Amino metabolism - AA II Flashcards
What are the 6 final products of degredation of ALL amino acids?
Differentiate btw gluco- and ketogenic products.
glucogenic:
- pyruvate
- OXA
- fumarate
- succinyl CoA
- α-KG
ketogenic:
- acetyl CoA
What is folate?
A deficiency can lead to.. ?
Why is it especially important during pregnancy?
Structure.
vit B9 (folic acid)
symptoms similar to vit B12 deficiency: megaloblastic edema, CNS problems
⇒ early administration during pregnancy decr. risk for spina bifida

Which enzyme forms tetrahydrofolate from folate?
Reaction.
dihydrofolate reductase = DHFR
in 2 steps, each step requires 1 NADPH/H+
folate → dihydrofolate (H2F) → tetrahydrofolate (H4F)
⇒ active form of folate, can enter folate cycle
What is the function of tetrahydrofolate?
List the main steps of the folate cycle and its products.
tetrahydrofolate = methyl-group donor
stepwise receiving more hydrogen during folate cycle
- H4F + Trp/His → methenyl-H4F (CH-H4F)
- … + Ser/Gly → methylene-H4F (CH2-H4F)
- … → methyl-H4F (CH3-H4F)
- … → transfer of CH3- to HomoCys, restoring H4F

Which first intermediates are formed in step 1 of the folate cycle?
How are these products used?
H4F either reacts w/
- His → formimino-H4F, or
- Trp → formyl-H4F
⇒ can further be used for nucleotide synthesis, or continue in folate cycle
What happens to formimino-H4F and formyl-H4F to continue in the folate cycle?
- formimino-H4F gives off NH4+
- formyl-H4F gives off H2O
→ to form methenyl H4F (CH-H4F)
What happens with CH-H4F in the folate cycle?
How can its product be used further?
CH-H4F + NADPH + Ser/Gly
→ CH2-H4F + NADP+
(methenyl becomes methylene)
⇒ either used for dTMP synthesis, or continues further in folate cycle
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of CH2-H4F in the folate cycle?
Reaction.
methylene H4F reductase = MTHFR
- *CH2-H4F** + NADH →
- *CH3-H4F** + NAD+
(methylene to methyl)
MoTHereFuckeR
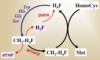
Draw the structures for
- Cys
- HomoCys
- Met
- Ser
- HomoSer

What is the function of the SAM cycle?
List the main products of all steps.
degradation of Met + activation of -CH3 groups
- Met → SAM
- … → SAH
- … → HomoCys
- last step = also last step of folate cycle, restores H4F and Met__

Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of Met in the SAM cycle?
Reaction.
Met adenosyl transferase
adenosyl-terminal of ATP transferred to -S of Met,
activation of -CH3 by formation of SAM
Met + ATP → PPi + Pi + S-adenosyl-Met (SAM)
Which group of enzymes use SAM as a substrate?
Reaction.
SAM dependent methylases
decarboxylation (energy rich -CH3) of SAM to form SAH
SAM + … → -CH3 + S-adenosyl-HomoCys (SAH)
Which enzyme catalyzes the conversion of SAH in the SAM cycle?
Reaction.
SAH hydrolase
hydrolysis
SAH + H2O → adenosine + HomoCys
Which enzyme catalyzes both, the last step of SAM and folate cycle?
Reaction.
HomoCys methyltransferase
remethylation of Met to start SAM cycle again
HomoCys + CH3-H4F + → Met + H4F
⇒ all original substrates reformed
What is another name for HomoCys methyltransferase?
What is its prosthetic group?
= Met synthase
→ prosthetic group: methylcobalamin (vit B12)
<u>NOTE:</u> also prosth. group of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
Describe the molecular effects of folate or vit B12 deficiency.
- ↑HomoCys, ↑adenosine in blood
- methyl-trap (↑methyl-H4F, ↓methylene-H4F)
- ↓ dUMP → decr. dTMP/purines levels/cell division
vit B12 def. also causes <u>methylmalonic aciduria</u> <em>(cf. own card)</em>

What are the 2 pathways that HomoCys can enter?
- SAM cycle (last step) → regeneration of Met and H4F
-
synthesis of Cys + α-ketobutyrate
→ eventually formation of succinyl-CoA
As a summary…
Which AAs are degraded to succinyl CoA?
- Ile
- Val
- Met
- Thr
Which enzymes are responsible for the formation of Cys from HomoCys?
Reactions.
How do you call the entire mechanism?
-
cystathionine synthase
HomoCys + Ser → cystathionine + H2O -
cystathionine lyase
cystathionine + H2O → Cys + α-ketobutyrate + NH4+
= transsulfuration
What is the prosthetic group fo cystathionine synthase?
PLP (vit B6)
What are the consequences of a cystathionine synthase deficiency?
no formation of cystathionine from HomoCys
→ ↑ HomoCys → hyperhomocystinemia
⇒ atherosclerosis, incr. risk of Alzheimer’s
Which AAs are converted to α-ketobutyrate?
- Met via HomoCys/cystathionine
- Thr by Ser-Thr dehydratase

What are the 2 mechanisms of Thr degradation?
Glucogenic or ketogenic?
-
Ser-Thr dehydratase (very low amount)
… → α-ketobutyrate → succinyl CoA (glucogenic) -
Thr aldolase
Thr → acetaldehyde + Gly (glucogenic/ketogenic)
… → acetyl-CoA
List the 3 steps that are necessary for degradation of α-ketobutyrate.
- α-ketobutyrate → proprionyl CoA
- … → D-methylmalonyl CoA
- via intermediate rearranged to succinyl CoA


