of the following muscles can show enlargement due to repetitive muscle contraction associated with clenching of the teeth in a patient?
a. Buccinator muscle
b. Masseter muscle
c. Temporalis muscle
d. Zygomatic muscle
b.Masseter muscle
Anesthesia Landmarks
IA
Teeth: Mandibular teeth to the midline (molar - central incisor)
Nerve: Inferior alveolar, mental, incisive nerve, lingual
Landmarks:
Medial surface of Ramus
mandibular foramen
pterygomandibular fold overlying raphe
- Which of the following muscles when contracted allows for the retraction of the mandible?
a. Masseter muscle
b. Temporalis muscle
c. Lateral pterygoid muscle
d. Medial pterygoid muscle
b.Temporalis muscle
Temporalis

broad fan-shaped muscle of mastication on each side of the head that fills the temporal fossa, superior to the zygomatic arch.
Temporal space is formed by the temporal fascia covering the temporalis muscle. Infratemporal space is bordered laterally by the medial surface of the mandible and the temporalis muscle.
originates from the temporal fossa – a shallow depression on the lateral aspect of the skull. Inserts on coronoid process
Action- retraction of mandible, elevating the mandible. Also allows freeway space at its physiologic rest position
Innervated by V3

What does the maxillary process form from?
The mandibular arch (During the fourth week of prenatal development, within the embryonic period, an adjacent swelling forms from increased growth of the mandibular arch on each side of the stomodeum, the maxillary process.)

in week 3 (embryonic period), the endoderm develops into what?
- ) respiratory/digestive system linings
- ) glandular cells
- ) liver/pancreatic cells
- ) Histologic features- Cuboidal
- ) Origin- Migrating cells from epiblast layer
Medial nasal processes
weeks 4-7
Endoderm
cells that locate in the middle with mesoderm between the epiblast and hypoblast layers and embryonic CT

When does implantation occur and how does it occur?
As the blastocyst grows by cleavage, it travels from the site where fertilization took place to the uterus.
By the end of the first week, the blastocyst stops traveling and undergoes implantation and thus becomes embedded in the prepared endometrium, the innermost lining of the uterus on its back wall.

When does the primitive streak form (“when do things form??”)
During the beginning of the third week of prenatal development within the embryonic period, the primitive streak forms within the bilaminar disc. This furrowed, rod-shaped thickening in the middle of the disc results from increased proliferation of cells in the midline area.

- The mandibular arch during the embryonic period of prenatal development is the:
a. fusion of the two paired mandibular processes.
b. swelling found superior to the stomodeum.
c. structure that gives rise to the lateral nasal process.
d. posterior part of the hard palate.
a.fusion of the two paired mandibular processes.
In week 1 (preimplantation), name the events that occur within the organism as it develops (in order):
- ) fertilization w/ sperm and ovum
- ) zygote undergoes mitosis (cleavage), to form a morula
- ) morula forms a blastocyst -2 layers now (trophoblast, embryoblast)
- ) Blastocyst implants in the endometrium.
- ) trophoblast layer gives rise to prenatal support tissue, embryoblast layer gives rise to the embryo.
What’s the neural tube?
As further growth of the neuroectoderm occurs, the neural tube is formed during the fourth week by the neural folds undergoing fusion at the most superior part. The neural tube forms the future spinal cord as well as other neural tissue of the CNS.

When do the paranasal sinuses form?
4th week
Some of the paranasal sinuses develop later during the fetal period, and others develop after birth.
All form as outgrowths of the walls of the nasal cavities and become air-filled extensions of the nasal cavities in the adjacent bones, such as in the maxilla and the frontal bone.’
The gingival tissue that adheres to the teeth is _____
attached gingiva
When do the maxillary and nasal processes form?
Maxillary process – 4th week
Nasal processes:
Frontonasal process – 4th week
Medial nasal processes – weeks 4-7
Lateral nasal processes – week 4
- Which of the following phrases concerning the second branchial arch during prenatal development is correct?
a. Called the mandibular arch
b. Contains Reichert cartilage
c. Forms into the muscles of mastication
d. Associated with the trigeminal nerve
b.Contains Reichert cartilage
When does the medial nasal and the maxillary processes form?
What happens when they form incorrectly?
The upper lip is formed from the fusion of the maxillary process with the medial nasal process.
This process starts at the beginning of the sixth week and is completed during the end of the seventh week of pregnancy.
When they form incorrectly, a cleft lip can occur.
The height of the _____ fold and the ______ are landmarks for the administration of the posterior superior alveolar nerve block.
mucobuccal; maxillary tuberosity
Anesthesia Landmarks

