EKG Flashcards
Differentiate the heart’s response to pressure vs. volume
- Pressure (such as increased afterload from systemic HTN) causes hypertrophy
- Volume overload such as seen in LV dysfunction or shunt causes dilation

Describe how hypertrophy changes EKG reads
Hypertrophy = increased muscle mass => increased in signal b/c more channels means more current

Saw tooth pattern of atrial flutter

Determining rhythm from EKG
(a) Source
(b) Regularity
Rhythm
(a) Source- SA nodal or ectopic? Look if there is a P wave before and in the same direction as each QRS- associated w/ sinus rhythm
(b) Regularity: 1:1 ratio of P-wave to QRS complexes
What is an isoelectric lead?
Wave that is travelling at a 90 degree angle to a particular lead won’t create a defleciton => lead is isoelectric to the wave of energy
Describe what the letters on an EKG represent
P = atrial depolarization
QRS complex = ventricular depolarization
T-wave = ventricular repolarization

EKG findings of acute pericarditis

- concave up ST segment elevation
- PR segment depression
- is not confined to a vascular territory (differentiating factor from STEMI)

Differentiate the cause of a positive vs. negative deflection on EKG
A wave traveling towards the (+) lead causes an upwards deflection on EKG
Wave traveling away from the (+) lead causes downward deflection
What do EKG leads measure?
EKG waveform is a measurement of the surface voltage btwn 2 leads
Describe technique for eyeballing HR on EKG
ex: Give the rate

Each dark vertical line count: 300 –> 150 –> 100 –> 75 –> 60 –> 50
ex: Rate around 90-95 (under 100 b/c just under 3 large boxes separate QRS complexes)

PVC on EKG
See a wide bizarre QRS followed by a compensatory pause (and next P-wave is buried w/in the widened QRS)

Locate the 6 precordial leads
V1 right of sternum at 4th intercostal space
V2 left of sternum at 4th intercostal space
V3 btwn sternum and midclavicular on left
V4 right below nipple line on left
V5 btwn midclavicular and axillary
V6 6th intercostal space axillary space

RVH on EKG
Large R-wave in V1 (and less so in V2 and V3)

What does the PR interval represent?
PR interval = delay of the signal thru the AV node
-makes sense b/c the P-wave is the SA node causing atrial contraction then the QRS is when the signal has gotten the AV node and the ventricles contract
Locate the 6 basic EKG leads
Basic leads: I, II, III
Augmented leads: AVR, AVL, AVF (on right ankle)

Rule of thumb for normal axis
Up in 1, Up in AVF
-b/c axis should be pointing down and left (1+ is to the pt left, AVF + is pointing down)

When are V7 and V8 added?
V7 and V8 can be added posterior to cover left circ territory

How does atrial hypertrophy appear on EKG
(a) Best seen in which lead
(b) RA vs. LA hypertrophy
Atrial hypertrophy => biphasic P-wave, best seen in V1
(a) V1 b/c is mostly right over the RA and is highest placed lead in the chest
(b) RA is closer to V1 => see RAH as large initial spike and see LA hypertrophy as second increased spike

What is a PVC?
Premature ventricular complex = early beat from a focus in the ventricle fires on its own then spreads
Which leads represent the territory of
(a) RCA
(b) LAD
(c) LCX
(a) RCA territory represented by II, III, aVF (inferior leads)
(b) LAD represented by V2,3,4 (anterior leads)
(c) Left circ represented by I, aVL, V5, V6 (lateral leads)
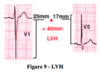
LVH on EKG
LVH criteria : heigh of S in V1 + height of R in V5 > 35 mm
-large S-wave in V1, large R-wave in V5
Precise measurements of time on EKG
(a) large box
(b) Small box
On EKG
(a) Large box = 200 msec = .2 sec
(b) Small box = 40 msec = .04 sec
- 5 small boxes to a large box
Describe what territory of the heart the precordial leads cover
V1-V2 are over the RV
V4,5,6 are over the LV primarily
V3 = transition lead approximately over the intraventricular septum
Then add V7 and V8 to cover mor eof the LV since most of the LV lies posteriorly

Which are the
(a) Lateral
(b) Inferior
(c) Anterior
leads
(a) Lateral leads = I, aVL, V5, V6
- Left circ distribution
(b) Inferior leads = II, III, aVF
- RCA distribution
(c) Anterior leads = V3,V4
- LAD distribution


