Chapter 12 - Transport Across Cell Membrane Flashcards
What is the propagation of an electrical signal within a neuron?
Action potential
Transporters, in contrast to channels, work by _____.
specific binding to solutes
A sodium-potassium pumps maintains the extracellular concentration of sodium at levels that about 20-30 times ______ than inside the cell.
higher
When an ion channel opens, therefore, ions usually flow through it, moving rapidly down their _________.
electrochemical gradients
The categories are * ions * nonpolar molecules * large uncharged, polar molecules. * small uncharged, polar molecules; and small nonpolar molecules. Rank the order of above of which enters the lipid bilayer the fastest/easiest to not being able to do so.
Fastest to No being able to enter…. 1. Small nonpolar molecules; 2. Small uncharged polar molecules; 3. Larger uncharged polar molecules; 4. Ions
_______ channels open and close in response to changes in membrane potential.
Voltage-gated Na+
What is the function of the transporter Na+-driven glucose pump (glucose-Na+ symport)?
active import of glucose
What is the energy source of the transporter Na+-driven glucose pump (glucose-Na+ symport)?
Na+ gradient
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily?
Small and hydrophobic
Which factors determine the force driving the passive transport of **CHARGED solutes** across the membrane?
Electrochemical gradient
What is the function of the K+ leak channel?
Maintenance of resting potential
The _______ pump use the movement of one solute, down its gradient to provide the energy. Which one was it? And the second solute?
coupled; sodium; glucose
The transfer of nutrients metabolites and inorganic ions across a membrane depends on ___________.
membrane transport protein
Cell membranes contain a variety of transport protein that function either as ______ or _____, each responsible for the transfer of a particular type of _____.
transporters; channels; solute
Name the gated ion channel @ 3

ligand-gated (intracellular ligand)
__________: A stimulus shift the membrane potential to a less negative value.
Depolarization
________ is the accumulation of electric charge across a membrane.
membrane potential
Vibrations cause linked ____ to move and ion channels to open.
stereocilia
Name the membrane transport proteins that move molecules that bind to a binding site and make a conformational change. This requires a solute + binding site.
transporter
What are two main types of membrane proteins?
Transporters and Channel Proteins
Name the pump on 2

Na+ driven symport
What are the 3 types of active transport?
ATP-driven pump
Coupled pump
Light-driven pump
Passive transport allows molecules to move ____ their concentration gradients (____)
down; downhill
Transporter proteins are highly _______.
selective
The Na+ concentration gradient of across the membrane is _____ energy, like water behind a dam.
stored
The rapid shift of ions changes the ________ because they carry a charge.
membrane potential
The action potential is a wave of _______ that spreads rapidly along the neuronal plasma membrane. This wave is triggered by a local change in the membrane potential to a value that is _____ negative than the resting membrane potential. The action potential is propagated by the opening of ______ channels. During an action potential, the membrane potential changes from ____ to ______. The action potential travels along the neuron’s ____ to the nerve terminals. Neurons chiefly receive signals at their highly branched ____.
depolarization; less; voltage-gated; negative; positive; axon; dendrites
What type of energy does Bacteriorhodopsin need?
light
What is the most abundant extracellular anion?
Cl-
Which membrane transport protein sometimes use active transport?
Transporter
Lipid bilayers are permeable to large uncharged, polar molecules. True or false?
False. It’s impermeable.
Ca2+-pumps in the plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum are important for _____________.
preventing Ca2+ from altering the activity of molecules in the cytosol.
In general, the ____ the molecules and the more ______, or nonpolar, it is, the more rapidly it will diffuse across the membrane?
smaller; hydrophobic
Lipid bilayers are permeable to ions. True or false?
False. It’s impermeable.
Symport means
both of them are moving the SAME direction
Ca2+ is an example of a(n) ______ pump.
ATP-driven
Cell membranes have proteins. True or False?
False?????????
Cell membrane exhibits _______ to transfer inorganic ions and small water-soluble molecules into and out of the cell.
selective permeability
Neurotransmitter binding opens _____ channels initiating membrane depolarization.
transmitter-gated ion channels
Lipid bilayers are permeable to small uncharged, polar molecules. True or false?
True
Name the membrane transport protein that allow molecules with the right size or charge can move through the protein. The protein is described as a bridge.
Channel proteins
How does an action potential spread along the cell membrane?
A change in membrane potential triggers the opening of nearby voltage-gated sodium channels in a one-way direction
What is the role of K+-gated ion channels in an action potential?
They provide the energy for the sodium-potassium pump to reestablish its resting potential.
Name an example of a voltage and ligand-gated ion channels.
neuron action potentials
The membrane potential is defined independently of the ____ of interest, whereas an electrochemical gradient refers to the particular _____.
solute; solutes
The cystolic side of the plasma membrane is usually at a ____ potential.
negative
Bacteriorhodopsin is an example of a ______ pump.
light driven
Which membrane protein can facilitate both active and passive transport of solutes
transporter
Transporters, in contrast to channels, work by ________________.
specific binding site
What are the two types of coupled pumps (transporters) that participate in coupled transport?
symport and antiport
Inhibitory neurotransmitters include ____ and _____.
GABA and glycine
Transferring glucose across the epithelial layer of the gut requires ______ and ______ transport.
active; passive
Cells use membranes to help maintain set ranges of ion concentrations inside and outside the cell. Which of the following ions is the most abundant inside a typical mammalian cell?
K+
After the Na+ ions rush in…
- Voltage-gated K+ ions also _____;
- The exit of K+ ions returns the membrane potential to its ____ state;
- _____ pumps returns the ion gradients to normal.
open;
resting;
Na+-K+
For the passive transport of a _______, its electrochemical gradient determines its direction of movement.
charged solute
What balances the the large amounts of anions such as HCO3-, PO4_3-, proteins, nucleic acids inside the cell?
The anion Cl- outside the cell.
Name the pump on 3

