ATA 21: Air Conditioning - Ventilation - Pressurisation - Pneumatics Flashcards
- With engines and APU running and APU bleed valve selected ON, the engine bleed valves:
(a) Open, X BLEED valve opens, APU bleed valve closes
(b) Close, X BLEED valve opens, APU bleed valve opens
(c) Close, X BLEED valve closes, APU bleed valve opens
(b) Close, X BLEED valve opens, APU bleed valve opens
With the PACK FLOW selector switch in NORM, opening of the APU bleed valve will
cause both the flow control valves to regulate in the:
(a) High flow mode
(b) Low flow mode
(c) Normal flow mode
(a) High flow mode
The amber FAULT light illuminates in the HOT AIR push button switch as a result:
(a) The hot air and trim valves run close
(b) Both pack valves close
(c) The turbine by-pass valve runs close
(a) The hot air and trim valves run close
Which of the following computers controls the cabin and cockpit conditioned air?
(a) One zone controller that passes information and instructions to two pack controllers for four zones
(b) Three zone controllers that pass information and instructions to two pack controllers for four zones
(c) Two pack controllers that pass information and requests to three zone controllers
(a) One zone controller that passes information and instructions to two pack controllers for four zones
When a temperature selector rotary knob is adjusted:
(a) Its associated trim air valve always moves to a different position
(b) No relationship exists between a temperature selector knob and the trim air valve
(c) A signal is sent to the zone controller requesting a different temperature and adjusts trim air valves accordingly
(c) A signal is sent to the zone controller requesting a different temperature and adjusts trim air valves accordingly
Pressurization indications may be found on which ECAM page/s:
(a) The in-flight ECAM cruise page, the cab press page and the door/oxy page
(b) Only on the cab press page
(c) Only on the bleed page
(a) The in-flight ECAM cruise page, the cab press page and the door/oxy page
The Ram Air Inlet valve is controlled…
(a) Automatically by the pack controller
(b) By the RAM AIR pushbutton
(c) By the Ditching pushbutton
(a) Automatically by the pack controller
Pressurization indications may be found on which ECAM page/s:
(a) The in-flight ECAM cruise page, the cab press page and the door/oxy page
(b) Only on the cab press page
(c) Only on the bleed page
(a) The in-flight ECAM cruise page, the cab press page and the door/oxy page
To change to the maximum descent cabin rate of 400 feet per minute you would….
(a) Go to the DES page and enter -400 in the DES CABIN RATE field
(b) Select it manually on the overhead panel
(c) Enter 400 in the DES CABIN RATE field on the CRZ page
(c) Enter 400 in the DES CABIN RATE field on the CRZ page
AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
1. RAM AIR pb
Selected ON (guard lifted) - The ram air inlet opens if differential pressure is less than ____ psi and the _______ pb is not selected ON.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
1. RAM AIR pb
Selected ON (guard lifted) - The ram air inlet opens if differential pressure is less than 1.0 psi and the DITCHING pb is not selected ON.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
2. PACK 1(2) pbs
- On (lights out) - The respective pack operates _________.
- Selected OFF - The respective pack flow control valve ______.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if the valve position ________ with the selected position or if a pack _____ occurs.
- The respective pack flow control valve closes _________.
- It does not illuminate when the valve _______ under normal conditions (e.g., engine start).
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
2. PACK 1(2) pbs
- On (lights out) - The respective pack operates normally.
- Selected OFF - The respective pack flow control valve closes.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if the valve position disagrees with the selected position or if a pack fault occurs.
- The respective pack flow control valve closes automatically.
- It does not illuminate when the valve closes under normal conditions (e.g., engine start).
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
3. PACK FLOW Selector
- Used to exercise _______ control over pack _______ by requesting the desired flow via the _______ controller.
- Regardless of switch position, the zone controller commands high flow when the _______ is supplying bleed air or only one _______ is operating.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
3. PACK FLOW Selector
- Used to exercise limited control over pack flow by requesting the desired flow via the zone controller.
- Regardless of switch position, the zone controller commands high flow when the APU is supplying bleed air or only one pack is operating.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
4. COCKPIT and CABIN Temperature Selectors
- Used to select the desired temperature in each ____.
- The positions of the temperature selectors on the AIR panel correspond with the following temperatures:
- COLD - [____°F]
- 12 o’clock - [____°F]
- HOT - [____°F]
Note: The cabin temp selector sets a reference temperature from which individual cabin zone temperatures are adjusted on the forward attendant’s panel.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
4. COCKPIT and CABIN Temperature Selectors
- Used to select the desired temperature in each zone.
- The positions of the temperature selectors on the AIR panel correspond with the following temperatures:
- COLD - [64°F]
- 12 o’clock - [76°F]
- HOT - [86°F]
Note: The cabin temp selector sets a reference temperature from which individual cabin zone temperatures are adjusted on the forward attendant’s panel.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
5. HOT AIR 1(2) Pbs
- On (lights out) - The hot air valves operate _______.
- OFF - The respective hot air valve _______.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if the duct temperature _______ predetermined temperature.
- The respective _______ air valve closes.
- The FAULT light _______ if the pb is selected OFF and the _______ condition no longer exists.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
5. HOT AIR 1(2) Pbs
- On (lights out) - The hot air valves operate normally.
- OFF - The respective hot air valve closes.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if the duct temperature exceeds predetermined temperature.
- The respective hot air valve closes.
- The FAULT light extinguishes if the pb is selected OFF and the overheat condition no longer exists.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
6. ENG 1(2) Bleed Pbs
- On (lights out) - The respective engine bleed valve operates _______.
- OFF - The engine bleed valve and _______ valve _______.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if any of the following occur:
- The bleed valve is not _______ during engine start or when the _______ bleed valve is open.
- An _______ is detected.
- An _______ is detected.
- A _______ leak is detected.
- The FAULT light _______ when the pb is selected OFF, provided the _______ condition no longer exists.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
6. ENG 1(2) Bleed Pbs
- On (lights out) - The respective engine bleed valve operates normally.
- OFF - The engine bleed valve and HP valve close.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if any of the following occur:
- The bleed valve is not closed during engine start or when the APU bleed valve is open.
- An overpressure is detected.
- An overheat is detected.
- A bleed leak is detected.
- The FAULT light extinguishes when the pb is selected OFF, provided the failure condition no longer exists.
VOL. II, 21.4.5
AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
7. APU Bleed Pb
ON -
- The engine bleed and HP valves ________.
- The crossbleed valve ________ if the crossbleed selector is in the ________ position.
- The air conditioning packs go to ________ flow.
- The APU Bleed valve opens if:
- APU N speed is greater than [_______%_],
- altitude is less than _______ ft_. (climbing) or _______ft_. (descending),
- and no leak is detected in the ________ or ________ side of the bleed system.
- APU N speed is greater than [_______%_],
Off (lights out) - The APU bleed valve ________.
FAULT - Illuminates amber if an APU bleed ________ is detected. The bleed valve closes ______________.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
7. APU Bleed Pb
ON -
- The engine bleed and HP valves close.
- The crossbleed valve opens if the crossbleed selector is in the AUTO position.
- The air conditioning packs go to high flow.
- The APU Bleed valve opens if:
- APU N speed is greater than [95%],
- altitude is less than 25,000 ft. (climbing) or 23,000 ft. (descending),
- and no leak is detected in the APU or left side of the bleed system.
- APU N speed is greater than [95%],
Off (lights out) - The APU bleed valve closes.
FAULT - Illuminates amber if an APU bleed leak is detected. The bleed valve closes automatically.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
8. Crossbleed Selector
- AUTO - The valve is normally _______ and _______ if the APU bleed valve is open.
- The crossbleed valve opens after a [_______] second delay.
- The valve _________ automatically if either BMC (Bleed Monitoring Computer) detects a bleed _______, unless an engine start is in progress.
- OPEN - _______ the automatic operation of the valve and manually _______ the valve.
- CLOSE - _______ the automatic operation of the valve and manually _______ the valve.
VOL. II, 21.4.5

