Day 8 A&E Flashcards
(72 cards)
Which intravenous induction agents is the preferred agent for day case anaesthesia?
Propofol has an elimination half life of four hours hence it has a short duration of action.
It is suitable for day case procedures and ITU sedation.
Etomidate is no longer used because it causes significant postoperative nausea and vomiting, has been associated with venous thrombosis and interferes with glucocorticoid production.
A 26-year-old man presents with a red and painful right eye. He also gives a history of episodic back pain and stiffness, particularly when he wakes up in the mornings.
What is the diagnosis?
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Gout vs Psuedo-gout (pyrophosphate arthropathy)

A 35-year-old businessman presents with a two week history of a swollen right knee. On further questioning, he admits that he has recently had unprotected intercourse during a business trip, and has developed a discharge from his penis.
What is the diagnosis?
reactive-arthritis
Reactive arthritis is a sterile synovitis which occurs following an infection. In this patient, the infection is likely to be sexually transmitted.
A 45-year-old woman has a fungating metastatic breast cancer and is increasingly distressed by the malodorous discharge from the affected breast, which is causing considerable social embarrassment.
How should she be treated?
Metronidazole may improve smells emanating from anaerobic organisms that infect fungating tumours.
INTRA VS EXTRACELLULAR FLUID
Which has a higher protein concentration
Which has a higher phosphate concentration
Which has a higher potassium concentration
Which has a higher osmolarity
Which has a higher pH
Which has a higher protein concentration
- extracellular
Which has a higher phosphate concentration
- extracellular
Which has a higher potassium concentration
- extracellular
Which has a higher osmolarity
- extracellular
Which has a higher pH
- intracellular
An 80-year old woman reports severe paroxysms of knife-like or electric shock-like pain, lasting seconds, in the lower part of the right side of her face.
What is the diagnosis?
How should she be treated?
Carbamazepine provides effective relief for this brief and intense stabbing pain within the distribution of the trigeminal nerve, known as trigeminal neuralgia. The usual dose is 100-400 mg, 8 hourly.
How is brain stem death confirmed?
Brain stem death (BSD) is confirmed by demonstrating the absence of brain stem reflexes, and is characterised by profound coma. Before the tests can be performed, several preconditions must be met unequivocally:
- the presence of apnoeic coma
- a defined cause of severe and irreversible brain damage and
- the exclusion of potentially reversible conditions which can mimic BSD (hypothermia can mimic BSD, so the core temperature must be above 34°C).
The tests must be performed by two doctors and then repeated following an interval determined by the clinical condition of the patient (not 24 hours apart).
The confirmatory tests include:
- fixed unresponsive pupils with absence of both the direct and consensual light reflexes (the pupils do not have to be dilated and pupil size is not a factor)
- absent corneal reflexes
- absent vestibulo-ocular reflexes
- absent motor activity after painful stimulation
- absent gag reflex
- absence of spontaneous respiration.
Name the drug
Discontinue 1 week before surgery.
Discontinue and replace with subcutaneous/intravenous equivalent 48-72 hours before surgery.
Inform anaesthetist and continue therapy up to and after surgery if appropriate.
Discontinue oral administration but replace with intravenous equivalent at induction.
Discontinue 1 week before surgery.
- Clopidogrel
Discontinue and replace with subcutaneous/intravenous equivalent 48-72 hours before surgery.
- Oral anti-coagulants
Inform anaesthetist and continue therapy up to and after surgery if appropriate.
- antihypertensives
Discontinue oral administration but replace with intravenous equivalent at induction.
- oral corticosteroids
Which ECG findings are associated with:
Hyperkalaemia
Wolff-Parkinson-White disease
Pericarditis
Hyperkalaemia
- widened QRS complex (>120 msec) when the potassium is >6.5
Wolff-Parkinson-White disease
- delta wave (notch) preceding the QRS complex
Pericarditis
- Pericarditis is associated with concave upward ST segment elevation on the ECG, versus convex upward ST segment elevation in MI.
A 52-year-old male in the post-operative ICU with a central line catheter develops spikes of fever.
Which of the following is the likely causative organism?
Coagulase-negative Staphylococci
Coagulase-negative Staphylococci are among the most commonly isolated bacteria in clinical microbiology laboratories.
Such coagulase-negative, novobiocin-susceptible Staphylococci as Staphylococcus epidermidis have emerged as a major cause of infection, particularly in hospitalised patients with indwelling foreign bodies and in immunocompromised patients.
What is the aetiology of carcinoid syndrome?
(3)
- usually occurs when metastases are present in the liver and release serotonin into the systemic circulation
- may also occur with lung carcinoid as mediators are not ‘cleared’ by the liver
- arise from enterochromaffin cells
What is pellagra
a deficiency disease caused by a lack of nicotinic acid or its precursor tryptophan in the diet.