H+ pump
What are 2 extracellular fluids?
sodium, chloride
The lipid bilayer of cell membranes are _______ to small non-polar molecules.
highly permeable
Channel mediated and transporter mediated solutes are _____ transport.
passive
Which type of transport requires energy?
active transport
Name the ion on 7

K+
Chemical signals = ?
neurotransmitters
Lipid bilayers are impermeable to nonpolar molecules. True or false?
False
Name the gated ion channel @ 4

mechanically-gated
What are the 5 roles of the voltage-gated ion channels in the generation of an action potential?
- Resting-state
- Depolarization;
- The rising phase of the action potential;
- The falling phase of the action potential;
- Resting-state
What is the function of the transporter Na+ pump (Na+-K+ ATPase)?
active export of Na+ and import of K+
The membrane potential refers to the ____ gradient.
voltage
Name the pump on 4

H+ -driven symport
In a sodium-potassium pump, what ion is pumped out of the cell? in the cell?
Na+; K+
Glucose (180 daltons) cross ___.
hardly
Lipid bilayers are permeable to nonpolar molecules. True or false?
True
An action potential is triggered by a ________ of a neuron’s membrane.
depolarization
The lipid bilayer of cell membranes are _______ to most large soluble molecules and to all ___.
highly impermeable; ions
Ca2+ pumps in the plasma membrane and ER are important for
preventing Ca2+ from altering the activity of molecules in the cytosol
The movement of charged molecules is controlled by the ______.
electrochemical gradient
What are 2 intracellular fluids?
potassium, phosphorus
The hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer creates a _____ to the passage of most _____ molecules.
barrier; Hydrophilic
Action potentials open ____ channels prompting release of _____ into the synapse.
Ca2+; neurotransmitters
What are the two forces that drive an ion across the plasma membrane?
chemical concentration gradient + electrical component = electrochemical gradient
Name the pump on 5

H+ pump
What 2 forces are the electrochemical gradient composed of?
1- the concentration gradient; 2- the membrane potential (the voltage gradient)
What are the three main types of gated ion channels?
voltage-gated
ligand-gated
mechanically-gated
What is permeable to water, but not freely permeable to electrolytes?
Cell Membranes
How much energy is required for passive transport?
None
Which of the following is a difference between transporters and channels?
Transporters can facilitate both active or passive transport solutes; channels facilitate only passive transport.
Name the pump on 6

