Chapter 33 Flashcards
(28 cards)
during the formation of the cardiac loop the primitive ventricls move ____?
The primitive atrial region moves_____?
Primitive ventricle moves ventrally and to the right.
Atrial region moves dorsally and to the left

There are 3 shuns in fetal circulation
What are they?
Ductus venosus
Foramen ovale
Ductus Arteriosus
What does the ductus venosus do
Blood from umbilical vein enters the inferior vena cava directly.
Bypasses the liver

What is the foramen ovale
Blood from Rt atrium to Lt atrium
40% of blood goes this way
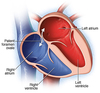
What is the ductus arteriosus
Direct from Pulmonary art to Aorta
This is because of high resistance in pulmonary vasculature of fetus

Most of the blood from foramen ovale goes where? Why?
To the head becuase it is rich in O2
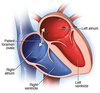
Cardiopulmonary Adjustments at Birth
With the decrese in pulomonay vascular resistance it triggers the release of what?
Prostaglandin PI2
This increases blood flow through the lungs.
Increases venous return to left atrium.
Reduce vascular resistance 5 fold
What causes the foramen of ovale to close
Left atrial pressure begins to exceed right atrial pressure
What is the following describing?
Underlying cause known in only 10% of cases.
Risk factors:
Prenatal:
Maternal rubella, IDDM, alcoholism, hypercalcemia.
Maternal age over 40.
Environmental:
Exposure to teratogens(like thalidomide).
Genetic:
Chromosomal aberrations.
Congenital heart defects
How long after birth does it take for the ductus arterious to close?
10-15 hours
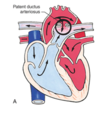
The following describe what?
Increased pulmonary blood flow.
Increased left EDV.
Increased workload.
Left ventricular hypertrophy.
Pulmonary hypertension.
Heart failure (HF).
Clinical manifestations:
If significant:
Bounding pulses.
Widened pulse pressure.
Murmur peaks in late systole.
Signs and symptoms of HF.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Blood begins to shunt left to right, from aorta to pulmonary artery

Name the following Atrial Septal Defects (ASD) Abnormal communication between the atria (most common 90%)
Opening found low in the septum.
Opening in center of septum.
Opening occurs high in the atrial septum
Ostium primum defect.
Opening found low in the septum.
Ostium secundum defect:
Opening in center of septum.
Sinus venosus defect:
Opening occurs high in the atrial septum
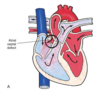
The following clinical manifestations are consistant with what?
Auscultation of a crescendo-decrescendo systolic ejection murmur.
Wide fixed splitting of 2nd heart sound
atrial septal defect (ASD)
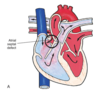
There are 4 types of VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECTS (VSD)
- Outflow tract to left ventricle immediately below aortic valve
- Occur low in ventricular septum between the trabeculae.
- Occur in the infundibulum below the pulmonary valve
- Occur posterior and inferior to membranous system
- Perimembranous
- Muscular
- Supracristal
- AV canal
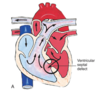
Which way does the blood typically shunt in Ventricular Septal Defects?
What increases over time?
Typically shunts from Left to Right
Increases volume overload which can eventualy reverse the shunt.
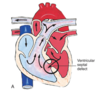
The following clinical manifestations indicate what?
Infants with large defect display symptoms of HF and failure to thrive.
Adults who develop pulmonary vascular resistance due to unrepaired defect , will be cyanotic and have clubbing.
Loud harsh, holosystolic murmur and systolic thrill can be detected.
ventricular septal defect
What are atrioventricular canal defect (AVC)
Nonfusion of endocardial cushions during fetal life.
Can involve all 4 chambers
Associated with Down Syndrome
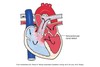
What are the 3 types of Atrioventricular canal defects (AVC)
- Complete AVC (CAVC)
- Partial AVC (PAVC)
- Transitional AVC (TAVC)

The following clinical manifestations are consistant with what?
At 4-12 weeks of age, when pulmonary vascular resistance drops children with CAVC defects begin to show symptoms of HF.
Middiastolic rumble at the left lower sternal border or apex.
Signs of HF
Atrioventricular Canal Defect AVC

Describe the 4 defects in Tetralogy of Fallot
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Rt ventricle hypertrophy (due to pulmonay stenosis)(causes change of shape of right vent, shape of a boot)
- Ventrical Septal Defect (usually high in septum)
- Overriding of aorta (straddles the ventricles)
Blood travels easier into aorta eaiser than pulmonary artery due to stenosis
Right to left shunt

What do the followin clinical manifestations indicate?
Sudden onset of dyspnea, cyanosis, restlessness and crying and exertion.
Infants often have difficulty feeding.
Squatting in older children to alleviate hypoxic spells.
Increases systemic resistance while decreasing venous return.
Typical heart murmur is pulmonary systolic ejection murmur
Tetralogy of Fallot
What is coarctation of the Aorta COA
Narrowing of the lumen of aorta that impedes blood flow

Is coarctation of aorta more common in males or females
What is is associated with 2/3 of the time
What syndrome can it be seen with
Males
bicuspid valve problems
Turners syndrome
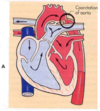
Higher pressures above the site of stenosis and lower pressures below the site is seen with what?
Corarctation of the aorta