Chapter 31 Flashcards
(43 cards)
What does Toponin I do?
binds to actin in thin myofilaments to hold the troponin-tropomyosin complex in place

What does Troponin T do?
Binds to tropomyosin to the thin filaments
binds to tropomyosin, interlocking them to form a troponin-tropomyosin complex

What does Troponin C do?
Binds to Ca2+ to thin filament for muscle contraction.

Depolarization of myocardial cell stimulates opening of VG Ca2+ channels in ______????
sarcolema

______ is released, causing the power stroke to occur.
Power stroke pulls actin toward the center of the ___ band
Pi (an inorganic phosphate group)
A band

If there is an increase in need of oxygen by the coronary blood vessels, what substance dilates the cornary blood vessels?
Adenosine
What are the site of inpulse fromation in the SA node?
P cells
Does the SA node or the AV node have thicker fibers?
AV node
(also more resistance to conductane)
The slower AV node allows for additional ventricular filling time
What are the layers of heart muscle
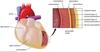
Does it start in Endocardium or Epicardium
Activation?
Deactivation?
Activation
Endocardium to epicardium.
Deactivation
Epicardium to endocardium
In phase 4 what is the voltage threshold
-40mV

What phase of cardiac pacemaker action potential does repolarization take place?
Phase 3

Discribe the phases of cardiac muscle action potential
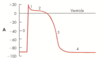
Phase 0: depolarization:
VG Na+ channels open.
Inward diffusion of Na+.
Phase 1: early repolarization:
VG Na+ channels rapidly close.
VG Ca2+ channels open
.
Phase 2: plateau phase:
Rapid reversal in membrane polarity to –15 mV.
Slow inward flow of Ca2+ balances outflow of K+.
Phase 3: rapid repolarization:
VG K+ channels open.
Phase 4: resting membrane potential:
-80 to –90 mV.
Explain what is occurring during each phase of the cardiac cycle
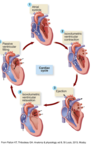
Rapid filling of ventricles:
AV valves open.
Atrial systole:
P wave occurs.
Atrial contraction.
Isovolumetric contraction:
QRS just occurred.
AV valves close.
Semilunar valves are closed.
Ejection:
Semilunar valves open.
AV valves are closed.
Isovolumetric relaxation:
T wave occurs.
Semilunar valves close.
AV valves are still closed.
Ventricular pressure drops below atrial pressure.
AV valves open.
First heart sound:
Second heart sound:
Third heart sound:(not normally heard)
Fourth heart sound:(only heard if pathologic)
First heart sound:
Produced immediately after QRS wave.
Rise of intraventricular pressure causes AV valves to close.
Second heart sound:
Produced after T wave begins.
Fall in intraventricular pressure causes semilunar valves to close.
Third heart sound:
Tensing of the chordae tendineae during rapid filling and expansion of the ventricle.
The third heart sound is normal in children, young adults, and some trained athletes.
Fourth heart sound:
It is a sign of a pathologic state.
Sound of blood being forced into a stiff/hypertrophic ventricle.
What does the intracardiac pressure venous C Wave represent?
Represents the bulging of the mitral valve into the left atrium during early systole.

What has the following influences?
Rate of impulse generation, depolarization, and repolarization of myocardium.
Strength of atrial and ventricular contraction.
Autonomic nervous system influences
What has the following influences?
§nnervates all parts of the atria and ventricles.
Shortens conduction time through the AV node.
Increases rhythmicity.
Enhances myocardial performance.
Sympathetic nervous system influences
Alpha 1 = Does what
Alpha 2= Does what
Beta 1 = Does what
Beta 2 = Does what
Alpha 1 = Constricts coronary arteries (NE)
Alpha 2= Vasodilation (by restricting NE release)
Beta 1 = Increases HR and force of contraction (NE)
Beta 2 = Causes coronary arterioles to dilate (Epi)
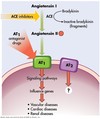
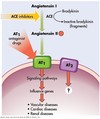
study this

Study pic
What does this defination describe?
states that the stroke volume of the heart increases in response to an increase in the volume of blood filling the heart (the end diastolic volume) when all other factors remain constant.
Frank–Starling law
How is Stroke Volume related to TPR?
SV inversely proportional to TPR.
Greater the TPR, the lower the SV
Laplace’s Law deals with what general topic
Wall tension
What is the formula for Cardiac Output?
CO = SV X HR