AIR_1
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR panel.
8. Crossbleed Selector
- AUTO - The valve is normally closed and opens if the APU bleed valve is open.
- The crossbleed valve opens after a [10] second delay.
- The valve closes automatically if either BMC detects a bleed leak, unless an engine start is in progress.
- OPEN - Overrides the automatic operation of the valve and manually opens the valve.
- CLOSE - Overrides the automatic operation of the valve and manually closes the valve.
VOL. II, 21.4.5
AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
1. Zone Temperatures
Displays the ________ temperature in each zone of the cabin.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
1. Zone Temperatures
Displays the actual temperature in each zone of the cabin.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
2. Zone Duct Temperatures
Displays the temperature of air in the ________ duct for each cabin zone.
Normally green, becomes amber above __________ temperature.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
2. Zone Duct Temperatures
Displays the temperature of air in the supply duct for each cabin zone.
Normally green, becomes amber above predetermined temperature.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
3. Trim Air Valves
Displays the positions of the trim air valves.
• Green - _________
• Amber – Valve ______
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
3. Trim Air Valves
Displays the positions of the trim air valves.
• Green - Normal
• Amber – Valve failure
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
4. Hot Air Cross Valve
Displays the _________ of the hot air cross valve.
Valve opens automatically when one HOT AIR supply has _________.
Normally _____-line_ green, the valve position can also be displayed:
- In-line green if the valve is _________ under normal conditions (not fully _________).
- Cross-line or in-line amber if there is a _________ between the valve and the _________ position.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
4. Hot Air Cross Valve
Displays the position of the hot air cross valve.
Valve opens automatically when one HOT AIR supply has failed.
Normally cross-line green, the valve position can also be displayed:
- In-line green if the valve is open under normal conditions (not fully closed).
- Cross-line or in-line amber if there is a disagreement between the valve and the commanded position.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
5. Hot Air Valves
Displays the ___________ of the hot air valves.
- ______-line green if the valve is open under normal conditions (not fully ___________ ).
- _______-line green if the valve is closed under normal conditions.
- ______-line or ___\_-line amber if there is a ____________ between the pb selection and the ___________ position.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
5. Hot Air Valves
Displays the position of the hot air valves.
- In-line green if the valve is open under normal conditions (not fully closed).
- Cross-line green if the valve is closed under normal conditions.
- Cross-line or in-line amber if there is a disagreement between the pb selection and the valve position.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
6. HOT AIR Label
Normally green, becomes amber if the respective pack flow ______\_ valve is closed.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
6. HOT AIR Label
Normally green, becomes amber if the respective pack flow control valve is closed.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
7. Forward Cargo Cold Air Valve
Displays the position of the forward cargo cold air valve. The valve is displayed:
- In-line green - Fully ________
- In-line amber - Failed ________
- Slant-line green - ________ open
- Slant-line amber - __ __________ or failed ________open
- Cross-line green - ________ closed
- Cross-line amber -________ closed
- Cross-line amber, and line indication also amber - At least one pack ________
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
7. Forward Cargo Cold Air Valve
Displays the position of the forward cargo cold air valve. The valve is displayed:
- In-line green - Fully open
- In-line amber - Failed open
- Slant-line green - Partially open
- Slant-line amber - In transit or failed partially open
- Cross-line green - Fully closed
- Cross-line amber - Failed closed
- Cross-line amber, and line indication also amber - At least one pack off
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
8. Bulk Cargo Heater Status
Normally green, becomes amber if the ________ fails.
The ________ varies between C (cold) and H (hot) with heater output which varies depending on the compartment ________ and the ________ temperature.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
8. Bulk Cargo Heater Status
Normally green, becomes amber if the heater fails.
The arrow varies between C (cold) and H (hot) with heater output which varies depending on the compartment temperature and the selected temperature.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
9. Cabin Fan Indications
FAN is displayed in amber on the ________ page if a cabin fan _______ or is selected OFF.
V2 21.4.3
AIR_3
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM COND page.
9. Cabin Fan Indications
FAN is displayed in amber on the COND page if a cabin fan fails or is selected OFF.
V2 21.4.3

AIR_4
Describe the function of the Hot Air system.
To maintain the selected zone temperatures, the zone controller:
- Adds hot air, via the _______ air valves, to the cool air supplied to the zones by the _________ unit.
- Hot air is only added to the zones that require air _________ than that supplied by the _________ unit.
VOL. II, 21.2.3.5

