CVS and Respiratory Anatomy Flashcards
What is the lymphatic drainage of the breast?
- breast medial to the nipple drains through intercostal spaces to lymph nodes within the thorax (internal mammary lymph nodes)
- lateral breast drains to lymph nodes in the axilla

What forms the anterior axillary fold?
The pectoralis major
what nervs innervate the pectoral muscles
Pectoralis Major:
- Lateral and medial pectoral nerve
Pectoralis Minor
- Medial pectoral nerve
What innervates serratus anterior and why is this clinically relevalnt
- Long thoracic nerve
- Part of the function of SA is to hold the scapula against the ribcage
- if this muscle is paralysed you get ‘wing’
where is the cephalic vein and why is it clinically relevant
it’s where pacemakers are inserted through a catheter that is threaded through to the tip of the right atrium and SA node

What are the articulations of the clavicle
Medially with the menubrium of the sternum: sternoclavicular joint
Laterally with the acromion of the scapula: acromioclavicular joint
which ribs attach to serratus anterior
upper 8
what innervates all 3 layers of the intercostal muscles
intercostal nerves (T1-T11)
External intercostals - which direction do they run, and what is their action
- 11 pairs
- run inferiorly and mediall y
- they elevate the ribs increasing thoracic volume
Internal and Innermost intercostals
- run inferiorly and laterally
- they reduce thoracic volume by depressing the ribcage
what is the main role of the intercostal muscles
and what is the clinical relevance
contrct just enought so that they don’t get sucked in/blown out with negative and positive pressures of breathing
in some patients, the pressure needed to breathe overcome the intercostal muscles and you can obserce ‘intercostal recession’ which is an important sign of advanced resp distress
what can the LIMA sometimes be used for
coronary bypass because it runs so close to the LAD
Label structures in this Left Lung hilum
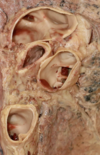

Label this Right Lung hilum


Label this lovely bit of heart


Label THIS lovely bit of heart

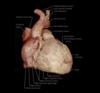
Label this third lovely bit of heart


LTLBOH


Does the phrenic nerve run anterior or posterior to the hilum of the lung?
Anterior
where does the left vagus branch to form the left recurrant laryngeal?
Under the arch of the aorta. The left recurrant laryngeal passes under the ligamentum arteriosum
What is the clinical significance of the nerve roots of the phrenic nerve?
painful stimulation of the diaphragm will be felt in the dermatomes supplied by the phrenic nerve nerve roots (C3, 4, and 5) this is typically in the side of neck and shoulder tip
Surfaces of the heart:
- Diaphragmatic: inferior
- Sterno-costal: anterior
- Base: posterior

What does the AVN recieve its blood supply from?
The posterior interventricular artery
What percentage of people have their posterior interventricular artery supplied by the left coronary, right coronary and how many by both?
- 90% supplied by the right coronary
- 30% supplied by the circumflex of the left coronary
- 20% supplied by arteries from each
i.e. 70% of people are right dominant, 10% of people are left dominant, 20% of people are codominant
What is the crista terminalis
- This is a ridge of modified muscle that seperates the trabeculatedaurocle from the smooth walled atirum
- The SA node is found in the upper half of the crista terminalis
What is the most posterior part of the heart
The left atrium
In what percentage of people is there a patency in the fossa ovalis
23% of adults
How might a heart valve fail?
- During systole the pressure in the heart is higher inside than outside
- any reduction in blood flow will affect the inside more than the outside
- the papillary muscles may die as a result and a dead one will rupture
- this will lead to sudden failure of the valve as it is not held in position during systole and there is regurgitation
How many leaflets does the aortic valve have?
3
Which is the only valve in the heart that doesn’t have 3 cusps? How many does it have
The mitral - it has 2
how many leaflets does the pulmonary valve have
3
What artery supplies the SA node?
The sinoatrial nodular artery
- in 60% of hearts this is a branch of the RCA
- in ~40% of hearts it is a branch of the left circumflex
which artery supplies the SA node is not related to dominance
stellate ganglion
A fusion of the first thoracic and inferior cervical ganglia
It lies anterior to the neck of the first rib and the C7 transverse process
It lies posterior to the common carotid, internal jugular and phrenic nerve
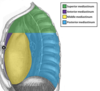
Label this heckin diagram


to what do the different colours correspond
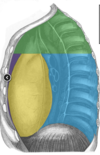
The border between the superior and inferior mediastinum is an imaginary line backwards from the sternal angle.
NB the inferior mediastinum is subdivided into anterior, middle and posterior
at the level of which vertebral body does the descending thoracic aorta start
lower edge of T4
Azygous system of veins
- drains blood from the body walls and mediastinal viscera
- empties into SVC
- Formed from:
- Azygous vein
- Hemiazygous vein
- Accessory hemiazygous vein

