Dermatology Flashcards
what are primary lesions
- initial eruption that developes spontaneously as a direct reflection of underlying disease
- appear quickly and disappear quickly
examples of primary lesions
macule or patch
papule or plaque
pustule
vesicle or bulla
wheal
nodule
tumor or cyst
what are secondary lesions
- evolve from primary lesions/artefacts induced by patients/external factors (trauma/biting/licking and medication)
- usually stay around for a much longer time period
which lesions can be primary or secondary
alopecia
scale
crust
follicular casts
comedo
pigmentary abnormalitites
examples of secondary skin lesions
epidermal collarette
scar
excoriation
erosion or ucler
fissure
lichenification
callus
what dis?

macule
flat spot ( <1 cm) on skin with change in skin color
what dis?

patch
= macule >1 cm
that is a type of mcule caused by bleeding into the skin
purpura, petechial, ecchymoses

a small, solid elevation in skin up to 1 cm in diameter is a _______
papule

what dis?

plaque
coalition of plaques forming flat-topped elevation
what is a pustule
small elevation of epidermis filled pus

what dis?

Vesicle
elevation of epidermis filled with clear fluid
what is a vesicle > 1 cm in diameter
bulla

sharply delineated lesion of edema is known as a ______
wheal
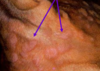
a solid raised palpable lesion > 1 cm
nodule
can include abscess (fluctuant lesion in dermis or SQ from pus)

what are these?

Nodule: Tumor
large palpable mass - Neoplastic
what is an epithelial lined cavity with solid or fluid material?
Cyst

what is alopecia?
absence of hair from area where it is normally present
what is an accumulation of loose fragments of skin
scale

what is an accumulation of dried serum/ exudate on the surface of the skin?
crust

what is an accumulation of keratin & sebaceous material stuck to a hair shaft
follicular cast
a dried hair follicle filled with debris is a ______
comedone

what is an epidermal collarette

scale arranged in a circular pattern
associated with a pustule, vesicle or bullae
linear abrasion of the skin is called ____
excoriation

what is an erosion
shallow ulcer that does not break the basal

a brea in the epidermis with exposure of the dermis is an _____
ulcer

what is a fissure
linear cleavage (cracks) in the epidermis or dermis caused by disease or injury

what is a thickening and hardening of the skin with exaggerated skin lines
lichenification

a _____ is localized hyperplasia of the statum corneum of the epidermis caused by pressure or friction
callus
elbows and lateral hock areas are common sites for callus formation in the dog

what things should be assesed in a dermatological examination
skin lesion type: primary vs secondary
skin changes: thick, fragile, thin
hair coat changes
distribution
cutaneous pain
parasites
other: lymph nodes, otitis, foot pad lesions
what does a superficial skin scrape test for?
surface mites
sarcoptes, notoedres, otodectes, cheyletiella, deodex gatoi in cats
T/F a negative superficial skin scrape rules out superficial mites
False
a negative skin scrape does not rule out mites
deep skin scrapes are used to diagnose________
most demodex species
what do you look for on a trichogram/ hair pluck
ringworm - hyphae or spores
follicle dysplasia
surface parasites - lice, mites
what can be seen on a scotch tape/acetate tape impression smear
bacteria, fungi and yeast
mites
what is the best method for testing for fleas
flea comb/ paper test

fecal floats can be use to diagnose _____
sarcoptes - difficult to find on the skin, may see in the feces
hookworms - skin lesions due to larval migration
what size needle is used for an FNA
21-23 gauge
a woodslamp can be used to diagnose ________
fungal infections
when should fungal culture be performed
all cats with skin disease
dogs with inflammatory skin lesions
how is a positive DTM determined
the media turns red and the same time the dermatophyte colony appears
saprophyte (non-pathogenic fungus) the colony is present for days before culture media turns red
indications for skin biopsy
nodules/tumors
ulcers/vesicles
severe acute generalized disease
mucosal lesions
footpad lesions
lesions unresponsive to normal therapy
skin biopsy techniques
punch biopsy
wedge/excisional biopsy
amputation - nail or toe
when is a bacterial culture and sensitivity indicated
cytology shows cocci and rods or just rods
cocci but no response to correctly administed antibiotics
deep pyoderma
chronic AB/GC therapy
GSD pyoderma
what is the gold standard for identifying environmental allergens
intradermal allergy testing

what are some disadvantages to allergy testing serology
no positive control
only detects circulating IgE
lab variations
false positives
grouped allergens/limited
not reliable for food allergens


