Chapter 15 Part 2: Specification of Neural Crest Cells Flashcards
(26 cards)
Neural crest cells are not identifyable until the emigrate (delamination) from the neural tube, but their induction and specification first occurs during ____ ____
Neural crest cells are not identifyable until the emigrate (delamination) from the neural tube, but their induction and specification first occurs during early gastrulation.
between the presumptive surface epidermis and the neural plate (neural tube which will form CNS)
placode
thickening in the surface ectoderm that will generate the eye lends, inner ear, olfactory epithelium and other sensory structures.
In the anterior region of the neural plate placodes will form which will develop into eye lens, inner ear, olfactory epithelium, etc.
cells in the neural plate border will become the ___ ___ and the ___
become the neural crest and the placodes (in the anterior region)
Continuous expression of Wnt and BMP = ___
If Wnt induces BMP followed by Wnt being turned off = ____
If Wnt induces BMP and then Wnt remains on = ____
Continuous expression of Wnt and BMP = epidermis
If Wnt induces BMP followed by Wnt being turned off = placodes
If Wnt induces BMP and then Wnt remains on = neural crest cells

in order for neural crest cells to be specified in ectoderm, Wnt must be on for a while, followed by BMP expression while Wnt stays on. What pathway is also turned on?
also requires SMAD pathway degradation in order to maintain intermediate concentrations of BMP.
In the neural plate, If only Wnt is present (block BMP via Noggin or FGFs), what are the results?
¡If only Wnt is present (block BMP via Noggin or FGFs) = Neural cells
The cells in the neural plate border between the neural plate and the epidermis will become the ___ ____ and (in the anterior region) the ____
The cells in this border between the neu- ral plate and the epidermis will become the neural crest and (in the anterior region) the placodes
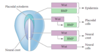
BMP and Wnt induce specific transcription factors in the ectoderm ___ ___ ___ specifiers
Border specifiers allow the border of the neural plate to create ___ ___ cells and dorsal ___ ____ cells. Neural plate border specifiers induce neural crest specifiers in cells that will become neural crest cells specifically
BMP and Wnt induce specific transcription factors in the ectoderm neural plate border specifiers
¡Border specifiers allow the border of the neural plate to create neural crest cells and dorsal neural tube cells
Neural plate border specifiers induce neural crest specifiers in cells that will become neural crest cells specifically. These neural crest specifiers include genes encoding the transcription factors FoxD3, Sox9, Snail (premigratory), and Sox10 (migratory)
Once cells are specified as neural crest cells (recall; cause different wnt and bmp signalling results in expression of neural plate border specifiers, which then induce neural crest specifiers), they will undergo ____ so they can leave the neural tube. How?
they will undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Because dif cells throughout the ectoderm express different cell adhesion molecules::
surface ectoderm = e-cad
premigratory neural crest cells: cad6b
neural tube cells: n-cad
neural crest cells migrate along the ___-___ axis, and often extend ____ to grab hold of extracellular matrix in front of them. They can migrate signularly or in a group
neural crest cells migrate along the ANTERIOR-POSTERIOR axis, and often extend LAMELLOPODIA to grab hold of extracellular matrix in front of them. They can migrate signularly or in a group
neural crest cells must undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition before leaving the neural trube. They lose their adhesive junctions (dif cadherin regulation expression) and separate from epithelium via ___. How is this process controlled?
neural crest cells must undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition before leaving the neural trube. They lose their adhesive junctions (dif cadherin regulation expression) and separate from epithelium via DELAMINATION.
Entire neural tube controls neural crest cell delamination because delamination is triggered by Wnt and BMP activation. Wnt is activated by BMPS. BMPs are produced in the dorsal region of the neural tube, and are usually negatively regulated by Noggin from somites and hinges. But whe Noggin is reduced, BMPs initiates Wnt and activate EMT in the neural crest cells.
Entire neural tube controls neural crest cell delamination because delamination is triggered by ___ and __ activation. ___ is activated by BMPS. ___ are produced in the ___ region of the neural tube, and are usually ___ regulated by ___ from notochord somites and hinges. But whe ___ is reduced, ___ initiates ___ and activate EMT in the neural crest cells.
Entire neural tube controls neural crest cell delamination because delamination is triggered by Wnt and BMP activation. Wnt is activated by BMPS. BMPs are produced in the dorsal region of the neural tube, and are usually negatively regulated by Noggin from somites and hinges. But when Noggin is reduced, BMPs initiates Wnt and activate EMT in the neural crest cells.

