Epidural Anesthesia ( Newby's Take) Flashcards
The objective for today's lesson is to become so badass in epidurals that when you walk into a room there is a crowd of midget clowns cheering and doing the wave
An epidural block can be performed at what levels?
- Lumbar
- thoracic
- Cervical
- Caudal
Epidurals have a wide rage of uses what are some areas of heathcare where the application of epidurals can be helpful
- operative anesthesia
- odstetric anesthesia and Analgesia
- Postop pain control
- chronic pain management
In the overall scheme of things an epidural can be used in different ways (think way to administer it)
- “Single shot”
- catheter that allows intermittent boluses or continuous infusion
Epidural Anesthesia:
a big advantage of epidural is that muscle blockade can range from _______ to ________
None to complete
Epidural Anesthesia:
everything (related to muscle blockade, pain control, etc) can be regulated and changed by what 4 factors?
- Drug Choice
- LA concentration
- Dosage
- Level of injection
Epidural Anesthesia:
the epidural space surrounds the Dura Mater in what directions?
- posterior
- laterally
- Anteriorly
Epidural Anesthesia:
the nerve roots travel in the dura mater and exit the spinal cord where (position not location)
Laterally
Epidural Anesthesia:
So we learned that the epidural space surrounds the Dura matter posteriorly, laterally, and anteriorly. The nerve roots travel iin this space and exit the spinal cord laterally. n the nerve roots then exit the ___1___ and travel peripherally to become peripheral nerves carrying both ___2__ and __3___ pathways
- Foraman
- Afferent
- Efferent
Epidural Anesthesia: Anatomy
What other 4 things (besides nerve roots) does the epidural space include
- Fatty connective tissue
- Lymohatics
- Venous plexus (Batson’s)
- Septa and Connective tissue bands
what is segmental blocks?
epidural or spinal?
epidurals are segmental blocks
why are spinals not considered segental blocks?
bc they block above and below
what is one of the most important aspects of placing an epidural?
getting the right spot! Remember epidurals are segmental blocks
Label this
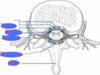
- Meninges
- Spinal Cord
- Spinal Nerve
- Epidural Space
- Vertebra

Epidural Anatomy: Name the structures found in the locations:
- Superior
- Inferior
- Lateral
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Fusion of the dura with the foramen magna
- Sacro-coccygeal membrane
- Vertebral pedicles and intervertebral foraminae
- Posterior longitudinal ligament and vertebral bodies
- Vertebral laminae and ligamentum flavum
Label this

- Dural sac
- Epidural vein
- Interlaminar space
- Lamina
- Ligamentum Flavum
- Supraspinous Ligament
- Intraspinous Ligament
- Spinous Process
- Transverse Process

LA or other solutions injected into the epidural space (steroids, Narcs) spread Anatomically.
So how is horozontal spread?
- is to the region of the dural cuffs with diffusion into the CSF and Leakage through the intervertebral foramen into paravetebral spaces
LA or other solutions injected into the epidural space (steroids, Narcs) spread Anatomically.
how is longitudinal spread?
preferentially cephalad in direction
odd fact he stated!
Clinidine binds where in r/t the synaptic cleft?
Presynaptically
What are 6 possiable sites of anesthetic action?
- Paravertebral Nerve roots
- intradural spinal roots
- Dorsal and Ventral Spinal roots
- Dorsal Ganglia
- spinal cord
- Brain (by diffusion)
Epidural physiology:
What facilitates the rapid diffusion of LA from the Epidural Space, throught the dura and into the CSF surrounding the nerve roots?
the dural cuffs or sleeves have arachnoid villi and granulations that reduce the THICKNESS of the dura matter thus facilitating transfer
the dural cuffs or sleeves have arachnoid villi and granulations that reduce the THICKNESS of the dura matter thus facilitating rapid diffusion of the LA from the epidural space through the dura and into the CSF surrounding the ther roots. then the LA diffuses into the nerve root it self, producing anesthesia to where?
that PARTICULAR dermatome (remember again segmental)
B/c Epidural anesthesia is ______ dependent, relatively large volumes of LA are needed to achieve a block that spans several dermatomes.
DIFFUSION
Max spinal Volume
Epidural volume
- 2 ml
- up to 15 ml
with an epidural the Block ONLY gets as high or low as you regulate it by what?
VOLUME
With epidurals _____ affects spread, so to get more levels give more _____
Volume
volume
With Epidurals:
The #1 factor to get action of epidural at a certain site is what?
The #2 factor is How much spread or how many dermatomes this is affected by what?
- location
- Volume
an epidural is not like a spinal in which everything distal to the level of the block is affected, an epidural is a differential block dependent on the ______ and ________?
volume
site of injection
Label this motha fucker