AIR_4
Describe the function of the Hot Air system.
To maintain the selected zone temperatures, the zone controller:
- Adds hot air, via the trim air valves, to the cool air supplied to the zones by the mixing unit.
- Hot air is only added to the zones that require air warmer than that supplied by the mixing unit.
VOL. II, 21.2.3.5

AIR_5
Recall the effect of a zone controller failure on the remainder of the air conditioning system.
If both channels of the zone controller fail:
- The pack controllers control temperature at a fixed output of [_______°F].
- _____ _______ and _____ _______ panel control of temperature and zone temperature regulation is no longer possible.
- PACK FLOW selector is ___________._
VOL. II, 21.2.3.2

AIR_5
Recall the effect of a zone controller failure on the remainder of the air conditioning system.
If both channels of the zone controller fail:
- The pack controllers control temperature at a fixed output of [68°F].
- Flight deck and forward attendant panel control of temperature and zone temperature regulation is no longer possible.
- PACK FLOW selector is inoperative.
VOL. II, 21.2.3.2

AIR_6
Understand control functions and indications on the CABIN PRESS Panel.
1. VALVE SEL Switch
Used to select which outflow valves are controlled __________.
- AFT - Allows the aft outflow valve to be controlled __________.
- BOTH - Allows both outflow valves to be controlled __________.
- FWD - Allows the forward outflow valve to be controlled __________.
VOL. II, 21.4.7

AIR_6
Understand control functions and indications on the CABIN PRESS Panel.
1. VALVE SEL Switch
Used to select which outflow valves are controlled manually.
- AFT - Allows the aft outflow valve to be controlled manually.
- BOTH - Allows both outflow valves to be controlled manually.
- FWD - Allows the forward outflow valve to be controlled manually.
VOL. II, 21.4.7

AIR_6
Understand control functions and indications on the CABIN PRESS Panel.
2. V/S CTL Switch
Used to control the position of the outflow valves in the _________ mode.
The switch is spring loaded to the neutral position and must be held in the desired position to move the selected outflow valve.
- UP - The selected outflow valves move toward the _________ position, cabin altitude ________._
- DN - The selected outflow valves move toward the _________ position, cabin altitude ________._
- Neutral - The selected outflow valves __ ____ move
VOL. II, 21.4.7

AIR_6
Understand control functions and indications on the CABIN PRESS Panel.
2. V/S CTL Switch
Used to control the position of the outflow valves in the manual mode.
The switch is spring loaded to the neutral position and must be held in the desired position to move the selected outflow valve.
- UP - The selected outflow valves move toward the open position, cabin altitude increases.
- DN - The selected outflow valves move toward the closed position, cabin altitude decreases.
- Neutral - The selected outflow valves do not move
VOL. II, 21.4.7

AIR_6
Understand control functions and indications on the CABIN PRESS Panel.
3. MODE SEL pb
- AUTO (lights out) - The ___________ system operates in automatic mode.
- MAN - The selected ________ valves are controlled manually using the _____________ switch.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if the pressure __________ fail.
VOL. II, 21.4.7

AIR_6
Understand control functions and indications on the CABIN PRESS Panel.
3. MODE SEL pb
- AUTO (lights out) - The pressurization system operates in automatic mode.
- MAN - The selected outflow valves are controlled manually using the MAN V/S CTL switch.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if the pressure controllers fail.
VOL. II, 21.4.7

AIR_6
Understand control functions and indications on the CABIN PRESS Panel.
4. LDG ELEV Selector
- AUTO - The active controller uses landing elevation information from the ______.
- Manual (out of the _______ position) - The active controller uses landing elevation information from the _____\_ selector.
VOL. II, 21.4.7

AIR_6
Understand control functions and indications on the CABIN PRESS Panel.
4. LDG ELEV Selector
- AUTO - The active controller uses landing elevation information from the FMS.
- Manual (out of the AUTO position) - The active controller uses landing elevation information from the LDG ELEV selector.
VOL. II, 21.4.7

AIR_6
5. DITCHING pb
Selected ON:
- All exterior valves below the water line:
- The ________ fans shut off.
- ________ and _____ outflow valves close.
- ______ overboard ______ valve closes.
- ______ flow control valves close.
- ______ air inlet closes.
Note: The outflow valves will not automatically close when the DITCHING pb is selected ON if the MODE SEL pb is in ______.
VOL. II, 21.4.7

