Adaptive humoral immunity Flashcards
is humoral immunity - adpative or innate?
Both!
innate- complement and cytokines
adpatice- antibody meidated specific immunity
protects agaisnt extracellular pathogens
what are BCRs
B cell recpeotrs- antibodies imbedde in there surface
plasma cells (B cells) secrete Antibodies whicha re a soluble form of BCR
Neutralisation, Opsonisation, complement activation
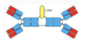
describe tbhe structure of antibodiees
light chain- one variable , one cosntant
heavy chain- one variable , multipe cosnatynt doamins (3 or 4)
2 identical light chians, 2 indeictla heavy gains
Varaibl;e region- Fab ragements
constnac- Fc grfament
what is the function of the Hinge region?
allows movement and therefore greater interactions with epitopes ( these are sites on antigen recognised by immune system)
describe the light chain of an Ig
1 variable and 1 contanrt domain
domain can either be K (kappa) or λ (lambda)
but same within one Ig
what are the 5 classes of immunogobluins - heavy chain determines the class
igM
IgD
IgG
IGA
IGE
Labell the following


name the hevay change for each of the immunoglobulin classses
γ (gamma; IgG)
α (alpha; IgA)
μ (mu; IgM)
ε (epsilon; IgE)
δ (delta; IgD)
which Igs have 3 constant regions and which have 4 and nohinge regions?
igG, igA, and IgD have 3 constant domains with hinge regions
igM and igE have 4 cosnatnt regions but no hinge region
which ig is secrted as a dimer
igA (also as a monomer)
which ig exists as a pentamer
igM
describe the role of IgG
4 subclasses (igG1-4)
named in there decreasing abudnance in serum
main coruclaotry ig fro secodnary immune response
can cross placenta- not found in secretions
describe igA
found in2 subclasses igA2 and IgA2
found in blood but also acts in defence of mucosal surfaces
secreted into gut and repsiroatyr and milk
cannot cross the placenta, bind to macrophages or mast cell receptors
J chain- dimer
describe igM
hgih mocleulcar weight
pentamer
due to size normally present in blood not tissues
main Ig in primary response
monomeric form- niave B cell surfacve
describe function of IgD
exists on surface of B cells (membrane cound)
BCR
first antivbodies to react to a new antigen before class switching
function unkwon

Describe IgE
invovled in defence agaisnt multicellular paraiste
allergic diseas-e asrthma
how do phagocytes bind to opsonised pathognes
phagocytes hae antibody Fc receptors-
what is VDJ and VJ random combination do?
we have multiple versions of variabel diveristy and joining gene segments
hevay chain- CDJ segements
ligh chain- VJ segments
used to geenrate diversity

what is the function of RAG?
recombination activign gene protein
binds th a random v segment and random segment and binds themtogether- pinches off the loop
induces a doubel stranded break in DNA
DJ recombination
RAG then binds to random V and new DJ section. - form another loop , Ds tbreak- DNA then repaied
VDJ reocmination- 10 million variabel combinations
this is repeasted for light chain but onyl chaisn V and J

how is diveristy during VDJ increased form 10 million (RAG)—-> 100 billion
Tdt ( terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase)
joins the VDJ messily
adding extra DNa bases- vriaable region differenet every time
Ds repair protein

what sydnrome kis caused by a mutation ins RAG
SCID- severe combine dimmunodeificneyc syndrome
where does CDJ reocmibation occur?
Ig light (VJ) heavy (CDJ)
TCR alpha (DJ) and beta (VDJ)
what is B cell tolerance
B cells exposed to antigens in the bone marrow - to see if they react tos elf antigens
if they react can reaarnagelight chain- receptor editing
25% do this- if they are still reactive theu are destpryed
if B cells are only exposed to antigens found in the bone marrow how do they have tolerance to antigens in the rest of the body?
broaldy antigens in bone marrow are the same as the antigne sene in lymhpatic tisse
because B cells are niaev onyl cirulate in lymphatic tissues then they shouldt react to any body tissues
if a B cell does encounter self antigen, peripherl mechanisms turn it off- Anergy
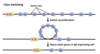
Describe B cell activation
B cells can recognise Antigens presenting by APC MHC type 2 but alos recognise antigens floating in the bodily fluids as they get tagged by complement
travel to in B area, lymphoid follciles- contaisn follicular dendiit cells tha display antigens to B cells

Describe the Germinal Centre in B cell activation
folliculaer denritic cell uptkaen ciruclating antigen- presnts
B cell engulfs the antigen and presents
meanwhoile a T cell has also be acivtaed by APC dendiritc cell
in the mollcile this T cell will meet its matching B cell presenting antigen.
B cell proliferates and replicates
Lymphoid follicke B cell rpaid prolifermaintion become germinal centres
this proliferation causes lymph nodes to swell during infection

describe the proccces that occur after B cell Activation by T cell in the germinal centre?
- somatic hypemutation- replication of B cell imperfect
- small errors in BCr- to get better fit to antigen
- best fit gets selected- Affifnity mautration
- B cell may do this many times
- Release of B cells
- Memeory B cells
- Palasma B cells
- also get Isotype class switching at same time as somatic hypemrutation

describe isotype class switching
occurs at the same time as somatic hypermutation
invovles swithcingthe FC constant region
in begiing typically IgM and soem IgD- can change to bets deal with infection at hand
cytokines help detemrine class swithcing
which 4 processes generate antibody diversity
combinatorial diveristy (VDJ)
junctional diveristy
affinity maturation
class switching
what are C exons
C- exons encode constanrt regions
hevay chain C gene segment are cluster of econs, encodes domains or a hinge region
different types determine class of antifodies
Cμ - IgM
Cδ- IgD
Cγ3, C γ1,Cγ2, Cγ4, - IgG
Cε - IgE
C α1,C α2- IgA
what is junctional diverity
formation of junctions between geen segemtns- nucleotides can be added or removed
junctional felxivbility- sligh variation in psotions of segm,ental joining when exons are spliced
Nucleotide addition- can be added by Tdt( terminal deoxynucleotidyl tranferase)
nucloetide deletion-
in combination with combinatroal and junctional diverity- 100 biullion different BCR receptros non functional in 2/3 - these b cells progenitors will nerv mature to B cells- maturity at the csot of many
what is affinity maturation/ somatic hypermutation? what is AID
process of making antibody a better fit for its antigen
when active B cells replicate they increase in number- express AID ( activation induced cytidine deaminase)- creates mutations in variable domain (VDJ)- somatic hypermutation
mutatiosn tightly regulateed
Ig wtih higher affinity as passively selected for

describe class swtichig? which enzyme is involved (hint same as enzyme involed in soamtic hypermutation)
first Ig BCr produced in naive B cell is IgM or IgD
differen calls of Ig have differen protperites better at differen functions
a single B cell cna produce different classes of Ig specific to same antigne
before each heavy chain C gene segment there is a DNa sequency called a switch site ( locus of class swithcing -rearrnagement occurs)
Activated By AID