- Spinal cord
- Pia mater
- Arachnoid mater
- Dura Mater
- Conus Medullaris
- Cauda equina
- Ligamentum flavum
- Epidural space
- Internal filum terminale
- Distal dural sac
- External filum terminale
- Coccyx
- Sacrum
- Aorta

Epidural Advantages:
the epidural tech has the advantage of better control of ____ and ____ blockade
level
and sympathetic blockade
Epidural Advantages:
the epidural tech allows for the placement of a continuous catheter which is especially useful forwhat 4 things?
- cases of unpredictable duration
- prolonged postop analgesia
- Chronic pain control
- Obstetric Analgesia and Anesthesia
What is teh spread of epidural anesthesia termed?
rostral spread
the distribution of an opioid within the cerebrospinal fluid during epidural administration; it is determined by fat and water solubility properties of the narcotic
to be able to choose the most appropriate anesthetic dose, concentration and volume of LA the anesthetist must be familiar with the variables that affect spread and duration of Epidural anesthesia.
what has more variables spinal or epidural?
Epidural
Baricity plays a very SMALL or LARGE factor in Epidurals
Small
Unlike epidurals what is the key factor in spread and distribution of the block with spinal anesthesia
Baracity
What are 9 factors that affect the level of an epidural block?
emphisise the 2 most important factors
- injection site
- Dose
- Volume
- concentration
- position
- Age
- Height and weight
- pregnancy
- Speed of injection
Ulinke spinal anesthesia the epidural produces a segmental block that spreads both ____ and ____
Caudally
Cranially (i think cephalad is a better term)
Based on the fact that Ulinke spinal anesthesia the epidural produces a segmental block that spreads both Caudally and Cranially what is te most important determinant of the spread of an epidural block?
Injection site!!
God damn I think he states this 4 million fucking times in his god damn slides it better be a fucking question of the damn fucking test
The injection site should be where for an epidural?
in the middle of the range of dermatomes that need to be anesthetized and closest to the main nerve roots involved
Caudal epidural blocks are largely restricted to _____ and _____ ______ dermatomes
Sacral
Low Lumbar
Thoracic levels can be reached by caudal approach only if _______ are given, and then the block is patchy at best bc of the distance that the anesthestic must travel
Large volumes 30mL
Lumbar LA injections of __mL tend to spread caudad to include all the sacral dermatomes
10 mL
Lumbar injection of __mL volumes produce much better quality sacral blocks and can also extend cranially to include the midthoracic levels
20mL
Thoracic injections tend to produce a _______ segmental band of anesthesia with minimal lumbar spread
symmetric
When using a thoracis approach, it is prudent to decrease your volume by about ____ to ____% to prevent cranially spread.
30-50%
when doing a thoracic epidural you want to use less volume to minimize crainial spread b/c what don’t you want to anesthetized and where is it located????? HMMMM
Cardiac Accelerator C4
is it generally feasable to produce surgical anesthesia in the low lumbar or sacral nerve distributions when using a thoracic injection site?
NOPE
Thoracic injections are ideally suited for procedures of where?
chest
upper abd
postop thoracotomy
within the range typically used for surgical anesthesia drug CONCENTRATION is relatively unimportant in determining what?
block spread!
What is the #1 way to tell density of block?
Concentration
_____ and _____ are important variables in determining both spread and quality of the epidural block obtained
Dose and Volume
Epidural: Dose, Volume , Concentration
if the drug CONCENTRATION is held constant, increasing the volume of LA (thus increasing the dose) results in significantly greater what?
Spread
Epidural: Dose, Volume , Concentration
if the drug CONCENTRATION is held constant, increasing the volume of LA (thus increasing the dose) results in significantly greater Spread.
Dose = what
dose = volume x concentration
Epidural: Dose, Volume , Concentration
if the drug CONCENTRATION is held constant, increasing the volume of LA (thus increasing the dose) results in significantly greater Spread.