AIR_6
5. DITCHING pb
Selected ON:
- All exterior valves below the water line:
- The cabin fans shut off.
- Forward and aft outflow valves close.
- Avionics overboard extract valve closes.
- Pack flow control valves close.
- Ram air inlet closes.
Note: The outflow valves will not automatically close when the DITCHING pb is selected ON if the MODE SEL pb is in MAN.
VOL. II, 21.4.7
AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
1. Pressurization Mode
- AUTO - Displayed in green when the active controller uses landing elevation information from the ________, becomes amber if both ________ fail.
- MAN - The active controller uses landing elevation selected using the ________ selector on the overhead CABIN PRESS panel.
- The field is blank if the MODE SEL pb is selected to ________ and the VALVE SEL switch is in the ________ position.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
1. Pressurization Mode
- AUTO - Displayed in green when the active controller uses landing elevation information from the FMS, becomes amber if both FMGECs fail.
- MAN - The active controller uses landing elevation selected using the LDG ELEV selector on the overhead CABIN PRESS panel.
- The field is blank if the MODE SEL pb is selected to MAN and the VALVE SEL switch is in the BOTH position.
_FMGECs_ Flight Management Guidance Envelope Computers
VOL. II, 21.4.4
AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
2. Landing Elevation
- Displays the elevation of the landing airport as selected from the ________ (auto) or the ______________ selector.
- The value is displayed in ________.
- It is not displayed if the ________ pb is selected to MAN and the ________ SEL switch is in the BOTH position.
- Replaced by two amber Xs if both ________ fail.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
2. Landing Elevation
- Displays the elevation of the landing airport as selected from the FMS (auto) or the LDG ELEV selector.
- The value is displayed in green.
- It is not displayed if the MODE SEL pb is selected to MAN and the VALVE SEL switch is in the BOTH position.
- Replaced by two amber Xs if both FMGECs fail.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
3. Cabin Differential Pressure
Normally green, becomes amber if __________ pressure is above or below a predetermined pressure.
NON LOD: Max Pos cabin differential pressure (relief valves) _______ psi
Max Neg cabin diff. _-______ psi
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
3. Cabin Differential Pressure
Normally green, becomes amber if differential pressure is above or below a predetermined pressure.
NON LOD: Max Pos cabin differential pressure (relief valves) 8.85 psi
Max Neg cabin diff. -0.73 psi
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
4. Cabin Vertical Speed
- Normally green, ________ green if the cabin vertical speed exceeds a ________ rate.
- On the Cruise___ page, the cabin vertical speed is normally a ________ display.
- If the MODE SEL pb is selected to ________, an ________ indication is displayed.
- The cabin vertical speed is also displayed on the ________ page (in digital format) when the system is in the automatic mode.
VOL. II, 21.4.4
AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
4. Cabin Vertical Speed
- Normally green, pulses green if the cabin vertical speed exceeds a predetermined rate.
- On the cruise page, the cabin vertical speed is normally a digital display.
- If the MODE SEL pb is selected to MAN, an analog indication is displayed.
- The cabin vertical speed is also displayed on the DOOR/OXY page (in digital format) when the system is in the automatic mode.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
5. Cabin Altitude
- Normally green, _________ green if the cabin altitude exceeds a _________ altitude.
- Displayed in red if cabin altitude exceeds [_________] feet.
VOL. II, 21.4.4
AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
5. Cabin Altitude
- Normally green, pulses green if the cabin altitude exceeds a predetermined altitude.
- Displayed in red if cabin altitude exceeds [9550] feet.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
6. Pressure Controller Label
- The active controller is displayed in ________.
- The _____\_ controller is not displayed.
- The respective controller is displayed in amber if a _______ occurs.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
6. Pressure Controller Label
- The active controller is displayed in green.
- The inactive controller is not displayed.
- The respective controller is displayed in amber if a fault occurs.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR 7 Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
7. VENT Label
Normally white, becomes ________ if low ______ air flow is detected.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR 7 Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
7. VENT Label
Normally white, becomes amber if low extract air flow is detected.
VOL. II, 21.4.4
AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
8. Safety Valve
- Normally the SAFETY label is _______ and the valve indication is _______._
- They both become _________ if any safety valve is open.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
8. Safety Valve
- Normally the SAFETY label is white and the valve indication is green.
- They both become amber if any safety valve is open.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
9. EXTRACT Label
Normally white, becomes amber if the _________ extract valve is in an abnormal position.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM CAB PRESS page.
9. EXTRACT Label
Normally white, becomes amber if the avionics extract valve is in an abnormal position.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
10. Pack Indications
- The PACK 1(2) labels are ________ and the triangles are _______ if the pack flow control valves are open.
- They become amber if the respective pack flow control valve is ________.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
10. Pack Indications
- The PACK 1(2) labels are white and the triangles are green if the pack flow control valves are open.
- They become amber if the respective pack flow control valve is closed.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
11. Overboard Extract Valve
- Displays the position of the __________ extract valve.
- Normally green, becomes amber if the valve is in an _______\_ position.
VOL. II, 21.4.4
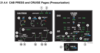
AIR_7
11. Overboard Extract Valve
- Displays the position of the avionics extract valve.
- Normally green, becomes amber if the valve is in an abnormal position.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
12. Forward and Aft Outflow Valve Indications
- Displays the positions of the forward and aft ________ valves.
- Normally the FWD (AFT) labels are ______ and the valve position indications are ______._
- They become amber if either of the following conditions are met:
- The respective outflow valve opens more than [_____%] in flight.
- Automatic control of the respective outflow valve ______.
- If an outflow valve is under manual control, ______ is displayed in ______ above the respective FWD (AFT) label.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
12. Forward and Aft Outflow Valve Indications
- Displays the positions of the forward and aft outflow valves.
- Normally the FWD (AFT) labels are white and the valve position indications are green.
- They become amber if either of the following conditions are met:
- The respective outflow valve opens more than [95%] in flight.
- Automatic control of the respective outflow valve fails.
- If an outflow valve is under manual control, MAN is displayed in green above the respective FWD (AFT) label.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
12. Forward and Aft Outflow Valve Indications
- Displays the positions of the forward and aft ________ valves.
- Normally the FWD (AFT) labels are ________ and the valve position indications are ________.
- They become amber if either of the following conditions are met:
- The respective outflow valve opens more than [________%] in flight.
- Automatic control of the respective outflow valve ________.
If an outflow valve is under manual control, ________ is displayed in green above the respective FWD (AFT) label.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_7
12. Forward and Aft Outflow Valve Indications
- Displays the positions of the forward and aft outflow valves.
- Normally the FWD (AFT) labels are white and the valve position indications are green.
- They become amber if either of the following conditions are met:
- The respective outflow valve opens more than [95%] in flight.
- Automatic control of the respective outflow valve fails.
If an outflow valve is under manual control, MAN is displayed in green above the respective FWD (AFT) label.
VOL. II, 21.4.4

AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
-
Ground:
- The aircraft is _________ by fully opening the _________ valves during ground operations.
- After landing, _________ cabin pressure is released _________ before the outflow valves are _________ opened.
- An _________ signal is sent to the outflow valves shortly thereafter.
VOL. II, 21.3.2.3 Pressurization Phases
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
-
Ground:
- The aircraft is depressurized by fully opening the outflow valves during ground operations.
- After landing, residual cabin pressure is released gradually before the outflow valves are fully opened.
- An open signal is sent to the outflow valves shortly thereafter.
VOL. II, 21.3.2.3 Pressurization Phases
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
- Takeoff:
- To avoid a _________ surge at rotation, the active ___________ pressurizes the aircraft to [____] psi when takeoff power is applied.
VOL. II, 21.3.2
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
- Takeoff:
- To avoid a pressure surge at rotation, the active controller pressurizes the aircraft to [0.1] psi when takeoff power is applied.
VOL. II, 21.3.2
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are _______ pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
- Climb - After lift-off, the ____ controller varies the ____\_ altitude with the ________ aircraft rate of climb.
VOL. II, 21.3.2
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
- Climb - After lift-off, the active controller varies the cabin altitude with the actual aircraft rate of climb.
VOL. II, 21.3.2
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
- Cruise - At the top of climb, the active controller maintains the _______ cabin altitude that is compatible with the maximum allowable __________ pressure.
- Cabin altitude will not exceed [_________] feet.
VOL. II, 21.3.2
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
- Cruise - At the top of climb, the active controller maintains the lowest cabin altitude that is compatible with the maximum allowable differential pressure.
- Cabin altitude will not exceed [8000] feet.
VOL. II, 21.3.2
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
- Descent - The active controller ___________ the cabin descent to reach landing field pressure altitude [_____] psi just prior to ___________ .
The target cabin altitude for landing is determined by information from either:
- The ______ for airport elevation and ___________ reference information.
- The ___________ selector on the overhead panel and the ___________ barometric reference setting.
VOL. II, 21.3.2
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
- Descent - The active controller optimizes the cabin descent to reach landing field pressure altitude [+0.1] psi just prior to landing.
The target cabin altitude for landing is determined by information from either:
- The FMS for airport elevation and barometric reference information.
- The LDG ELEV selector on the overhead panel and the captain’s barometric reference setting.
VOL. II, 21.3.2
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
- Abort - Returns the cabin altitude to the ______\_ elevation if the aircraft does not climb after takeoff (begins a descent prior to climbing above [______] feet msl or does not climb more than [_______] feet).
- If a climb is subsequently initiated, the normal pressurization scheduled is _________.
VOL. II, 21.3.2
AIR_8
Describe the six phases of the cabin pressurization system when operating automatically.
There are six pressurization phases when the system is operating automatically:
- Abort - Returns the cabin altitude to the takeoff elevation if the aircraft does not climb after takeoff (begins a descent prior to climbing above [8000] feet msl or does not climb more than [5000] feet).
- If a climb is subsequently initiated, the normal pressurization scheduled is resumed.
VOL. II, 21.3.2
AIR_9
Describe the effect of losing one pressure controller.
- Two independent pressure controllers provide __________ operation of the pressurization system.
- If one pressure controller fails, the other controller becomes _________._
VOL. II, 21.3.3.1
AIR_9
Describe the effect of losing one pressure controller.
- Two independent pressure controllers provide automatic operation of the pressurization system.
- If one pressure controller fails, the other controller becomes active.
VOL. II, 21.3.3.1

AIR_9
Describe the effect of losing Both controllers.
- Two independent pressure controllers provide ___________ operation of the pressurization system.
- If both automatic pressure controllers fail, the ___________ valves must be controlled directly using the ___________ mode.
- Each outflow valve has a ___________ dedicated to manual operation.
- The outflow valves can be operated manually, either ___________ or ___________.
VOL. II, 21.3.3.1
AIR_9
Describe the effect of losing Both controllers.
- Two independent pressure controllers provide automatic operation of the pressurization system.
- If both automatic pressure controllers fail, the outflow valves must be controlled directly using the manual mode.
- Each outflow valve has a motor dedicated to manual operation.
- The outflow valves can be operated manually, either together or independently.
VOL. II, 21.3.3.1

AIR_10
Demonstrate ability to operate pressurization system manually.
- Selecting the MODE SEL pb to _______ on the CABIN PRESS panel switches the pressurization system to the manual mode.
- The __________ switch is used to select which outflow valves are controlled manually.
- Both outflow valves can be controlled __________ or the forward or aft outflow valve can be controlled __\_________.
- Selecting only __________ outflow valve allows the_______ pressure controller, if available, to control the other valve.
Example: If both automatic motors for the FWD outflow valve fail:
- Selecting the MODE SEL pb to ________ and the __________ switch to FWD allows the crew to manually operate the FWD outflow valve while the active controller operates the AFT.
- The MAN V/S CTL switch is used to control the position of the __________ valves in the manual mode.
- The switch is spring loaded to the neutral position and must be held in the desired position to move the selected outflow valve.
VOL. II, 21.3.3.1

AIR_10
Demonstrate ability to operate pressurization system manually.
- Selecting the MODE SEL pb to MAN on the CABIN PRESS panel switches the pressurization system to the manual mode.
- The VALVE SEL switch is used to select which outflow valves are controlled manually.
- Both outflow valves can be controlled simultaneously or the forward or aft outflow valve can be controlled independently.
- Selecting only one outflow valve allows the active pressure controller, if available, to control the other valve.
Example: If both automatic motors for the FWD outflow valve fail:
- Selecting the MODE SEL pb to MAN and the VALVE SEL switch to FWD allows the crew to manually operate the FWD outflow valve while the active controller operates the AFT.
- The MAN V/S CTL switch is used to control the position of the outflow valves in the manual mode.
- The switch is spring loaded to the neutral position and must be held in the desired position to move the selected outflow valve.
VOL. II, 21.3.3.1

AIR_11
Demonstrate ability to switch pressurization control systems.
- The active controller switches if the MODE SEL pb is selected to ______ for at least ______ seconds and then back to __________.
VOL. II, 21.3.2.1.1
AIR_11
Demonstrate ability to switch pressurization control systems.
- The active controller switches if the MODE SEL pb is selected to MAN for at least three seconds and then back to AUTO.
VOL. II, 21.3.2.1.1
AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
1. FWD and BULK ISOL VALVES pbs
- On (lights out) - The forward (bulk) cargo ventilation system operates __________.
- OFF - The forward (bulk) cargo ______ and ______ isolation valves close.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if an ______or ______ isolation valve is not in the ______ position or if ______ is detected in the respective cargo compartment.
VOL. II, 21.4.6

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
1. FWD and BULK ISOL VALVES pbs
- On (lights out) - The forward (bulk) cargo ventilation system operates normally.
- OFF - The forward (bulk) cargo inlet and outlet isolation valves close.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if an inlet or outlet isolation valve is not in the selected position or if smoke is detected in the respective cargo compartment.
VOL. II, 21.4.6

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
2. COOLING Selector
- Used to adjust the __________ of conditioned air mixed with __________ (__________) air.
- OFF - The __________ air valve closes and no __________ air is added.
- NORM - The cold air valve partially __________.
- MAX - The cold air valve fully __________ and the __________quantity of conditioned air is provided.
VOL. II, 21.4.6

