שיעור 6-7 - מעברי פאזה מגנטיים Flashcards
(26 cards)
explain the difference between a ferromagnet and a paramagnet
what is the order parameter for the ferromagnet -> paramagnet phase transition?
for a ferromagnet M is not 0 for h = 0
for a paramagnet M = 0 for h = 0
thus, M is the order parameter for the phase transition between the two
Is dipole-dipole interactions the source of the interaction between spins?
No, this type of interacton is too weak to explain the spin interaction
the actual source for it is the exchange interaction.
Write the hamiltonian of the non interacting spins model
examine it for the limits of very small and very large tempertures
find the average magnetization in this model and explain why it cant be used to describe ferromagnetism

Starting with the hamiltonian for non interacting spins, make the Weiss correction to the magnetic field and derive the value of M in this model. Use it to find the curie temperture, which is the critical temperture of the ferromagent-paramagnet phase transition

in the weiss model, we take heff = h+ C<m></m>
how does C scale with system size

starting with the Heisenberg model, explain the assumption we have to make to get the Ising model.

which other model is the Ising model identical to? explain

examine the Ising model for h = 0 and J > 0 (ferromagnet) and J < 0 (anti-ferromagnet)
what can we derive from it regarding the order parameter of the anti-ferromagnet?

you are a theoretician who is supposed to model a certain magnetic transition. you found a model which has M != 0 at zero temperture, and M = 0 at infinite temperture. Does this model have a phase transition?

name the two symmetries in the Ising hamiltonian. explain the first
שתי הסימטריות הן סימטריה להיפוך בזמן וסימטריית
sub lattice

הסבר מדוע אין התייחסות בקורס לאפקטים קוונטיים

using mean field theory, find the Curie tempertue

analize the Weiss model in both low and high temperture limits, indicate the phase transitions that occure in the model

draw the h-T curve for a magnetic system, and the equivilant P-T curve of the liquid-gas transition. draw h-M curve for T=0, what is the order of this phase transition
transition at h=0 t=0 is first order, as there is a jump in M
transition at Tc is cont’

explain the meaning of a universality class

what are the critical exponents, define alpha beta gamma and delta
critical exponents define the behaviour of phisical properties around the critical point

explain the similarities between the ising model and the lattice gas model. why do they have the same critical exponents?
they have the same critical exponents since they are essentialy the same model (the hamiltoninan is the same)

write down the spatial (or spin-spin) correlation function. can it be used to mesure the correlation between spins?
define long range order
and it cannot be used to mesure correlation. since it is not 0 for very large distances.
if G is not 0 at infinity we say that the system has long range order. in other words there is an ordered phase. without long-range order, no phase transitions can occure
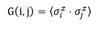
in what cases is long range order a stable state of a system. what can we deduce from this?
according to Mermin Wagner Theorem, long range order is unstable for systems with a continious symmetry and dimensions <= 2. as such there can be no phase tranistions in such sytems
define lower and upper critical dimension
lower critical dimension - the last dimension for which no phase transition occurs in a system
upper critical dimension - the first dimension for which a phase transition occurs in a system
think of the XY spin model, where the spin vector can move in the x-y plane. in this model the interaction between spins is isotropic, meaning there is rotation symmetry. what is the lower critical dimension of this model
since the symmetry of this model is continious, according to Mermin-Wagner therorem the lower critical dimension for this system is at least 2.
write the expression for isothermal susceptibility.
what is the fluctuation-dissipation relation related to it

חומר פרואלקטרי הוא חומר בעל פולריזציה חשמלית שניתנת להיפוך על ידי שדה חשמלי חיצוני
נשים לב כי כאמור הפולריזציה שונה מאפס גם כאשר השדה החשמלי החיצוני הוא אפס (בדומה לפרומגנט). למה פרופורציונלית הסספטביליות האיזותרמית של חומר זה

explain the failing of mean field theorem
how can it be corrected
the theorem includes an overestimation of universality, meaning the critical exponents recieved from it are independant of dimension (which isnt the case in reality). if one assumes that all spins are nearest neighbours of each other, the main field theorem is exact.





