B4.023 - Mechanisms of Ventilation Flashcards
what are the 4 components of respiration
Ventilation
Alveolo-capillary diffusion
blood gas transport
capillary-cell diffusion
for ventilation to occur what 2 things have to happen
- create airflow 2. stretch the lungs
what is PTp
Transpleual pressure =Palv - Ppl ~ change in volume/compliance
what is PPl
pressure in pleural space, usually negative to help lungs expand
what are the opposing tendencies of thorax and lungs
thorax tends to expand lungs tend to recoil these opposing forces create a subatmospheric pressure in thoracic cavity
what is transpulmonary pressure
pressure needed to keep lungs open
what do each of these lines represent


why does pleural pressure drop as you inspire
because the lungs are opening and volume is increasing, and tendency of lungs to recoil is increasing dropping pleural pressure
what is happening in the red

forced exhalation and inhalation
what does this represent in a lung

increased resistance
what does this represent in the lung

decreased compliance
in any given lung a higher volume means what
you have a higher PTp
higher flow means what
higher resistance
to have an increase in flow what else has to increase
difference between Patm and Palv has to increase
at all times in the lung PB - Ppl = what
(PB-Palv) + (Palv-Ppl)
what happens when you breath in and then pause mid breath
Ppl drops, flow stops, volume stays the same, Palv is 0
PTP STAYS THE SAME!!!

What happens to lung pressures in the case of a stiff lung
flow stays the same
Ppl has to decrease a lot more
higher Ptp

what happens to lung pressures in the case of increased airway resistance
alveolar and plaural pressures drop so Ptp stays the same

how do you measure compliance
Pulmonary compliance = change in lung volume / change in Ptp
what is the change in lung compliance if Ppl changes to -10

compliance goes up
from 2500/10 –> 2500/5
lung is easy to inflate but hard to compress
what does the slope of this line represent

compliance
what are 2 main factors of elastic properties of lung
elastic fibers in lung - tether and stretching
surface tension
in the setting of emphysema what happens
you lose elastic fibers which make the lungs more compliant but harder to deflate
rubber band –> celofane bage
what is laplaces law
pressure needed to keep alveoli open is inversely related to radius of alveoli
P=2ST/radius
what happens if two differently sized alveoli are connected
the smaller will collapse into the larger one
as lung volume becomes smaller during forced expiration. the tendency of alveoli to collapse increases
what is surfactant
a lipoprotein that acts as a detergent, lowers ST lowering pressure needed to keep alvioli open
what happens to effective concenatration of surfactant as radius decreases
it increases, works better in smaller alveoli
what happens if there is insufficient surfactant?
- decreased compliance
- atelectasis
- pulmonary edema
where is the site of highest airway resistance
nose
what accounts for 10% of total resistance in airways
airways <1mm diameter
how do you calculate total airway resistance
PB-Palv/airflow
indentify each component of this graph


what is TV
tidal volume, how you breath normally
what is TLC
max inspiration volume
what is IRV
inspiratory reserve volume, amount of air above TV you can breath in
what is ERV
expiratory reserve volume, amount of air you can exhale other than RV and under what you normally exhale (TV)
what is RV usually in percentage
20%
what is VC
total amount you can exhale from max inspiration except residual volume
what is FRC
volume in lungs at end of normal expiration
what is normal FEV1/FVC
.7-.8
what is forced vital capacity
most you can exhale
what is FEV1
amount you can exhale in 1 second
What does this graph represent


what do a, b, c correspond to in this graph

a = highest effort
b = normal
c = least effort
what is the value of the flow volume loop
demostrates effort dependent and independent states of expiration
what does effort independent mean on flow volume loops
no matter how hard you expire you cant change slope of line
why cant you change the slope of effort independent portion of flow volume loops
greater flow = greater resistance
the alveoli sustains increased pressure due to diaphragm relaxation, with maximal effort youre contracting lungs fast as possible and the pressure is increasing, so is pleural pressure. This intra thoracic pressure increase narrows alveolar pressures and increases resistance
what is dynamic airway compression
inherent aspect of lungs that slows flow and increases resistance
responsible for effort independent portion of volume flow loop
When you forcefully contract lungs to exhale the alveolar and pleural pressures both increase significantly, this increases pressure on airways and increases resistance
what do lines a and b respresent
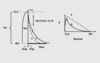
a. normal airway resistance
b. moderate increase in airway resistance
what does line c represent here

severe increase in resistance
Note: increased residual volume bc you cant exhale as much as you normally would
what are some mechanisms of increased airway resistance (pathology)
Contraction of BSM: Asthsma
narrowing of airway lumen: chronic bronchitis
loss of elastic recoil : ephysema
equation for resistance
resistance = PB-Palv/airflow
equation for compliance
compliance = change in volume/change in Palv - PPl