MSA
Nerve: Middle superior alveolar
Teeth: maxillary molars
Landmarks:
maxillary mucobuccal fold
maxillary 2nd premolar

in week 3 (embryonic period), the ectoderm develops into what?
- ) skin epidermis
- ) CNS
- )NCC’s
- ) mammary & cutaneous glands
- ) Histologic feature-Columnar
- ) Origin- Epiblast layer
- The _____ are rounded areas of specialized, thickened ectoderm found at the location of developing special sense organs.
a. placodes
b. branchial arches
c. branchial pouches
d. processes
a.placodes
In addition, during the third week, another specialized group of cells, the _____ cells, develop from neuroectoderm.
neural crest
- The philtrum of the upper lip forms during sixth week of prenatal development from the:
a. mandibular processes.
b. medial nasal processes.
c. lateral nasal processes.
d. nasal placodes.
b.medial nasal processes.
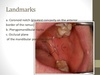
Parts of free gingiva
Gingival margin
gingival sulcus
junctional epithelium
free gingival groove
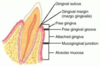
Frontonasal process
4th week
- The medial nasal processes are involved directly in the formation of the embryo’s _____ of the nose during prenatal development.
a. bridge
b. sides
c. bridge and sides
d. nasal placodes
a.bridge
Which of the following local anesthetic nerve blocks uses the apex of the maxillary canine for a landmark during administration?
a. Infraorbital nerve block
b. Anterior superior alveolar nerve block
c. Middle superior alveolar nerve block
d. Posterior superior alveolar nerve block
b.Anterior superior alveolar nerve block
_____ is a layer in trilaminar embryonic disc derived from hypoblast layer.
Endoderm
What happens in the second branchial arch - what forms from it?
Forming within the second branchial arch, which is also known as the hyoid arch, is cartilage similar to that of the mandibular arch, Reichert cartilage. Most of it disappears during development; however, parts of it are responsible for a middle ear bone, a process of the temporal bone, and parts of the hyoid bone.
facial nerves, muscles of facial expression, PB digastric muscle, stylohyoid muscle
Free gingiva
closely adapted around each tooth but not attached
keratinized

- When do the paranasal sinuses develop during prenatal development?
a. Preimplantation period
b. Embryonic period
c. Fetal period
d. Fetal period and after birth
d.Fetal period and after birth
Anesthesia Landmarks
PSA
Teeth: Maxillary molars
Nerve: Posterior superior alveolar
Landmarks:
Maxillary tuberosity
PSA foramina
maxillary mucobuccal fold
maxillary second molar
in week 3 (embryonic period), name the events that occur within the organism as it develops (in order):

- ) development of primitive streak w/in the disc (creating bilateral symmetry)
- ) epiblast layer cells migrate toward hypoblast layer to become mesoderm and embryonic endoderm.
- ) formation of trilaminar embryonic disk (mesoderm, endoderm, ectoderm)
- ) CNS development (brain, spinal cord begin)
A.) ectoderm creates neuroectoderm, within neural plate, that thickens to form neural groove.
B.) Neural groove deepens to become surrounded by neural folds
C.) neural folds meet and fuse to form neural tube.
5.) Formation of somites (38-paired cuboidal segments of mesoderm)

Process of reproductive cell production that ensures correct number of chromosomes
Meiosis
- Which period of prenatal development is characterized by increased cellular differentiation?
a. Unattached conceptus
b. Embryonic period
c. Preimplantation period
d. Fetal period
c.Preimplantation period
Neuroectorderm
a specialized group of cells that differentiates from the ectoderm. Eventually develops the neural tube