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
2. COOLING Selector
- Used to adjust the quantity of conditioned air mixed with inlet (cabin) air.
- OFF - The cold air valve closes and no cold air is added.
- NORM - The cold air valve partially opens.
- MAX - The cold air valve fully opens and the maximum quantity of conditioned air is provided.
VOL. II, 21.4.6

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
3. BULK HOT AIR pb
- OFF - The heating element and the heater _________ shut off.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if a bulk cargo compartment ______ duct _________ is detected.
- The FAULT light extinguishes if the pb is selected _________ and the _________ condition no longer exists.
VOL. II, 21.4.6

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
3. BULK HOT AIR pb
- OFF - The heating element and the heater fan shut off.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if a bulk cargo compartment inlet duct overheat is detected.
- The FAULT light extinguishes if the pb is selected OFF and the overheat condition no longer exists.
VOL. II, 21.4.6

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
4. FWD and BULK Temperature Selectors
- Used to select the _________ temperature in the respective compartment.
- COLD - [_____° F]
- 12 o’clock - [____°_F]
- HOT - [___\_°F]
Note: ______ cargo temperature control is not available.
VOL. II, 21.4.6

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
4. FWD and BULK Temperature Selectors
- Used to select the desired temperature in the respective compartment.
- COLD - [41° F]
- 12 o’clock - [59°F]
- HOT - [77°F]
Note: Aft cargo temperature control is not available.
VOL. II, 21.4.6

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
5. VENTILATION EXTRACT pb
- AUTO (lights out) - The ________ ventilation system operates normally.
- OVRD - The ________ extract valve partially opens and the ________ extract valve closes.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if low air flow is detected in the ________ compartment (e.g., ________ fan fault)
VOL. II, 21.4.8

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
5. VENTILATION EXTRACT pb
- AUTO (lights out) - The avionics ventilation system operates normally.
- OVRD - The overboard extract valve partially opens and the underfloor extract valve closes.
- FAULT - Illuminates amber if low air flow is detected in the avionics compartment (e.g., extract fan fault)
VOL. II, 21.4.8

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
6. CAB FANS pb
- On (lights out) - The cabin fans operated ________._
- Selected OFF - The cabin fans _____ ____.
VOL. II, 21.4.6

AIR_12
Understand the control functions and indications on the AIR CARGO and VENTILATION panels.
6. CAB FANS pb
- On (lights out) - The cabin fans operated normally.
- Selected OFF - The cabin fans shut off.
VOL. II, 21.4.6
AIR_13
State the flow of avionics vent air during normal and abnormal situations.
- Avionics ventilation air is vented overboard through either the __________ extract valve to the __________ outflow valve area or through the__________ extract valve.
- The overboard extract valve is located on the __________ of aircraft, aft of the __________ .
- When the aircraft is on the ground with the engines Shutdown :
- the overboard extract valve __________ ,
- the underfloor extract valve __________ , and air is vented __________ .
- When the aircraft is __________ , or an engine _______ __________ , or if the __________ pb is selected ON:
- the overboard extract valve __________
- and the underfloor extract valve __________ and air is vented to the __________ outflow valve area.
The FAULT light in the EXTRACT pb on the VENTILATION panel illuminates if ________air flow is detected in the __________ compartment (e.g., extract __________ fault).
- The FAULT light extinguishes if the EXTRACT pb is selected to __________ .
- If the aircraft is on the ground, an external warning horn sounds in the nose gear area after [_____] minutes.
- If the EXTRACT pb is selected to OVRD, the __________ extract valve partially opens and the __________ extract valve closes.
- In this configuration __________ pressure provides the airflow necessary for __________ ventilation.
VOL. II, 21.2.6.2

AIR_13
State the flow of avionics vent air during normal and abnormal situations.
- Avionics ventilation air is vented overboard through either the underfloor extract valve to the forward outflow valve area or through the overboard extract valve.
- The overboard extract valve is located on the bottom of aircraft, aft of the nosewheel.
- When the aircraft is on the ground with the engines shutdown:
- the overboard extract valve opens,
- the underfloor extract valve closes, and air is vented overboard.
- When the aircraft is in flight, or an engine is running, or if the DITCHING pb is selected ON:
- the overboard extract valve closes
- and the underfloor extract valve opens and air is vented to the forward outflow valve area.
The FAULT light in the EXTRACT pb on the VENTILATION panel illuminates if low air flow is detected in the avionics compartment (e.g., extract fan fault).
- The FAULT light extinguishes if the EXTRACT pb is selected to OVRD.
- If the aircraft is on the ground, an external warning horn sounds in the nose gear area after [5] minutes.
- If the EXTRACT pb is selected to OVRD, the overboard extract valve partially opens and the underfloor extract valve closes.
- In this configuration differential pressure provides the airflow necessary for avionics ventilation.
VOL. II, 21.2.6.2

AIR_14
Describe the operation of the lavatory and galley ventilation system.
- Lav and galley ventilation is fully ___________.
- On the ground or when differential pressure is less than [______] psi an ________ extract ______ draws ______ air from the lavs and galleys through an extract duct and exhausts it overboard through a ______ at the ______of the aircraft.
- When the aircraft is pressurized, ______ pressure forces air from the lavs and galleys through the ______ duct and out the __________.
VOL. II, 21.2.8
AIR_14
Describe the operation of the lavatory and galley ventilation system.
- Lav and galley ventilation is fully automatic.
- On the ground or when differential pressure is less than [1.0] psi an electric extract fan draws cabin air from the lavs and galleys through an extract duct and exhausts it overboard through a venturi at the rear of the aircraft.
- When the aircraft is pressurized, differential pressure forces air from the lavs and galleys through the extract duct and out the venturi.
VOL. II, 21.2.8

AIR_16
Recall how the bulk cargo compartment is heated. (-323 and -302 ONLY)
- An _______ _____ blows cabin air over an _________ heating element, through an inlet _________ valve, and into the cargo compartment.
- An _______ fan draws air from the _________ compartment, through an _________ isolation valve to the _________ outflow valve area.
VOL. II, 21.2.7.3
AIR_16
Recall how the bulk cargo compartment is heated. (-323 and -302 ONLY)
- An electric fan blows cabin air over an electric heating element, through an inlet isolation valve, and into the cargo compartment.
- An extract fan draws air from the cargo compartment, through an outlet isolation valve to the aft outflow valve area.
VOL. II, 21.2.7.3

