Amino metabolism - AA III Flashcards
As a summary..
Which AAs are degraded to pyruvate?
- Trp → Ala
- Gly → Ser
- Cys
REMEMBER: pyruvate → OXA
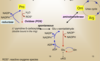
How can Ala be converted to pyruvate?
via ALAT = reversible transamination
α-KG + Ala → glu + pyruvate
What are the 2 pathways how Ser can be synthesized?
Where does it happen?
from
-
3-P-glycerate (intermediate of glycolysis)
→ in cytoplasm -
Gly by the action of Ser hydroxymethyl transferase
→ in mitochondrium
<u>NOTE:</u> SHMT catalyzes also reverse reaction, hence synthesis and degradation to another AA
How is Ser synthesized in the cytosol?
Where does it happen?
List its 3 steps.
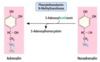
synthesized from 3-P-glycerate in cytosol
- 3-P-glycerate → 3-P-pyruvate
- …. → 3-P-Ser
- …. → Ser
Which enzyme catalyzes the first step of synthesis of Ser from 3-P-glycerate?
Reaction + structures.
P-glycerate dehydrogenase
3-P-glycerate + NAD+ → 3-P-pyruvate + NADH

Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of 3-P-pyruvate to eventually synthesize Ser?
Reaction + structures.
P-serine transaminase
transamination of 3-P-pyruvate, 3-P-Ser formed

3-P-pyruvate + Glu → 3-P-Ser + α-KG
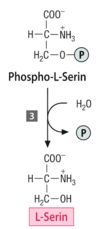
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of 3-P-Ser to synthesize Ser?
Reaction + structures.
P-Ser phosphatase
3P-Ser + H2O → Ser + Pi
What are the 4 mechanisms of degradation of Ser?
Products.
-
to pyruvate
- Ser-Thr dehydratase
- Ser-pyruvate aminotransferase
- to Cys: cystathione synthase/lyase:
- to Gly: Ser hydroxymethyl transferase
<u>NOTE:</u> SHMT catalyzes also reverse reaction, hence synthesis and degradation to another AA
How can Gly be synthesized?
Enzyme + reaction.
Where does it happen?
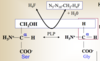
Ser hydroxymethyl transferase = SHMT
this isoenzyme in cytosol
Ser + H4F ⇔ CH2-H4F + Gly + H2O
NOTE: can be considered part of catabolizing pathways of Ser, or anabolizing pathway of Gly
What is the physiological role of Gly?
- inhibitory NT in NS
- used for purine synthesis
- conjugates, e.g. bile acids
- heme biosynthesis
Where are the isoenzymes of SHMT located?
Function.
- cytosolic SHMT: Ser → Gly
- mitochondrial SHMT: Gly → Ser
As a summary..
What is the importance of SHMT?
- synthesis of Gly from 3P-glycerate (through Ser)
- synthesis of Ser from Gly
- synthesis of methyl-group donor
What is the prosthetic group of SHTM?
PLP
How is the CH2-H4F that is necessary for the synthesis of Ser from Gly generated?
Which enzyme catalyzes this reaction?
Gly cleavage complex
degrades a second Gly
Gly + H4F + NAD+
→ HCO3- + NH4+ + CH2-H4F + NADH
What is the cause of nonketotic hyperglycinemia?
Consequences?
deficiency of Gly cleavage complex
→ mental deficiency, early death
Gly = inhibitory NT
Ser is pretty important for cell membranes.
Why?
can be used to form
- sphyngosine → incorporated into sphyngolipids
- ethanolamine
- choline
What is the biogenic amine of Ser?
Reaction + structures.
Function?
ethanolamine
Ser → ethanolamine + CO2
= second-most-abundant head group of phospholipids

As a summary…
Which AAs are converted to acetoacetate?
acetoacetate → acetyl CoA
- Lys
- Leu
- Phe → Tyr
- Trp
Which enzyme catalyzes the formation of choline?
Reaction + structures.
Function?
SAM dependent methylase
ethanolamine + 3 SAM → choline + 3 SAH
→ forms part of phospholipids

As a review..
How is Cys synthesized?
Which enzymes in its formation?
cystathione synthase/lyase
replace Ser-OH attached to HomoCys by -SH in 2 step reaction

What are the 2 degradational pathways of Cys?
What is the final product?
either degraded to
- 3-mercapto pyruvate, or
- sulfinyl pyruvate
→ eventually oxidized to pyruvate

Which enzymes are responsible for the formation of sulfinyl pyruvate?
Reaction steps + structures.
Which structures does it eventually form?
synthesized in 2 steps from Cys
- cysteine dioxygenase: Cys → Cys-sulfinate
- transamination:… → sulfinyl pyruvate
⇒ forms pyruvate + bisulfite

How is 3-mercapto pyruvate synthesized?
Which structures does it eventually form?
formed via transamination from Cys
⇒ -SH forms thiosulfite + pyruvate

How is sulfate formed?
Differentiate btw its 2 pathways.
originally derived from Cys
- 3-mercapto pyruvate → thiosulfite
- Cys sulfinate → sulfinyl-pyruvate → bisulfite
⇒ form sulfate