B4.37 - Evaluating Pulmonary Function Tests Flashcards
(42 cards)
Indications for PFT
Screening
Evaluation of respiratory symptom or sign
Grading severity of respiratory disease
Following progression of respiratory disease
Monitoring response to therapy
Monitoring occupational, drug or radiation toxicity
Predicting prognosis
predicting post op pulmonary risk
assessing disability/impairment
what does spirometry measure
how fast and much you air you breath out
what are teh ATS acceptability criteria for FVC
Good start of test
Smooth continuous curve
Satisfactory exhalation
what determines if the start of the test was good enough
extrapolated voluem <5% of FVC or 150 mL
what is the minimun time an exhalation must be for it to be acceptable
6 seconds
10 is prefered
what are ATS reproducability criteria for FVC
after 3 acceptable maneuvers, the two largest FVC adn FEV1 are within i150 mL of each other
what is depicted her

excellent effort
the goal
what is depicted here

hesitating start
what is depicted here

submaximal effort
what is depicted here

rainbow curve
normal in young, non smoking females

early termination

coughing

subject briefly stopped exhaling
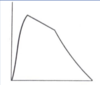
the “knee”
normal in young non smokers
what are gas dilution methods
nitrogen washout and helium dilution
takes advantage of inert, poorly soluble gas of known concentration
a way to measure lung volume
what is a non gas way of measuring lung volume
body box
equation for Vf (unknown lung volume)
Vf = (change in V/change in P) (PB)
what is TLC
total lung capacity
FRC + IC
or
RV + VC
what is RV
residual volume
FRC - ERV
what is the reference equation used for finding reference ranges for spirometry
from NHANESIII
FEV1 - 80-120
FVC - 80-120
what is an obstructive pulmonary defect
a disporportionate reduction of maximal airflow from the lung with respect to the maximal volume (FVC) that can be displaced from the lung. Indicates expiratory airlow limitation
what is a normal FEV/FVC
>.7 is the cutoff for normal
what do these indicate and why

Obstructive pulmonary defect
because the FEV1/FVC ration is low and expiratory phase of flow/volume loop is lower than expected indicating an issue with exhalation
causes of obstructive pulmonary defect
Asthma
COPD
bronchiectasis
Obliterative bronchiolitis
LAM
Diffues panbronchiolitis






