Bacteria 3 (gram +ve): Diphtheria Flashcards
What bacterium causes diptheria?
- Corynebacterium diptheria: aerobic gram+
- humans only reservoir, spreads from person to person

How does Corynebacterium Diptheria cause disease?
- common in developing world
- spread via nasopharyngeal secretions
- highest incidence in young children (3 - 6mo) after waning of maternal antibody)
- unusually potent toxin -> inhibits protein synthesis
- most potent effects: heart - myocarditis, nerves - demyelination, kidneys - ATN

What are the symptoms of diptheria?
- Typically childhood
- incubation a few days
- Faucial diphtheria most common – fever/sore throat, pseudomembrane, lymphadenopathy, foul odour. Can progress to tracheo-layrngeal diphtheria which can lead to tracheal obstruction/stridor.
- Malignant diphtheria is the most severe – rapid progression and “bull’s neck appearance” with rapid extension of pseudomembrane. Rapid cardiac involvement leading to heart-block.
- Cutaneous diphtheria causes skin lesions/ulcers – usually chronic but mild. variable appearance, can infect any skin wound/break. Most typically ulcerative

What is a classical sign of diptheria (MCQ key words)?
- Hallmark is the grey-white pseudomembrane - adherent to underlying tissue and bleeds when pulled away
- Scenario will typically be a child from a country to low immunisation levels who presents with classic clinical signs including pseudomembrane.
- Remember that it can also cause cardiotoxicity, neurotoxicity, etc
- TRIAD: Pseudomembrane on one or both tonsils, surrounded by inflammatory zone, Strong unpleasant odour, Painful dysphagia
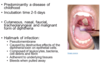
How is it diagnosed?
Culture from mucosal lesion - often negative if abx were given
Test the cultures for toxin production:
- Elek’s test: immune reaction of toxin with anti-toxin
- PCR: detects toxin DNA sequence

How do you treat diptheria?
- Penicillin or macrolides – 2/52 and confirm elimination of C diphtheria before cessation, Diphtheria antitoxin, Vaccination as well (infection not protective)
- Isolation of suspected cases and immunisation for close contacts
- Treatment may require intensive care if respiratory/neurological complication
Other types of management:
- Tracheostomy in case of resp obstruction (trachelaryngeal membrane breaks off and blocks airways)
- cardiac involvement: ITU - ?pacing

Where is diptheria most prevalent?
SE asia and across hot spots in the developing world
Skin infections with Corynebacterium diphtheriae are now more common than nasopharyngeal disease in the West
What contributed to occasional resurgence of diptheria in the past?
- social factors (break up of soviet union -> immigrants, worse living conditions etc)
- cessation of free immunisation
- large accumulations of infected and susceptible children and adults
- new biotype of c. diptheria bacteria
What is the characteristic appearance of the bacterium?
“Chinese letter arrangements”
Different biotypes according to colony formation

Bull’s neck appearance (malignant diptheria)
- >50% mortality rate
- produces heart block

Cutaneous diptheria appearance
Ulcer
Normally lower legs, feet and hands

What are the two major dangerous complications of diptheria?

How do you prevent diptheria?
DTP vaccine:
- 6 weeks of age: 3 doses, 4 weeks apart
- Age 5 booster
- Age 13 - 15 booster
At risk popualtion: displaced people
- immunise, diagnose, treat, isolate suspected cases
- immunise all children under 5