For example notice the dose increases and VOLUME increases but the concentration remains the same thus you get a greater spread without changing the concentration
give me the doses
15 ml and 20 mL of 0.25 % Lidocaine
15mL x 2.5 mg/mL =37.5 mg
20 mL x 2.5 mg/mL = 50 mg
so after everything I just went over we now know that the CONCENTRATION of the LA generally affects the _____ of the block not the ______
DENSITY
SPREAD
Epidural: Dose, Volume, and Concentrations
So continued from all the info we now know.
- a small volume of a more concentrated LA will produce what in a block?
- Now take that same DOSE and double the volume and what will happen?
- Very limited but very STRONG
- SPREAD increases but weaker block
Epidural: Dose, Volume, and Concentration
the increase in block level is NOT in direct proportion to volume increase. Thus Doubling the VOLUME will NOT double the block spread. it is a NON-linear relationship and doubling the volume will only increase the level about ___-__ the origional # of segments
1/3-1/2
Epidural: Dose, Volume, and Concentration
the same relationshiop exist with DOSE; doubling the dose will usually only increase the level block the same ___ -___ of the origional segments blocked
1/3-1/2
Epidural: Dose, Volume, and Concentration
recommended amts of LA differ as to which level is being injected:
- Cervical/thoracic doses are ___ - __ mL per segment
- Lumbar level doses are ___-____mL per segment
- 0.7-1
- 1.25-1.5
Epidural: Dose, Volume, and Concentration
why do the volumes get smaller the more crainial you are in the epidural space? for ex why give 0.7- 1 mL per segment in thoracic and 1.25-1.5 in the lumbar
due to the narrowing of the spinal canal as iot progresses cranially
Epidural: Dose, Volume, and Concentration
****** remember this slide****
using a lower concentration anesthetc can sometimes give u a differential block! the lower the concentration means the dose is lower and there is less LA to penetrate the nerve roots so the block acts more ________ an the nerves, differentially blocking sensory and pain fibers over larger muscle fibers in the center os the nerves
periperally
Epidural: Dose, Volume, and Concentration
Based off the last slide!!
- Bupivicaine 0.25%, 20mL tends to provide what type of block?
- then if Bupivicaine 0.5% 20 mL is given what type of block is provided?
- tends to provide a sensory block, but leaves the motor fibers intact so a pt can push when needed
- provides a sensory block as well as a a motor block paralyzing the muscles at the levels of the block so NO pushing is going to be possible
studies on epidural anesthesia r/t positioning showed that which position is better? sitting or lateral?
either it’s your choice! data showed that here was little to no difference
- Studies in epidurals have showed what in r/t age?
- why?
- what effect does this have on the dermatome coverage?
- showed that there is a greater spread in older pt’s
- b/c there is thought to be less comliant epidural space and dura mater
- at most an increase in NO more than 3-4 dermatomes
epidural and height and weight
- what do the studies say concerning height and weight r/t epidural spread?
- what is teh exception?
- no clinical signicicance
- except for MAYBE in extremly tall >6’6” or very short < 4’10” or in morbidly obese
Epidural anesthesia: Pregnancy
what do studies say about epidural spread r/t pregnancy?
- some show greater spread at term and early pregnancy
- other studies show no significant differences in spread of pregos vs non-pregos
Epidural and spead of injection
- what do the studies say about spread of epidural r/t speed of injection
- no study has shown it to make a difference
- infact drugs should be injected slowly into the epidural space the avoid a rapid increase in CSF pressure, H/A, and increased ICP
(spinals use spead for spread)
Epidural anesthesia: speed of injection
All slutions should be injected in increments of ____mL every _____ min and titrated to the disired level.
- 3-5 mL
- 3 min
Epidural anesthesia: speed of injection
if a catheter had been placed and you are injecting through it, what needs to be done prior to every injection? and why?
- aspirated
- to show no CSF is present
Epidural anesthesia: speed of injection
what is an advantage of an epidural of spinal r/t speed of injection
- gradual administration of medication slows rate of onset of level and controls development of sympathetic block