- The maxillary processes on each side of the developing face partially fuse with the mandibular arch on each side to create the:
a. philtrum.
b. tubercle.
c. labial commissures.
d. lower lip.
c.labial commissures.
What best characterizes the first week of prenatal development so that the blastocyst splits into smaller and more numerous cells?
a. Implantation
b. Mitotic cleavage
c. Meiosis
d. Fertilization
b. Mitotic cleavage
* The first week of prenatal development is best characterized by further mitotic cleavage, in which the blastocyst splits into smaller and more numerous cells as it undergoes successive cell divisions by mitosis. During fertilization, the final stages of meiosis occur in the ovum; this process is the joining of the ovum’s chromosomes with those of the sperm. By the end of the first week, the blastocyst stops traveling and undergoes implantation, thus becoming embedded in the prepared endometrium, the innermost lining of the uterus on its back wall.*
Interdental papillae
Extensions of unattached gingiva between adjacent teeth
keratinized fills embrasure spaces

Anesthesia Landmarks
ASA

Nerve: Anterior superior alveolar
Teeth: maxillary anterior teeth
Landmarks:
maxillary mucobuccal fold
canine eminence
maxillary canine

- How many processes are considered major during facial development so that they become the centers of growth for the face?
a. Two
b. Three
c. Four
d. Five
d.Five
Which muscle of facial expression compress the cheeks during chewing assisting the muscles in mastication?
a. risorus
b. buccinator
c. mentalis
d. orbicularis oris
e. masseter
b. buccinator
The mucogingival junction is a line of demarcation between the attached gingiva and the:
a. buccal mucosa.
b. marginal gingiva.
c. gingival sulcus.
d. alveolar mucosa.
d. alveolar mucosa.
In week 2 (embryonic period), name the events that occur within the organism as it develops (in order):

- ) implanted blastocyst grows via proliferation + morphogenesis.
- ) leads to the formation of bilaminar embryonic disc (epiblast EB layer
[high columnar cells], and hypoblast HB layer [small cuboidal cells]).
- ) suspension of the disc in endometrium between amniotic cavity (EB) and the yolk sac (HB) (embryo sac).
- ) Placenta joins embryo, allowing oxygen, CO2, nutritional, and hormonal substances to exchange.
- Which of the following muscles when unilaterally contracted deviates the mandible to one side?
a. Masseter muscle
b. Lateral pterygoid muscle
c. Medial pterygoid muscle
d. Temporalis muscle
b.Lateral pterygoid muscle
Mucogingival junction
The line that marks the connection between the attached gingiva and the alveolar mucosa on the facial surfaces of all quadrants and the lingual surfaces of the mandibular arch

The first week of prenatal development is best characterized by further ______ cleavage, in which the blastocyst splits into smaller and more numerous cells as it undergoes successive cell divisions by _____.
mitotic; mitosis
Ectoderm
layer in trilaminar embryonic disc derived from epiblast layer and lining stomodeum. Gives rise to the skin epidermis the CNS

A process that takes plce during tissue growth or regeneration, which is different than mitosis that takes place during fertilization
Mitosis
- From the following list of muscles, select which are considered muscles of mastication. (Select all that apply.)
a. Buccinator
b. Risorius
c. Platysma
d. Temporalis
e. Masseter
d. Temporalis
e. Masseter
Anesthesia Landmarks
Mental
Teeth: None
Nerve: Mental
Landmarks:
Mandibular premolars
mental foramen
mandibular mandibular fold
Attached gingiva
Part of the gingiva that is tightly connected to the cementum on the root (cervical third) and to the connective tissue cover of the alveolar bone

- Surrounding the teeth in the alveoli and covering the alveolar processes is the _____, which is composed of a firm pink tissue.
a. gingiva
b. minor salivary glands
c. Fordyce spots
d. linea alba
a.gingiva
Which of the following muscles has two bellies, giving the muscles two different origins?
a. lateral pteryoid
b. geniohyoid
c. thyrohyoid
d. stylohyoid
a. lateral pteryoid
Endoderm
layer in trilaminar embryonic disc derived from hypoblast layer

