cervical/vulvar path Flashcards

Cervical transformation zone: transition from stratified squamous epithelium (of vagina) to transitional epithelium (uterus)
What you evaluate on a pap smear

Pap smear:
squamous cells and endocervical glandular cells
Red cell are mature
Blue cells are immature
Dark, fluffy cells (arrow) are from the T-zone
Compare nucleus:cytoplasm ratio

Clue cells; squamous cells covered by gardnerella organism, have dusty appearance; sign of BV

Fungal forms seen on pap smear; often seen in pregnant women

Trichomonas seen on pap smear; tiny blue dots with “halos” can see swimming around on slide.

HSV seen on pap smear; most genital HSV is HSV 2; on path see multinucleation and marginating chromatin
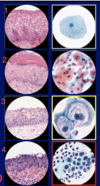
Cervical Bx/Pap smear
1) Normal/negative
2) ASCUS
3) LSIL
4) HSIL

Dysplasia of cervix at squamocolumnar jxn
cervical bx

Moderate cervical dysplasia: CIN2

Adenocarcinoma In Situ (glandular lesion) of endocervical glands; not invasive; related to HPV; bottom slides are stained for p16 (tumor marker).
vulva

VIN 2+ (vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia); leads to surgical excision of the carcinoma in situ;
Left= H&E slide, can’t tell if just atrophy vs. HGSIL
Right= stained for p16 a tumor marker–>VIN
clinical sxs may be white, itchy vulva
vulva

Lichen Sclerois; autoimmune condition targeting the vulva; by this H&E image unable to distinguish LS vs. SCC.
vulva

Extra-mammary Paget’s Dz; see adenocarcinoma in-situ from glandular cells beneath the epithelium. NOT melanoma.
Grossly see pigmented spots on vulva.
vulva

Melanoma of vulva; looks similar to Paget’s dz but has melanin.
vulva

Vulvar cancer; depth of invasion is really important; only 1 mm invasion neede to metastasize to broad ligament, pelvic lymph nodes and peri-aortic nodes.


