3.2.1.4 - Structure of Prokaryotic Cells Flashcards
Identify the missing label.

Attachment protein

The nucleic acid in a virus is enclosed within a protein coat called a…
capsid
Do prokaryotes have a nucelus?
No
Most of the success of bacteria is down to…
their small size
Plasmids are useful to scientists when they perform
genetic engineering e.g. transfer of human insulin gene to bacterial cells.
Sometimes a virus will have an additional layer of lipid called a..
lipid envelope
How do bacteria store energy?
- Glycogen granules
- Oil droplets
Describe the structure of the genetic information of a prokaryotic cell.
- Main circular strand of DNA not in a nucleus
- Smaller circular pieces of DNA (plasmids)
What is the function of a plasmid?
Small, self replicating circles of DNA that give bbacteria resistance to antibiotics.
Attachment proteins can be found where on a virus?
- In the lipid envelope (if the virus has one)
- In the capsid (if the virus does not have a lipid envelope.
What are the main differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
- Eukaryotic cells are larger
- The DNA of Eukaryotic cells is found in a nucleus.
- Eukaryotic cells have organelles with membranes (mitochondria/chloroplasts etc.)
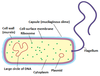
Identify the missing label.

Large circle of DNA

What is meant by a membrane bound organelle?
An organelles that has its own phospholipid bilayer.
Identify the missing label.

Lipid envelope

Identify the membrane bound organelles of a eukaroytic cell that would not be present in a prokaryotic cell.
- Mitochondrion
- Chloroplasts
- Nucleus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Vacuoles
- Lysosomes
Identify the missing label.

Genetic material (RNA)

Identify the missing label.

Cell-surface membrane

Identify the missing label.

Capsule

Identify the missing label.

Reverse transcriptase enzyme

Identify the missing label.

Cell wall (containing murein)

The outer layer of mucilagionus slime around a bacterial cell is called the…
capsule
Do prokaryotic cells contain membrane-bounded organelles e.g. mitochondrion?
No
How small are bacteria?
0.1-10 µm
Are viruses generally bigger or smaller than bacteria?
smaller