AIR_17
Recall how the forward cargo compartment is ventilated. (-200 and -323 ONLY)
- Air from the ________ and around the ________ cargo compartment passes through two inlet ________ valves and enters the ________ cargo compartment.
- An electric extract ________ draws air through an ________ isolation valve to the ________ outflow valve area.
- To cool the compartment, cold air supplied by pack _______ , passes through a _____ air valve and is mixed with the ______ air.
- To warm the compartment, hot air supplied by ___ ___ 1 is mixed with inlet air through the________ cargo trim air valve.
- The ventilation controller operates the inlet and outlet ________ valves and the extract ________ .
- If the inlet and outlet isolation valves are open, the extract fan ________ and ventilation is provided.
VOL. II, 21.2.7.2
AIR_17
Recall how the forward cargo compartment is ventilated. (-200 and -323 ONLY)
- Air from the cabin and around the forward cargo compartment passes through two inlet isolation valves and enters the forward cargo compartment.
- An electric extract fan draws air through an outlet isolation valve to the forward outflow valve area.
- To cool the compartment, cold air supplied by pack two, passes through a cold air valve and is mixed with the inlet air.
- To warm the compartment, hot air supplied by HOT AIR 1 is mixed with inlet air through the forward cargo trim air valve.
- The ventilation controller operates the inlet and outlet isolation valves and the extract fan.
- If the inlet and outlet isolation valves are open, the extract fan runs and ventilation is provided.
VOL. II, 21.2.7.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
1. High Pressure (HP) Bleed Valves
- In-line green - Valve ________
- Cross-line green - Valve ________
- Cross-line amber - Valve ________ and respective engine is ______ ________or valve disagreement in ________ position.
VOL. II, 36.3.2
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
1. High Pressure (HP) Bleed Valves
- In-line green - Valve open
- Cross-line green - Valve closed
- Cross-line amber - Valve closed and respective engine is not running or valve disagreement in closed position.
VOL. II, 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
2. Bleed Valves
- ________ as HP bleed valve (below) plus:
- In-line amber - Valve disagreement in the _____\_ position.
- In-line green - Valve _____
- In-line amber - Valve disagreement in the ____ position
- Cross-line green - Valve _____
- Cross-line amber - Valve ______ and respective engine is not running or valve disagreement in _______ position.
VOL. II, 36.3.2
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
2. Bleed Valves
-
Same as HP bleed valve (above) plus:
- In-line amber - Valve disagreement in the open position.
- High Pressure (HP) Bleed Valves
In-line green - Valve open
Cross-line green - Valve closed
Cross-line amber - Valve closed and respective engine is not running or valve disagreement in closed position.
VOL. II, 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
3. Bleed Air Temperature
- Normally green, becomes amber if an _________ exists, or ______ temperature is detected with wing _______ on.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
3. Bleed Air Temperature
- Normally green, becomes amber if an overheat exists, or low temperature is detected with wing anti-ice on.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
4. Bleed Air Pressure
- Normally green, becomes amber if the pressure is ________ or _______ a predetermined pressure.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
4. Bleed Air Pressure
- Normally green, becomes amber if the pressure is above or below a predetermined pressure.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
5. Engine Labels
- Normally white but become amber when ______ of the corresponding engine is below _______.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
5. Engine Labels
- Normally white but become amber when N2 of the corresponding engine is below idle.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2
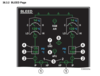
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
6. APU Bleed Valve
- In-line green - Valve ________
- Cross-line green - Valve ________
- Cross-line amber - Valve not fully ____ with ________ BLEED pb selected ON
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
6. APU Bleed Valve
- In-line green - Valve open
- Cross-line green - Valve closed
- Cross-line amber - Valve not fully open with APU BLEED pb selected ON
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2
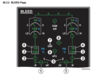
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
7. GND Label
- Displayed in white when the aircraft is on the _________ to indicate where ______ ground air enters the _________ duct.
- It does not provide any indication of whether the_________ _________ connection is in use or not.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
7. GND Label
- Displayed in white when the aircraft is on the ground to indicate where HP ground air enters the crossbleed duct.
- It does not provide any indication of whether the ground air connection is in use or not.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
8. Crossbleed Valve
- In-line green - Valve _________
- Cross-line green - Valve _________
- Amber - In _________ or valve _________ with commanded position
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2
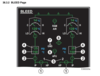
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
8. Crossbleed Valve
- In-line green - Valve open
- Cross-line green - Valve closed
- Amber - In transit or valve disagreement with commanded position
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
9. Pack Outlet Temperature
- Displays the temperature of conditioned air ________ the pack.
- Normally green, becomes amber if the temperature exceeds a ___________ temperature.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
9. Pack Outlet Temperature
- Displays the temperature of conditioned air exiting the pack.
- Normally green, becomes amber if the temperature exceeds a predetermined temperature.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
10. Temperature Control Valve
Displays the __________ of the pack’s temperature control valve.
- Valve position varies between:
- C (Cold) - More bleed air passes through the _______ heat exchanger and ________ resulting in a colder pack outlet temperature.
- H (Hot) - Less bleed air passes through the _______ heat exchanger and _______ resulting in a hotter pack outlet temperature.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
10. Temperature Control Valve
Displays the position of the pack’s temperature control valve.
- Valve position varies between:
- C (Cold) - More bleed air passes through the main heat exchanger and turbine resulting in a colder pack outlet temperature.
- H (Hot) - Less bleed air passes through the main heat exchanger and turbine resulting in a hotter pack outlet temperature.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
12. Pack Flow
Displays actual pack air _______ rate.
- The 12 o’clock position represents _____% airflow rate.
- Flow varies between:
- LO - [____%] airflow.
- HI - [_____%] airflow.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
12. Pack Flow
Displays actual pack air flow rate.
- The 12 o’clock position represents 100% airflow rate.
- Flow varies between:
- LO - [70%] airflow.
- HI - [130%] airflow.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
13. Pack Flow Control Valve
- Displayed in-line green if the valve is ______ (not fully _______).
- Displayed cross-line amber if the valve is fully _______.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
13. Pack Flow Control Valve
- Displayed in-line green if the valve is open (not fully closed).
- Displayed cross-line amber if the valve is fully closed.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
14. Ram Air Valve
Displays the position of the ram-air inlet valve.
- Normally cross-line green (closed). Can also be displayed:
- In-line green - _________
- In-line amber - ________________
- Slant-line amber -__ _____
- Cross-line amber - _________ _________
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
14. Ram Air Valve
Displays the position of the ram-air inlet valve.
- Normally cross-line green (closed). Can also be displayed:
- In-line green - Open
- In-line amber - Failed open
- Slant-line amber - In-transit
- Cross-line amber - Failed closed
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
14. Ram Air Valve
Displays the position of the ram-air inlet valve.
- Normally cross-line green (_______).
- Can also be displayed:
- In-line green - _______
- In-line amber - _____ _______
- Slant-line amber - _____ _______
- Cross-line amber -_____ _______
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
14. Ram Air Valve
Displays the position of the ram-air inlet valve.
- Normally cross-line green (closed).
- Can also be displayed:
- In-line green - Open
- In-line amber - Failed open
- Slant-line amber - In-transit
- Cross-line amber - Failed closed
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
15. Pack Bypass Valve
Displays the status of the pack bypass valve.
- An ________ is only displayed if the valve is open.
- If the compressor/turbine section of the pack fails, the pack bypass valve _______ and the arrow is displayed in ________.
- The arrow is displayed in amber if it fails in the ________ position.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2
AIR_18
Discuss normal and abnormal indications on the ECAM BLEED page as they relate to the air conditioning system.
15. Pack Bypass Valve
Displays the status of the pack bypass valve.
- An arrow is only displayed if the valve is open.
- If the compressor/turbine section of the pack fails, the pack bypass valve opens and the arrow is displayed in green.
- The arrow is displayed in amber if it fails in the open position.
VOL. II, 21.4.2 36.3.2