Fusion (what does it mean?)
Fusion is the joining of embryonic tissue of two separate surfaces, elimination of a furrow between two adjacent tooth germs unite to form large tooth.

in week 4 (embryonic period), name the events that occur within the organism as it develops (in order):
(Hint/trick to remember-fold, feed, face)

- ) trilaminar embryonic disk undergoes anterior (cephalic) and lateral embryonic folding (endoderm inside ecto+meso)
- ) formation of tube that becomes future digestive tract from cephalic (oropharyngeal membrane) to caudal (cloacal membrane) end. (Foregut [anterior], Midgut [posterior], Hindgut[posterior])
- ) Development of face and neck (primitive eyes, ears, nose, oral cavity, and jaw areas)

Epiblast
superior layer from the bilaminar embryonic disc composed of high columnar cells.

- From which embryonic layer is mesoderm derived during prenatal development?
a. Epiblast layer
b. Hypoblast layer
c. Endoderm
d. Neuroectoderm
a.Epiblast layer
- The pink labial mucosa or buccal mucosa meets the redder _____ at the mucobuccal fold.
a. marginal gingiva
b. attached gingiva
c. alveolar mucosa
d. interdental papilla
c.alveolar mucosa
Which of the following locations is the BEST injection site for the inferior alveolar local anesthetic nerve block?
a. Medial to the pterygomandibular fold
b. Lateral to the pterygomandibular fold
c. Superior to the pterygomandibular fold
d. Inferior to the pterygomandibular fold
b.Lateral to the pterygomandibular fold
What is Reichert cartilage?
Reichert cartilage is cartilage in the second branchial arch that eventually disappears.
When does the facial development start, what week?
4th week (within the embryonic period)
- The anterior part of the foregut and will form the primitive pharynx and the foregut is originally derived from the:
a. endoderm embryonic cell layer.
b. mesoderm embryonic cell layer.
c. ectoderm embryonic cell layer.
d. neural crest cells.
a.endoderm embryonic cell layer.
- Which of the following can occur that mainly involves the abnormal development of one or more structures from ectoderm within the embryonic period?
a. Treacher Collins syndrome
b. Ectodermal dysplasia
c. Congenital syphilis
d. Fetal alcohol syndrome
b.Ectodermal dysplasia
Transient facial paralysis can occur with which INCORRECTLY administered local anesthetic block?
A. Posterior superior alveolar block
B. Middle superior alveolar block
C. Nasopalatine block
D. Inferior alveolar block
E. Mental block
D. Inferior alveolar block
cell division that occurs in phases and results in two daughter cells
Mitosis
- Found in early prenatal development, the neural tube will form in the future which of the following structures?
a. Heart
b. Spinal cord
c. Face
d. Digestive tract
b.Spinal cord
Free gingival groove
a shallow linear demarcation between free gingiva and attached gingiva