- the spinal is all or none where epidural can be brought up slowly
Epidural Anesthesia: Summary
Drug Volume
- larger volume gives more spread than small volumes
Epidural Anesthesia: Summary
site on injection
- the epidural space increases in volume in the cervico-caudad direction
- thus a given volume will produce greater spread in the cervical > thoracic > lumbar > sacral
- onset is fastest and most intense in the dermatomes nearest the site of injection
Epidural Anesthesia: Summary
raised abdominal pressures
- smaller volumes may be needed inpregnancy and morbid obesiyty
Epidural Anesthesia: Summary
patient position
- prolonged sitting position may reduce upward spread
- earlier onset of block in dependent side in lateral position
*
Epidural Anesthesia: Onset of Blockade
the onset of an epidural can usually be detected within ___ min in the dermatomes immediately surrounding the injection site
5 min
Epidural Anesthesia: Onset of Blockade
the time to PEAK effect differs somewhat among different LAs
- shorter acting drugs usually reach their maximum spread in ___-___ min
- Longer acting LAs usually reach their maximum spread in ___-___ min
- 15-20 min
- 20-25 min
Epidural Anesthesia: Onset of Blockade
increaseing the ____ of LAs speeds the onset of both motor and sensory block
DOSE
Epidural Anesthesia: Duration of Blockade
the duration of the blockade depends on what 4 factors
- The LA itself
- Dose given
- Pt age
- Use of adrenergic agonist
Epidural Anesthesia: Duration of Blockade
your choice of LA is the most important factor in determining the _______ of the block
duration
Epidural Anesthesia: Duration of Blockade
name the LA
__1__ is the shortest, __2__ and __2__ are intermediate, and __3__ and __3__ produce the longest lasting epidural blocks
- Chlorprocaine
- Lidocaine & Mepivicaine
- Bupivacaine & Ropivacaine
Epidural Anesthesia: Duration of Blockade
Bupivicaine
- is the opposite of what drug?
- in low doses seems to have a preferential _____ block with minimal ____ effect
- that is why it is an ideal drug for _____ analgesia. thus eliminating pain while preserving muscle function
- Etidocaine
- sensory; motor
- Obstetric (they can push)
Epidural Anesthesia: Adrenergic Agonists
what is the most common adrenergic agaent added to epidural LAs
epinephrine
Epidural Anesthesia: Adrenergic Agonists
epinephrine in a concntration of what is the most common adrenergic agent added to epidural LAs
5 mcg/mL
1:200,000
(I always have a little problem remebering the mcg conversion probally b/c I am a dumb ass but this is now how I remember it if anyone cares… 1:200,000 means in math 1,000 mg in 200,000 so if you do the math you get 0.005mg or 5 mcg/ml or you can convert it into mcgs up front and do the math as 1,000,000 mcg in 200,000 which then equals 5mcg/mL or just do it you way! I just need to show proof why I answer something)
Epidural Anesthesia: Adrenergic Agonists
Epinephrine 5mcg/ml, has been shown to prolong blocks of lidocaine and mepivicaine by as much as __%
80
Epidural Anesthesia: Adrenergic Agonists
epinephrine has been shown NOT to significantly prolong bthe duration of anesthesia when added to concentrated solutions of ______ and ______ used for surgical anesthesia
bupivacaine
Ropivacaine
Epidural Anesthesia: Adrenergic Agonists
as stated epinephrine does not increase the block when added to high concentrations of bupivacine and ropivacaine in surgical anesthesia, but what about when added to more dilute concentrations of bupivacaine used for OB
it has beenshown to incrase the duration and quality of block
(but no one knows why?)
Epidural Anesthesia: Adrenergic Agonists
although NEVER proven why is it thought that epinephroine prolongs the duration of a block
throough vasoconstriction it slows systemic absorption and elimination
It is often easier to deal with a block that is too high or too long than to cover uo for a block that is too low or not dense enough
justa little tip!! enjoy it, embrase it
tip #2
i’s always better to have a little more than a little less, especially with regional anesthesia
as in all great things in life
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
what should always be immediatly avail when doing an epidural?
emergency equipment and monitors
Name the positions as extension or flexion?