AIR_19
Understand the priority of pneumatic systems for pack operation.
The APU bleed air has priority over _________ bleed air.
When the APU Bleed pb is selected on:
- The APU bleed valve opens if:
- APU N speed is greater than [______%]
- Altitude is less than _________ft. (climbing) or _________ ft. (descending),
- and no leak is detected in the APU or _________ side of the bleed system.
- The engine _________ and _________ valves close.
- The crossbleed valve opens if the crossbleed selector is in the _________ position.
VOL. II, 36.2.3.2
AIR_19
Understand the priority of pneumatic systems for pack operation.
The APU bleed air has priority over engine bleed air.
When the APU Bleed pb is selected on:
- The APU bleed valve opens if:
- APU N speed is greater than [95%]
- Altitude is less than 25,000 ft. (climbing) or 23,000 ft. (descending),
- and no leak is detected in the APU or left side of the bleed system.
- The engine bleed and HP valves close.
- The crossbleed valve opens if the crossbleed selector is in the AUTO position.
VOL. II, 36.2.3.2

AIR_20
Identify if high and/or low pressure ground supplied air is connected.
- The white ________ indication on the ______page is displayed when the aircraft is on the ground to indicate where ____ ground air enters the crossbleed duct.
- When ______ ground air is in use, the bleed air temperature and pressure indications on the ______ page display the temperature and pressure of the ______ air if the engine bleed valves are ______.
- There are no other indications that ______ ground air is in use.
- ______ sources may be used to supply low pressure (LP) conditioned air ______ to the mixing unit for aircraft heating and cooling.
- ______ low pressure connections on the bottom of the aircraft allow one or two ground air sources to be connected to the aircraft.
- There are no direct flight deck indications that __________ __________ air is in use.
VOL. II, 21.2.4.1
36.2.5

AIR_20
Identify if high and/or low pressure ground supplied air is connected.
- The white GND indication on the bleed page is displayed when the aircraft is on the ground to indicate where HP ground air enters the crossbleed duct.
- When HP ground air is in use, the bleed air temperature and pressure indications on the BLEED page display the temperature and pressure of the HP air if the engine bleed valves are closed.
- There are no other indications that HP ground air is in use.
- External sources may be used to supply low pressure (LP) conditioned air directly to the mixing unit for aircraft heating and cooling.
- Two low pressure connections on the bottom of the aircraft allow one or two ground air sources to be connected to the aircraft.
- There are no direct flight deck indications that ground conditioned air is in use.
VOL. II, 21.2.4.1
36.2.5

During flight how can you change pressurization controllers?
(a) cycle the LDG ELEV auto knob out of the auto position then back to
auto
(b) switching the cabin press mode sei pushbutton to MAN for at least 3 seconds then returning it to auto.
(c) cycle the cabin pressurization man V/S CTL switch
(b) switching the cabin press mode sei pushbutton to MAN for at least 3 seconds then returning it to auto.
During takeoff, when will the ram air inlet and outlet flaps close:
(a) As soon as the undercarriage is selected up
(b) When the thrust lever is at or above CL and wheel speed is at or above 70 kts
(c) When thrust levers are above idle and wheel speed is at or above 70kts
(b) When the thrust lever is at or above CL and wheel speed is at or above 70 kts
If Ram air is being supplied to the mixing unit during an emergency, what temperature will this ram air be?
(a) Ambient
(b) The temperature selected by the zone controller
(c) 20°
(a) Ambient
What function does the DITCHING Pb carry out:
(a) Closes the outflow valve, pack flow control valves, and the emergency ram air inlet only
(b) Closes the outflow valve, pack flow control valves, emergency ram air inlet and the avionics ventilation overboard valve only
(c) Closes the avionics ventilation overboard valve, the emergency ram air inlet, pack flow control valves only
(b) Closes the outflow valve, pack flow control valves, emergency ram air inlet and the avionics ventilation overboard valve only
The cargo vent AFT ISOL VALVES fault light indicates:
(a) Isolation valve has closed and the fan stopped
(b) Cargo smoke warning system is faulty
(c) Either inlet of outlet isolation valve is not in selected position
(c) Either inlet of outlet isolation valve is not in selected position


