Brain and Blood Supply Flashcards
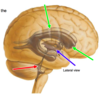
Blue Arrow
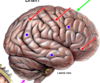
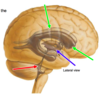
Lateral Fissure
carotid canal runs through the _____ bone
temporal
Red Arrows

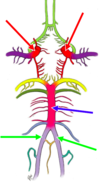
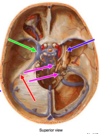
Anterior cerebral artery
(from internal carotid)
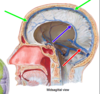
Green Arrow

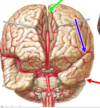
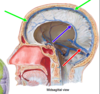
Meningeal dura
Green Arrow

Falx cerebri
the main continuation of the internal carotid artery
middle cerebral artery
Green Arrow
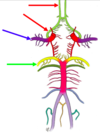
Posterior cerebral artery
(from basilar)
the postcentral gyrus is _______ to the central sulcus. which is the _____ cortex
posterior
sensory
Red Arrow

reflection of dural folds
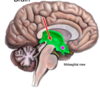
Blue dot
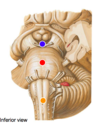
midbrain
a seperation between the dura mater and the periosteum is referred to as
dural fold
fissure between hemispheres of the cerebrum
longitudinal fissure
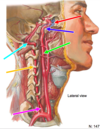
Blue Arrow

Carotid canal
red dot

subarachnoid space with cerebral spinal fluid
blue arrow
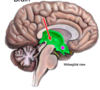
3rd ventricle
Green Arrow

Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
(from vertebral)
the meningeal fold within the longitudinal fissure
falx cerebri
Red Arrow

Internal carotid arteries
Blue Arrow
Inferior sagittal sinus
Purple Arrow

Inferior petrosal sinus
Blue Arrow

Middle cerebral artery
(from internal carotid)
fissure between cerebrum and cerebellum
transverse fissure
Red dot

pons
Red Arrow
Superior petrosal sinus
Purple Arrow
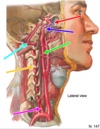
Vertebral artery
the 4th ventricle is located between _________
the two halves of the cerebellum
Blue Arrow

Anterior communicating artery
(connects both anterior cerebrals)
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
blood (usually arterial) escapes into the subarachnoid space
most commonly a ruptured aneurysm
Green Arrow

meningeal dura
Red Arrow
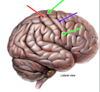
Postcentral gyrus
sensory cortex
Red Arrow

Anterior spinal
(from vertebrals)
Blue Arrow

Precentral gyrus
motor cortex
red arrow

4th ventricle
Red Arrow

Straight sinus
Dural border hematoma
blood (usually venous) forces open a space within the sublayers of the dura
Green Arrow

lateral lakes
Green Arrow

Internal Carotid Artery
Blue Arrow

periosteal dura
Green Arrow

Central Sulcus
light blue line
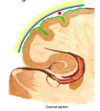
periosteal layer
Red Arrow

Jugular foramen
Green Arrow
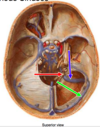
Transverse sinus
Green Arrow
Cavernous sinus
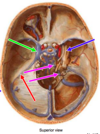
(lateral surface of sella turcica)
Green Arrow

Straight sinus
structure that connects the third and fourth ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
Red Arrow
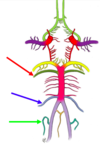
Superior cerebellar artery
from basilar