Dermatology Flashcards
(101 cards)

Karposi’s sarcoma
Principles of skin examination
Inspect, describe, palpate, systemic check
Inspect
General observations Site and number of lesions If multiple - pattern of distribution and configuration
Describe
S.C.A.M Size, Shape Colour Associated secondary change Morphology, Margin (border)
Pigmented lesion
A.B.C.D Asymmetry Irregular border two or more Colours within the lesion Diameter >6mm
Palpate
Surface Consistency Mobility Tenderness Temperature
Systematic check
Examine the nails, scalp, hair, mucous membranes and general examination of all systems

Concentric rings - erythema multiforme
What is shown and list the risk factors for this type of lesion?

Venous Ulcer
Risks for venous ulcers
Varicose veins.
Previous deep vein thrombosis in the affected leg.
Phlebitis in the affected leg.
Previous fracture, trauma, or surgery.
Family history of venous disease.
Symptoms of venous insufficiency: leg pain, heavy legs, aching, itching, swelling, skin breakdown, pigmentation and eczema.
What is shown and list the risk factors for this type of lesion?

Arterial Ulcer
Risks for arterial ulcers
Coronary heart disease.
History of stroke or transient ischaemic attack.
Diabetes mellitus.
Peripheral arterial disease including intermittent claudication.
Obesity and immobility.
What is shown? Name some differential diagnoses

Erythema Nodosum
Streptococcal infection.
Sarcoidosis.
Tuberculosis (TB).
Other infections. Infections such as chlamydia, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Yersinia enterocolitica
Certain medicines.
Inflammatory bowel disease.
Pregnancy. Occasionally, pregnancy can trigger erythema nodosum.
Certain cancers, including lymphoma and leukaemia

Atopic eczema
Shortly after starting a medication this person developed…

Stevens Johnson syndrome
This is a form of toxic epidermal necrolysis, is a life-threatening skin condition, in which cell death causes the epidermis to separate from the dermis. The syndrome is thought to be a hypersensitivity complex that affects the skin and the mucous membranes. The best known causes are certain medications (such as lamotrigine), but it can also be due to infections, or more rarely, cancers

Candida Albicans

Urticaria

Melanoma

Pitting

Henoch Schonlein

Herpes Zoster

Thrombophlebitis

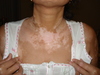
Keloid Scar

Seborrheic Keratosis

Excoriation eczema

Naevus flammus - Vascular malformation