Dermatology Flashcards
Chronic, itchy, blistering, papulo-vesicular blisters - elbows, scalp, shoulders and ankles.

Dermatitis herpetiformis
Seen in patients with gluten sensitive enteropathy - coeliac disease.
Diagnose with a skin biopsy and positive test of coeliac disease with anti-ttp antibodies.
Management: gluten free diet and Dapsone (antibiotic) to reduce itch.

Neurofibromatosis
Autosomal dominant genetic disorder causing lesions in the skin, nervous system and skeleton. Type 1 is more common, type 2 has CNS tumours rather than skin lesions.
Diagnosis for type 1: at least 6 cafe au lait spots, axillary or inguinal freckles, neurofibromas etc.
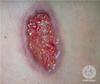
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Associated with Crohn’s disease
Painful nodules or pustules break down to leave a progressively enlarging ulcer
Purulent necrotic surface with blue black raised inflamed border
Urgent referral to dermatologist for immunosuppression and wound care

Tuberous sclerosis
Autosomal dominant condition characterized by a triad of cutaneous abnormalities, mental retardation, and seizures
The skin lesions are: ash leaf hypopigmentation (usually earliest sign), periungual fibromata (nodules around nails), shagreen patches (normal coloured plaques firm texture), and adenoma sebaceum (raised red papules on face, particularly around nose).

Pellagra
Dermatitis, diarrhoea, dementia.
Nicotinic acid (vit B3) deficiency.

Arterial ulcer
Punched out appearance, well demarcated, occurs at pressure points of foot, painful. Skin surrounding ulcer is shiny, erythematous and hairless.
Hx of peripheral vascular disease.

Venous ulcer
Usually large, shallow, painless, located at the medial malleolus. Hx of DVT. Measure ankle brachial BP.