H+ pump
Potassium ion channel uses which membrane transport protein?
channel
In a Ca2+ pump, the ATPases work in a/the ____ way as a the Na+ pump.
same
Name the pump on 1.
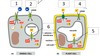
Na+ pump
The Na+ pump undergoes a series of conformational changes as it exchanges Na+ ions for K+. True or false?
True
Electrical signals are converted to chemical signals and vice-versa at ___.
synapses
If Na+ channels are opened in a cell that was previously at rest, how will the resting membrane potential be affected?
It becomes more positive.
The categories are the following: long, nonpolar molecules; large uncharged, polar molecules; small uncharged; polar molecules. Which one penetrates the lipid bilayer the easiest and fastest?
small nonpolar molecules
What is the energy source of the transporter Na+ pump (Na+-K+ ATPase)?
ATP hydrolysis
Which membrane transport protein always use passive transport?
channel
What is an example of an ATP-driven pump?
Na+-K+ pump
Lipid bilayers are impermeable to large uncharged, polar molecules. True or false?
True
Both Na+-K+ and Ca2+ pumps are ____ transport.
active
What is the most abundant extracellular cation?
Sodium
Charges need to balance inside and outside of the cell. True or false?
True
Excitatory neurotransmitters include ____ and _____.
acetylcholine and glutamate
What balances the high Na+ outside the cell?
The high K+ inside the cell
In most animal cells, the negative value of the resting membrane potential across the plasma membrane depend mainly on the ____ gradient and the operation of ______ leak channels.
K+; K+-selective
Glycerol (92 daltons) diffuse the lipid bilayer ____ rapidly.
less
The main components of the cell membranes are _______ and _____. _____ are also important.
lipids and protein; carbohydrates
Lipid bilayers are impermeable to small uncharged, polar molecules. True or false?
False
Ion channels in the inner ear is an example of what type of channel?
mechanically-gated ion channel
What is the energy source of the transporter Na+-H+ exchanger?
Na+ gradient
Name the gated ion channel @ 2

ligand-gated (extracellular ligand)
An example of a coupled pump is ______.
glucose-Na+ symport
The Ca2+ pump keeps the cystosolic Ca2+ concentration ____.
low
What is responsible for moving glucose from the gut lumen into intestinal epithelial cells?
glucose-sodium symport
Channels are the protein but involved only in passive transport.
True or false?
True
Is a glucose transporter a passive or active transport?
Passive transport
Active transport allows molecules to move ____ their concentration gradients (_____).
against; uphill
Ion channels allow the passage of molecules via _______, but they are not open pores.
passive transport
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily?
small and hydrophobic
Cells use membranes to help maintain set ranges of ion concentrations inside and outside the cell. Which of the following ions is the most abundant outside a typical mammalian cell?
Na+
Lipid bilayers are impermeable to ions. True or false?
True
What is the difference between the Ca2+ pump and a Na+-K+ pump?
Ca2+ pumps return to their original conformation without a requirement for binding and transporting a second ion.
Uncharged polar molecules like water (18 dalton) and ethanol (46 daltons) are small enough to ___ diffuse across.
small
Name the gated ion channel @ 1

voltage-gated
K+ has a very small _______ gradient across the membrane even though its concentration is _____.
electrochemical; large
What determines if a solute movement moves across the membrane via active or passive transport?
concentration gradient of a solute
The most abundant lipid is a
phospholipid
The diffusion of ___ ions propagates the action potential along the axon.
Na+
In a Na+-K+ pump, how many sodium ion are pumped out? how many potassium ions are pumped in
3; 2
Small nonpolar molecules such as O2 (molecular mass 32 daltons) and CO2 (44 daltons) _____ diffuse across the membrane.
rapidly
Glucose-Na+ is what type of coupled pump?
symport
For a cell to avoid being torn apart by electrical process, they need to make balance. True or false?
True
What happens in the falling phase of the action potential?
Most Na+ channels become inactivated, many K+ channels have opened
___________- membrane potential moves towards a positive value.
depolarization
An example of a light driven pump is
Bacteriorhodopsin
What is the function of the transporter Na+-H+ exchanger?
active export of H+ ions, pH regulation
What happens in the rising phase of the action potential?
Depolarization opens most Na channels, while the K+ channels remain closed.
What is the energy source of all transmembrane pumps (transport) that are not driven?
ATP Hydrolysis


