Development of Immune Cells; B and T Lymphocytes and Immune Receptor Diversity Flashcards
(36 cards)
• Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) can be identified as CD[] cells that lack any mature lymphocyte phenotypic markers (e.g. CD3 and CD4/CD8 for T cells, CD19 or CD20 for B cells, etc.)
• Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) can be identified as CD34+ cells that lack any mature lymphocyte phenotypic markers (e.g. CD3 and CD4/CD8 for T cells, CD19 or CD20 for B cells, etc.)
Cytokines that induce hematopoietic activity in the Myeloid lineage?
IL-3, IL-5 and GM-CSF: Induce hematopoietic activity in the Myeloid lineage..
Cytokines used to increase neutrophils, platelets and monocytes in patients receiving drugs that kill progenitor cells?
G-CSF, GM-CSF (and IL-3)
Cytokines that induce hematopoietic activity in the Lymphoid lineage?
IL-3 and IL-7: Mediate hematopoietic activity in the Lymphoid lineage. IL-3 for B cell and IL-7 for B, T and NK cells development/survival.
B cell development takes place in the [], while T cell development takes place in the [].
B cell development takes place in the bone marrow, while T cell development takes place in the thymus.
For the heavy chain of the BCR/Ig and the TCR b chain, 3 segments must be successfully recombined: [].
For the heavy chain of the BCR/Ig and the TCR b chain, 3 segments must be successfully recombined: variable (V), diversity (D) and joining (J) segments.
For the light chain of the BCR/Ig and the TCR a chain, 2 segments must be successfully recombined: [].
For the light chain of the BCR/Ig and the TCR a chain, 2 segments must be successfully recombined:variable (V) and joining (J) segments (no D gene segments).
Name of the enzyme that combine different V-D-J segemnts?
V-D-J recombinase
V-D-J Recombinase Components
- RAG-1 and RAG-2 proteins (Recombinase-Activating Gene) are lymphoid-specific, and work like scissors to cut the DNA open, and initiate the recombination of V-D-J gene segment.
- DNA repair enzymes come in next, to join the ends and repair the double stranded DNA breaks.
* The convention is to refer to this process as V-D-J rearrangement, even though the D gene segments are not present in Ig light chain or TCRa chain rearrangement.
V-J recombination is for…
…Ig light chain or TCRa chain.
V-J-D recombination is for…
…heavy chain of the BCR/Ig and the TCR b chain.
junctional diversity
There is a second, very important strategy for creating receptor diversity also occurring during this somatic recombination process, termed junctional diversity - removal and/or additiona of nucleotides.
exonucleases
Exonucleases may non-specifically remove nucleotides from the ends of the VD-J segments during the recombination process.
terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase (TdT)
The terminal deoxyribonucleotidyl transferase (TdT) enzyme can randomly insert nucleotides into the sites where the VD-J segments are rejoined (called “Ninsertions” for nontemplate encoded insertions).
Although all three CDRs that make up the regions that recognize antigen (CDR1, CDR2, and CDR3) are encoded within the V-D-J recombined segment, [] are entirely contributed by the V segment.
Although all three CDRs that make up the regions that recognize antigen (CDR1, CDR2, and CDR3) are encoded within the V-D-J recombined segment, CDR1 and CDR2 are entirely contributed by the V segment.
. It is the [] that spans the V- (D)-J joins, which means that most of the antigen specificity and variability of immune receptors is attributed to [].
. It is the CDR3 that spans the V- (D)-J joins, which means that most of the antigen specificity and variability of immune receptors is attributed to CDR3.
In addition to the V-D-J rearrangement (involved in the variable region of the antigen receptors), choices are made at this time about the [] regions of the Ig/BCR and TCR as well.
In addition to the V-D-J rearrangement (involved in the variable region of the antigen receptors), choices are made at this time about the constant regions of the Ig/BCR and TCR as well.
*This is particularly important for B cells, in which the constant region determines the isotype of the resulting antibody.
*For B cells, the Heavy chain is responsible for providing the constant region. During B cell development, the µ Constant Heavy chain is always utilized – it is the closest to the V-D-J segments. That chain gets replaced by other chains only after naïve B cells have been activated by antigen.



•After the common lymphocyte progenitor commits to the B cell lineage, the cell undergoes proliferation in response to the cytokines IL-3 and IL-7 to generate B cell precursors called pro-B cells. These cells have not yet begun to recombine and generate their antigen receptors.


- Pro-B cells then undergo somatic gene recombination in the Heavy chain. All B cells first rearrange their heavy chain locus to express µ. If this is successful, these cells are allowed to continue their development as pre-B cells. Some of the heavy µ chain is expressed on the cell surface with surrogate light chains as a pre-BCR.
- The expression of the pre-BCR is a survival checkpoint for the pre-B cell. If the pre-BCR can successfully make it to the surface and form a complex with the Iga and Igb signaling components, the cell is allowed to undergo another round of proliferation. This also signals the cell to shut down all concurrent rearrangement at the second heavy chain locus on the other chromosome – a process called allelic exclusion – to make sure that each cell only expresses a single antigen receptor


•Pre-B cells next rearrange their light chains, which are then paired with µ and delivered to the cell surface for a second survival checkpoint - if the cell has generated a functional IgM on the surface, the cell is allowed to live as an immature B cell.

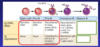
•The final maturation step for B cells is the co-expression of IgD along with IgM on the B cell surface. Note that these receptors still express the same Variable domains, thus are still specific for the same antigens. Once the cell is IgD+ IgM+ it is considered a mature naïve B cell, and is now able to respond to antigen in the secondary lymphoid organs.

What is the final step that the B cell has to go through before leaving the bone marrow?
•Prior to leaving the bone marrow, the negative selection process tests B cells for their capability to bind self-antigens. This mechanism works to eliminate B cells that might trigger autoimmune responses to normal tissue antigens. Any B cell whose BCR binds strongly to self-antigens found in the bone marrow dies by activationinduced cell death.
AT what point in development does the B cell have its first checkpoint?
- The expression of the pre-BCR is a survival checkpoint for the pre-B cell. If the pre-BCR can successfully make it to the surface and form a complex with the Iga and Igb signaling components, the cell is allowed to undergo another round of proliferation.
- This also signals the cell to shut down all concurrent rearrangement at the second heavy chain locus on the other chromosome – a process called allelic exclusion – to make sure that each cell only expresses a single antigen receptor