What do the muscles of mastication work with to accomplish movements of the mandible?
a. Maxillae
b. Temporal bone
c. Temporomandibular joint
d. Zygoma
e. Hard palate
c. Temporomandibular joint
- Which of the following muscles inserts onto the coronoid process?
a. Lateral pterygoid muscle
b. Masseter muscle
c. Medial pterygoid muscle
d. Temporalis muscle
d.Temporalis muscle
- How many pairs of somites form the cuboidal segments of mesoderm within the embryo during the third week of prenatal development?
a. 12
b. 18
c. 38
d. 42
c.38
Which muscle listed below is MOST superficial in regard to location?
a. masseter muscle
b. medial pterygoid muscle
c. lateral pterygoid muscle
d. superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
c. lateral pterygoid muscle
- The fusion of the maxillary and medial nasal processes to form the upper lip is completed during the end of the _____ week of prenatal development, when the grooves between the processes are obliterated.
a. fourth
b. fifth
c. sixth
d. seventh
d.seventh
The ______ _____ block provides anesthesia for the pulp tissue of ALL the mandibular teeth as well as for the associated facial periodontium of the mandibular anteriors and premolars, but it is NOT recommended to use bilaterally due to complications with swallowing.
inferior alveolar
During the beginning of the third week of prenatal development within the embryonic period, the primitive streak forms within the bilaminar disc. The primitive streak causes the disc to have _____, with a right half and left half.
bilateral symmetry
From the following list of oral cavity landmarks, select those that need to be noted before administering a clinically effective posterior superior alveolar nerve block. (Select all that apply.)
a. Mucobuccal fold
b. Coronoid notch
c. Maxillary first molar
d. Maxillary tuberosity
a. Mucobuccal fold
d. Maxillary tuberosity
Which of the following descriptions concerning the masseter muscle is CORRECT?
a. most superficial muscle of the facial expression
b. originates from the zygomatic arch
c. insert on the medial surface of the mandible’s angle
d. depresses the mandible during jaw movement
b. originates from the zygomatic arch
How does the mandibular arch form (basically)?
After formation of the stomodeum but still within the fourth week, two bulges of tissue appear inferior to the primitive mouth: the two mandibular processes. These processes consist of a core mesenchyme formed in part by NCC’s that migrated to the facial region to join with the mesoderm; they are covered externally by ectoderm and internally by endoderm. These paired mandibular processes then fuse at the midline to form the mandibular arch.

If there is failure of migration of the neural crest cells to the facial region, _____ syndrome develops in the embryo.
Treacher Collins
Which of the following muscles is considered a muscle of mastication?
a. buccinator
b. risorius
c. mentalis
d. masseter
e. corrugator supercilii
d. masseter
Which of the following local anesthetic blocks has the SAME injection site as the incisive local anesthetic block?
A. Nasopalatine block
B. Greater palatine block
C. Inferior alveolar block
D. Buccal block
E. Mental Block
E. Mental Block
The mental foramen is usually located between the apices of which of the following mandibular teeth?
A. First and second molars
B. Second and third molars
C. First and second premolars
D. First premolar and canine
C. First and second premolars
- Which of the following facial structures is formed from the mandibular arch during prenatal development?
a. Forehead
b. Lower face
c. Philtrum
d. Nose
b.Lower face
in week 3 (embryonic period), the mesoderm develops into what?
- ) connective tissue (such as skin dermis, cartilage, bone, blood, muscle).
- ) excretory and reproductive organs
- ) histologic features- varies
- ) origins- migrating cells from epiblast layer
- When do the paranasal sinuses develop during prenatal development?
a. Preimplantation period
b. Embryonic period
c. Fetal period
d. Fetal period and after birth
d.Fetal period and after birth
- What is the exact term for the process that affords the development of specific tissue structure or differing form due to embryonic cell migration and inductive interactions?
a. Folding
b. Morphogenesis
c. Proliferation
d. Appositional or interstitial growth
b.Morphogenesis
- If there is failure of migration of the neural crest cells to the facial region during prenatal development, _____ can develop in the embryo.
a. ectodermal dysplasia
b. fetal alcohol syndrome
c. Down syndrome
d. Treacher Collins syndrome
d.Treacher Collins syndrome
The ______ is a landmark for the administration of the inferior alveolar nerve block.
coronoid notch
- From the following list of oral cavity landmarks, select those that need to be noted before administering a clinically effective inferior alveolar nerve block. (Select all that apply.)
a. Occlusal plane
b. Maxillary tuberosity
c. Pterygomandibular fold
d. Coronoid notch
e. Mandibular notch
a. Occlusal plane
c. Pterygomandibular fold
d. Coronoid notch
- The facial development that starts in the fourth week will be completed later in the _____ week within the fetal period.
a. fifth
b. sixth
c. eighth
d. twelfth
d.twelfth
After fertilization, the zygote then undergoes _____ , or individual cell division, that splits it into more and more cells due to cleavage.
mitosis


