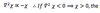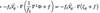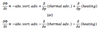chapter 4 Flashcards
(62 cards)
The QG Thermodynamic Equation
This equation can be derived from
the thermodynamic energy equation in pressure coordinates
the following is the
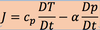
the thermodynamic energy equation in pressure coordinates
describe each term in the equation
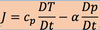
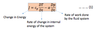
cp and a in the following equation means
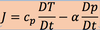

describe the following terms in the equation
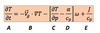

this is called
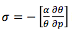
static stability parameter

is a positive number for a stable atmosphere, and a negative number for an unstable atmosphere.
the following is the
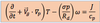
the quasi geostrophic (QG) thermodynamic energy equation in pressure coordinates
in this equation the …………………. is simply substituted for ……………………………..
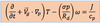
geostrophic wind is simply substituted for the actual wind in the advection term
the following terms are


the above equation states that

temperature change at a particular location and height is a function of temperature advection by geostrophic wind and vertical motion.
Warm temperature advection result in

cold temperature advection result in

Ascent vertical motion result in

Decent vertical motion result in

Diabatic effects:
Diurnal (day and night) l heating/cooling plays a major role in temperature changes near the surface
(5) is the
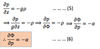
hydrostatic equation in height coordinates (x, y, z)
(6) is the
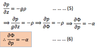
the hydrostatic equation in pressure coordinates
the geopotential tendency
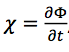
the following is the
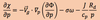
QG thermodynamic energy equation
Note that equation 5 and 7 are identical, which are written in different forms, because
in a hydrostatic atmosphere, do Φ⁄do p is proportional to the temperature (T) of the layer.
the following is the

QG vorticity equation
The geopotential tendency equation is derived from
The QG Thermodynamic Energy Eq.
QG Vorticity Eq.
For a sinusoidal disturbance having a zero mean value, the
horizontal Laplacian of a field is proportional to the negative of the field