Clinical Correlations III: Atherosclerosis Flashcards




















ankle brachial index
- normal 1
- <0.4 = severe disease
Your patient has started Nicotine Patches and he is also watching his diet. Is there anything else your patient may due that would increase vascularization of the lower extremity and improve his claudication?
Exercise increases collateral formation and has been shown to improve claudication much more effective then platelet aggregation inhibitors clopidogrel and ASA.

•collateral formation
A 60 year old male with hyperlipidemia, DM Type 2, and HTN presents to your clinic with buttock pain and calf pain bilaterally. The pain is aggravated by activity such as walking and when he stops walking it resolves. He also complains of erectile dysfunction which is not improved with Sildenafil. On exam he has very weak pulses 1+ femoral bilateral and you can barely feel popliteal pulses. Ankle pulses are also barely palpable. Where do you think the stenosis is in the arterial tree?
1-popliteal artery • 2- femoral artery • 3- external iliac • 4-Aorta just before the bifurcation
- 1-popliteal artery
- 2- femoral artery
- 3- external iliac
- 4-Aorta just before the bifurcation
- Internal illiac supplies pelvis including through pudendal artery penile artery
- External iliac becomes common femoral

A 55 year old female presents with a 3x5 ulcer over the right medial malleolus. (see photo) She has 2+ pulses on both the right and left femoral, popliteal and PT/DP. Which of the following clinical factors would be most consistent with these findings?
• 1- A history of prior anti-coagulation • 2- A history of smoking • 3- A history of Von Willebrand Disease • 4- A history of hyperlipidemia

- 1- A history of anti-coagulation
- 2- A history of smoking
- 3- A history of Von Willebrand Disease
- 4- A history of hyperlipidemia
• A 70 year old male presents with a ulcer over the dorsum of left foot. (see photo) He has bilateral claudication and bilateral pain over the dorsum of the feet over the metatarsal heads at rest. He has a 50 pack year history and is trying to stop smoking. He has had 2 MIs in the past and has undergone 2 coronary artery stenting procedures. What physical finding is most consistent with this clinical picture?

- 1- Left sided pulses (femoral, popliteal, DP/PT ) 1+ ; and all pulses on the right side 2+
- 2- Left and right sided pulses- 1+femoral and popliteal, and absent ankle pulses
- 3- Large varices over the back of the calf
- 4- Large varices along the path of the great saphenous vein.
• Distal ulcers often represent arterial insufficiency, venous insufficiency or diabetic ulcer –try to identify the etiology of this ulcer:

•arterial
• Distal ulcers often represent arterial insufficiency, venous insufficiency or diabetic ulcer –try to identify the etiology of this ulcer:

•diabetic
• Distal ulcers often represent arterial insufficiency, venous insufficiency or diabetic ulcer –try to identify the etiology of this ulcer:
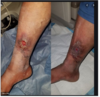
•venous
• How do you treat these ulcers? • If these patient needed surgery (colon resection) what do you think would be there major risk factor and why? • 1- arterial disease • 2- venous disease • 3- Type 2 DM
• A 35 year old with a very strong family history of MI and stroke. He is noted to have xanthomas over the elbow and eyelid. His labs are as follows. He has Type 2 DM He has a BMI of 38 • TG 850 mg/dL ( 60mg/dL) • LDL 120 mg/dL (normal < 100 mg/dL)
What would be a reasonable treatment plan?
- Statin to lower TG and cholesterol
- Add if target not reached HDL inhibits CETP-and TG: Fenofibrate/Niacin /Omega 3
- Add Fenofibrate (increase LPL) or Niacin or Omega 3-
- Increase HDL decrease TG (increases LPL activity)
- Another doctor began 2 drugs one to lower his cholesterol and another drug to lower his TG and raise his HDL. • The following day the patient presents to the ED complaining of flushing, fever and light headedness. His BP is 120/65 and prior was 130/80 the day before. You obtain the above history. Which drug was most likely used to lower this patients TG?
- 1- Atvorstatin • 2- Fenofibrate • 3- Niacin • 4- Omega-3
- 1- Atvorstatin
- 2- Fenofibrate
- 3- Niacin
- 4- Omega-3
• The main mechanism of flushing vasodilation and decrease diastolic pressure is due to which of the following • 1- PGE2 • 2- IL-6 • 3- Thromboxane • 4- PGE1
- The main mechanism of flushing vasodilation and decrease Diastolic pressure in this patient due to which of the following
- 1- PGE2
- 2- IL-6
- 3- Thromboxane
- 4- PGE1
- The same patient has a aortic stenosis murmur grade 2/6 noted in the chart from prior visits. Based on your knowledge of pressure gradients and murmurs what do you expect the murmur to be in the patient now after taking Niacin. • 1- 1/6 • 2- 2/6 • 3 - 3/6
- If this was a mitral regurgitation murmur would the murmur be louder or softer in this same patient?
- The same patient has a aortic stenosis murmur grade 2/6 noted in the chart from prior visits. Based on your knowledge of pressure gradients and murmurs what do you expect the murmur to be in the patient now after taking Niacin.
- 1- 1/6
- 2- 2/6
- 3 - 3/6
- Due to lower SVR increase pressure gradient between LV and aorta During LV contraction increase flow due to lower SVR–> increase murmur.
It would be softer because if you decrease SVR, pressure gradient increases between LV and Aorta (SVR). Increases flow forward across the AV less blood goes back into LA
- Gradient between the LV and LA does not change
- That is why in MR if the patient has HTN they should be treated aggressively. Improve foreword flow SV and CO