Where do the right and left vagus nerve pass through the diaphragm relative to the oesophagus
Pass through with the oesophagus at the level of T10
Left in front of the oesophagus and the right behind
briefly describe the journey of the thoracic duct:
from cystern of chyli
it goes up on the posterior right side of the oesophagus
it drains all the lymph from the lower half of the body into the blood stream at the confluence of the left subclavian vein and the internal jugular at the left side of the neck
so it crosses the body - right to left
Where does the greater splanchnic nerve arise from and what does it supply
Ganglia on the sympathetic chain from T5-9
it supplies the foregut
where does the lesser splanchnic nerve arise from and what does it supply?
Ganglia on the sympathetic chain from T10-11 and it supplies the midgut
Where does the least splanchnic nerve arise from and what does it supply?
Ganglia on the sympathetic chain from T12 and it supplies the hindgut
where does the sympathetic nerve upply to the head and neck come from? Why is this clinically relevant?
through the T1 ganglion of the sympathetic chain (the stellate ganglion)
Damage to this ganglion will cause loss of sympathetic innervation to the face and eye
No facial sweating, drooping eye lid, constricted pupil and eye slightly draw in.
HORNERS
which nerve enters the deep surface of the sternocleidomastoid
CN XI Spinal accessory nerve
What are the infrahyoid muscles?
Group of 4 muscles located inferior to the hyoid and between the two SCMs
Attachements are obvious from the names
- Superficial
- Sternohyoid
- Omohyoid: arises from scapula (omo)
- Deep
- sternothyroid
- thyrohyoid
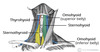
Label this bad boy


arterial supply to the thyroid gland
two sets of paired arteries
- Superior thyroid artery
- first branch to come off the external carotid
- supplies superior and anterior portions
- Inferior thyroid artery
- arises from thryocervical trunk of subclavian
- supplies posterior inferior aspects
venous drainage of the thyroid gland
- Superior, middle veins drain into the internal jugular
- The inferior drains into the brachiocephalic
what does the carotid sheath contain?
carotid artery
jugular vein
vagus nerve
whats going on here?

These are scans of the thyroid
the left one is normal and the right one has a thyroxine producing tumour
due to negative feedback, overproduced thyroxine leads to very low TRH and TSH and therefore the healthy throid is not stimulated and doesn’t produce much thyroxine
how can you tell the difference between a lump in the thyroid and a lump in a lymph node?
thyroid one will elevate with swallowing
How many ganglia does the cervical portion of sympathetic chain have
3
Superior, middle and inferior
in some cases the inferior is fused with the first thoracic and forms the stellate ganglion
at the level of which vertebral body does the common carotid bifurcate?
At around the level of the 4th cervical vertebra
what does the glossopharyngeal nerve do?
- general sensation anf taste to the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
- general sensation to the oropharynx
- tympanic branch supplies middle ear and the eustachian tube
- also supplies motor to stylopharyngeus muscle
stylopharyngeus
- supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve
- takes origin from the styloid process of the skull

through which nerve does the carotid sinus signal to the brain?
the glossopharyngeal
what does the superior laryngeal nerve innervate?
- Internal branch:
- sensation to the larynx above the vocal cords
- is the afferent nerve of the cough reflex
- External branch:
- motor to cricothyroid muscle
- this is the only muscle of the larynx not innervated by the RLN
- motor to cricothyroid muscle
what does the recurrant laryngeal nerve innervate
- Motor to all muscles except the cricothyroid
- Sensation to the larynx below the glottis
what is this nerve, what are its branches called, what do they innervate and what structure is this all happening in?
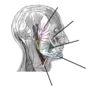
Facial nerve - Two Zulus Buggered My Cat
the facial nerve enters the deep posterior aspect of the parotid gland before it splits - cancer of the parotid can cause facial paralysis

where does the duct from the parotid gland drain into the mouth?
a papilla adjascent to the second molar
why might patients who’ve had a brain ste, stroke have trouble swallowing?
- Glossopharyngeal provides sensation to back of pharynx
- Vagus provides motor and sensory innervation to the larynx
- Damage to either of these may result in loss of control of swallowing
- The larynx may remain open during swallowing
- Fluid can pass into the lungs
where is the SA node located
on the medial side of the junction between the SVC and the right atrium
describe the histological structure of the heart vlaves
- thick collagen fibres with occasional strands of elastic tissue
- both surfaces are covered by endothelial cells
describe the divisions of cellular component of blood
- cells = 45% of blood
- 44% is erythrocytes
- White cells and platelets constitute 1%
- Of that 40-75% are neutrophils
- Lymphocytes 20-50%
- Eosinophils ~5%
- Monocytes 1-5%
- Basophils ~1%
what can an eosionphil also be called?
an acidophilic lymphocyte
NB in histology they can be identified by their dark pink granules
what can a basophil also be called
a basophilik leukocyte
from which cells are platelets derived?
megakaryocytes