Investigations for carcinoid syndrome (2)
urinary 5-HIAA
plasma chromogranin A y
A 60-year-old woman has developed bowel obstruction secondary to inoperable ovarian cancer. She is complaining of colicky abdominal pain which is not controlled by high doses of morphine.
How should she be treated?
Hyoscine butylbromide (more commonly known by its trade name, Buscopan) is an antimuscarinic which can be used to treat pain associated with smooth muscle spasm.
An 80-year-old man with spinal metastases from prostate cancer complains of increasingly severe back pain, despite being on a high dose of oral morphine, regular NSAIDs, and alendronic acid. Spinal cord compression is ruled out by MRI scanning.
What is the best next treatment step?
Radiotherapy is often helpful in bone pain from metastatic cancer.
A 91-year-old woman with multiple myeloma complains of severe abdominal pain, vomiting and constipation.
Her serum calcium is 3.6 mmol/L.
How should she be treated?
Abdominal pain, vomiting and constipation are symptoms of hypercalcaemia.
The first line treatment is intravenous rehydration.
Bisphosphonates (for example, intravenous pamidromate) are also used, but take longer to act.
To visualise the vocal cords, the tip of a Macintosh laryngoscope should be inserted into what?
The Macintosh laryngoscope blade has a small bulbous tip, which is designed to sit in the vallecula.
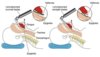
Actions of metoclapromide
(5)
Stimulates upper gastrointestinal motility
increases gastroesophageal sphincter tone
decreases gastric acid secretion
Acts on central dopaminergic receptors
Increases gastric fluid pH
How do the following drugs relieve pain in cancer?
Pinaverium
Carbamazepine
Clodronate
Corticosteroids
Nifedipine
Oxybutynin
Pinaverium is used to reduce the pain duration in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Carbamazepine is in use for the treatment of neuropathic pain of malignancy, diabetes and other disorders.
Clodronate inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption and is used to treat malignant bone pain and the associated hypercalcaemia.
corticosteroids are used to treat pain from central nervous system tumours. Reducing the inflammation and oedema relieves the pain caused by neural compression.
Nifedipine helps relieve painful oesophageal spasm and tenesmus associated with gastrointestinal tumours.
Painful bladder spasm may be relieved by oxybutynin.
Which one of the listed diagnoses is typically associated with the following conditions?
Eisenmenger’s syndrome
Ankylosing spondylitis
Syphilitic aortitis
Which one of the listed diagnoses is typically associated with the following conditions?
Eisenmenger’s syndrome
- Ventricular septal defect
Ankylosing spondylitis
- Aortic regurgitation
Syphilitic aortitis
- Aortic regurgitation
A 65-year-old man presents with a six month history of deteriorating breathlessness.
He is found to have aortic stenosis.
Which physical sign provides the best clinical marker of the severity of the valvular disease?
Length of the murmur
In cases of aortic stenosis, the murmur tends to become longer as the disease is more severe because of the longer ejection time needed.
You are asked to see a 55-year-old patient two days after undergoing a left total knee replacement. He complains of weakness of movement of his right foot since surgery.
He had a spinal anaesthetic and wonders if this was the cause although no complications were reported at the time.
He is otherwise well and clinical examination confirms suspected foot drop as there is weaked dorsiflexion of his right foot.
What is the likely cause?
Poor intra-operative positioning and padding
- Prolonged pressure on the common peroneal nerve during anaesthesia is a well documented cause of post-operative foot drop.
- One must ensure adequate padding on the fibula head when positioning patients under general or regional anaesthesia for long periods of time.
An elderly woman with severe ischaemic heart disease complains of stiff, painful hands, neck, knees and feet.
Examination of the hands reveals Heberden’s nodes.
What is the diagnosis?
What is the treatment?

osteoarthritis
paracetamol