Sox2 is expressed by cells of the neural ___, and represses ____. But: this TF in the premigratory neural crest cell region represses Sox2, resulting in cross-repression: which helsp to regine boundaries between neural tube epithelium, premigratory neural crest cells, and surface ectoderm.
Sox2 is expressed by cells of the neural ectoderm, and represses snail2. But: this TF in the premigratory neural crest cell region represses Sox2, resulting in cross-repression: which helsp to regine boundaries between neural tube epithelium, premigratory neural crest cells, and surface ectoderm.
from dorsal region of neural tube, BMP is highly expressed because:
it is not as influence from inhibitory noggin being secreted by the ventral aspect (notochord).
from dorsal region of neural tube, BMP is highly expressed because it is not as influence from inhibitory noggin being secreted by the ventral aspect (notochord). The presence of increased dorsal Bmp, and subsequent upregulation of dorsal Wnt wihtin the premigratory region of NCs will cause the upregulation of ___ and __- genes in the premigratory nerual crest cells. What does this do?
upregulation of snail 2 and zeb2 genes in the premigratory crest cells. Snail2 represses Ncad, Ecad, and Sox2, promoting delamination

Cadherin 6B is only expressed in apical premigratory neural crest cells. What does it upregulate?
it activates RhoA and actomyosin contractile fibers to facilitate apical constriction and initiate delamination.
recall that cad6B and delamination is actually ultimately controlled by neural tube through Wnt and BMP
Cadherin6b activates ____and ___contractile fibers to facilitate apical constriction and initiate delamination.
Cadherin6b activates RhoA and actomyosin contractile fibers to facilitate apical constriction and initiate delamination.
What type of Wnt signalling is involved in establishing the polar activity of RhoA and Rac1 along the migratory axis of the migrating neural crest cells.
NOncanonical Wnt signalling.

When neural crest cells contact one another, they experience ___ __: they stop and turn away and migrate in opposite direction
contact inhibiition

Summary: Prior to delamination, the different regions of ectoderm in the area of the neural crest can be identified by their expression of different cell-cell adhesion molecules: surface ectoderm expresses E-cadherin, premigratory neural crest expresses cadherin 6B, and the neural tube expresses N-cadherin

The Wnt and BMP signals lead to the expression of the “core EMT regulatory factors” (e.g., Snail-2, Zeb-2). Sox2 is expressed by the cells of the neural ectoderm (plate/fold/tube) and functions in part to transcriptionally repress Snail-2 expression in these regions such as in the tube and above on surface. The more dorsally expressed Snail-2 in the premigratory neural crest region cross-represses Sox2 expression. This cross-transcriptional repression helps to refine the boundaries between the neural tube epithelium (N-cadherin), premigratory neural crest (cadherin 6B), and surface ectoderm (E-cadherin);
Driving Force Behind Contact Inhibition (neural crest cells touch each other and then move opposite directions)
Contact inhibition involves the ____ of both neural crest cell’s _____ to prevent ____ from continuing to grow on the contacting surface. New ____ then form, directing the cells away from the point of contact. This process is caused by ___ and _____. Outline.
Contact inhibition involves the depolarization of both neural crest cell’s cytoskeletons to prevent extensions from continuing to grow on the contacting surface. New protusions then form, directing the cells away from the point of contact. This process is caused by Wnt and RhoA.
When crest cells come into contact with each other (not with the neural tube or overlying epithelium), the NONCANONICAL PATHWAY ACTIVATES RHOA. RhoA causes the breakdown of cytoskeleton in lamellipodia required for migration.