- extension
- flexion

label the pic as extension or flexion

- extension
- Flexion

Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
Name the most commonly performed epidural in order from most common to least common
- Lumbar
- caudal
- thoracic
- Cervical
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
today most high thoracis and cervical epidurals are performed under what and by whom
- flouroscopic guidance
- pain specialist
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
as you can see from the diagram
- the lumbar region is at or greater than a 90 degree angle
- thoracic is more acute
- and cervical is between the 2

Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
WHy is the lumbar region is by far the eastiest area to perform an epidural? (4 reasons)
- angle of spinous process
- larger spaces b/t spinous processes
- easialy identifiable locations (illiac crest)
- epidural width the greatest
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
with a spinial the practicioner looks to find CSF to confirm by peircing the dura to find proper location. in an epidural where does the practicioner want to place the tip.
into the fat filled space DEEP to the ligamentum Flavum and SHALLOW the DURA
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
is performed with what gauge neddles?
16
17
0r 18
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
what tyoe tipped needle
blunted
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
name the epidural needles

- Standard Tuohy
- Blunt tip
- Crawform needle (thin walled)
- Weiss winged needle

Label

- Dura
- Spinal
- Epidural
- Touhy needle

Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
lets go name the steps!!!! start from the begining you are doing this mother fucker and need to own it
- identify landmarks and plan interspace of insertion
- position pt
- sterile prep and drape with insertion site in center of drap (where hole is located)
- Local anesthetic (lido 1% plain) 1-2 mL wioth 25 g skin needle
- firmly place back of your NON-dominant hand against the patients skin below the epidural needle
- grasp the needle (and eventually the hub once epidural space is found b/t your thinb and index finger of NON-dominant hand) (called the Bromage grip)
- the epidural needle is placed bevel up and introduced into the skin
- passed slowly throught th esupraspinous ligament and seated in the interspinous ligament before stylet is removed (** you can tell the needle is in the interspinous ligament by letting go of the needle it should be supported in the same position, and not drop down)
- After stylet removed the needle is advenced using the LOR tech
- As the syringe/needle combo is advanced pressure is applied to the plunger of the syringe by “bouncing” or intermittently applying pressure to the plunger
- the pattern is move-bounce-move-bounce-move-bounce until LOR is obtained
- as the needle passes throught the ligamentum flavum, resistance increases and you may feel a distinct pop as you pass through it
- once throught the LF you will experience an immediate LOR and then the tip of the needle will be in the epidural space
- once the eidural space is reached pass your stylet throough the needle to make sure there is no tissue plugs possiably blicking the flow of CSF (with an inadvertent Dural punture)
- Once in is confirmed begin by injecting a TEST DOSE of 3 cc of LA with epi (lido 1.5 w/epi)
- watch monitor at look for HR increase within 30 sec (intravascular)
- question the pt on ringing in ears metalic taste in mouth or cirum-oral numbness or punding in chest
- wait 3 min to assess for numbness or weakness in LE (dural injection)
- is all good give meds or pass catheter
just some pics

Just a pic

Just a pic

Label this

- Ligamentum flavum
- Epidura; Space
- Dura
- Cauda quina
- Supraspinous ligament
- Intraspinous ligament
- Ligamentum flavum
- Epidural space
- Dura

Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
the local for skin is usually what? b/c it usually found in the kit and alays consitant
1-2 cc 1% plain
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
what is the “grip” called when doing the epidural
Bromage grip
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
the needle goes in with the bevel in what direction?
up
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
when is the stylet removed
when in the intraspinous ligament
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
what is used to obtain LOR
glass syringe filled with either 3-4 cc of air or NS or mixture of both
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
once usuing LOR tech the needle should be advanced how much at a time and the retested for LOR
0.5-1cm at a time
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
the syringe needle combo is advanced applying pressure the needle or syringe?
needle
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
in younger pts in OB you may not notice a distinct “pop” what might you only notice
LOR
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
once in the epidural space why do you replace the stylet?
to remove any tissue to asses for CSF leakage
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
what is teh typical test dose
3 cc of lido 1.5% with epi
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
if u inject intravascular you will see an increase in HR how fast
30 sec
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
besides watching HR with test dose what might you want to ask the pt with the test dose?
- Ringing/buzzing in ears
- metallic taste
- circum-oral numbness
- punding in chest
*
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
if you happen to inject the test dose in the dural space what might the pt have that you want to assess for? and how long does it take to show up?
- numbness or weakness or pins and needle sensation in LE
- 3 minutes
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
pros to advancing catheter first
- you can slowly raise the level of anesthesia and have better control and less incidence of sympathetic block
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
cons of catheter placement first
- cath may not go into correct space
- may come out on nerve root
- may kink or coil
- thus giving a useless epidural or patchy at best
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
pros of injection first
- LA opens up and distends epidural space makiing it easier to pass catheter
- if catheter fails you still have a complete block for a while
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
regardless what tech is used as you pas the catheter the patient should be warned that while movement of catheter they may feel what?
and why?
- electrical shock or funny bone feeling
- b/c cath tip brushing up against nerve root or two as it is passed in epidural space
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
as the cath is passes you may feel initially some rersistance at the tip, what should you do?
give a slightly stringer push
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
the catheter should be inserted between what depths
3-5 cm
no more than 3-5 black lines
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
NEVER do what with the catheter?
pull back throught the needle once it has been inserted
Epidural Anesthesia: Technique
whay do you never want to pull the catheter back throught the needle?
- there is a possibility to catch the catheter on the needle tip and shear or cut the tip off
- then it becomes a permanent new addition to the epidural space and will be there for the rest of the patients life!!! way to fuck that up
what are the 2 most dreadful words by an SRNA performing an epidural?
WET TAP
PDPH occurs in up to __% of pts who have a dural puncture with a touhy needle?
75%
WET TAP:Treatment
how do you treat it with consevation tech
- IV fluids
- analgesics
- IV/PO caffine
- lying flat in dark room
WET TAP:Treatment
what are invasive treatment tech
- epidural blood patch
- although invasive it is effective 90% of the time
Caudal anesthesia:
used for what sx’s
- anorectal sx in adults
- pediactrics
Caudal anesthesia:
Caudal anesthesia involves needle ot catheter penetration of the ______ ________ covering the sacral hiatis
Sacrococcygeal ligament
Caudal anesthesia:
the sacral hiatus is created by the unfused __ and ___ lamina
S4 and S5
Caudal anesthesia:
the sacral hiatus can be felt as a grove or notch where?
aboove the coccyx and b/t 2 bony prominences, “the sacral Cornua
Caudal anesthesia:
pic of sacral hiatus

Caudal anesthesia:
how is the block performed?
- The posterior Superior Illiac Spines and the sacral Hiatus form a triange
- pt placed prone or lateral decubitus
- sterile prep
- needle or cath is inserted at 45 degree angle to the skin until a “pop” is felt
- then the angle is droped and advanced aspirating for blood or CSF Q 1-2 cm
LAbel this pic

- Sacrococcygeal ligament
- Sacral hiatus
- Sacral canal
- Dural sac

Label this

- PSIS
- PSIS
- Sacral hiatus

Caudal anesthesia:
advantage for adults with anorectal procedures
can provide dense sacral sensory blockade with limited cephalad spread
Caudal anesthesia:
usual dose of anesthetic
15-20cc of 1.5-2% lidocaine with or w/o epi
Caudal anesthesia:
shuld be avoided in pt’s with what
pilionidal cyst


