3 - Zill - Lower Extremity Flashcards
Innominate Bone
Pelvis
Attachment of lower extremity
Hallux
Big Toe
Fibula and Tibia
Fibula - Lateral, not part of knee
Tibia - Medial, shin, lower part of knee
Thigh vs Leg
Thigh - upper leg around femur
Leg - lower leg around tibia and fibula
Ankle
Functionally two joints
1 between tibia, fibula, and talus
1 between talus and other foot bones
How do the arms and legs develop in utero?
Homology; they rotate in different directions during future development
What is the orientation of hands and feet in utero?
Homologous orientation, face medially
Upper exremities rotate laterally
Lower extremities rotate medially
Dermatomes of Toes
L4 Big Toe
L5 Middle Toes
S1 Little Toe
Flexion and Extension of Hip and Knee
Hip - Flex Anterior, Extension Posterior
Knee - Flex Posterior, Extension Anterior
Abduction v Adduction
Abduction - Move away from midline
Adduction - Move toward midline
Movement of the Foot
Flexion/Extension
Inversion/Eversion
Dorsiflexion = Lift foot from ground
Plantar Flexion = Push on gas pedal
- -
Inversion = Sole faces medially (most common)
Eversion = Sole faces laterally (less common)
Three Major Bones of Pelvis
Socket?
Midline between pubic bones
Ilium (“wing”)
Ischium (sit-bone)
Pubis (front of pelvis)
- -
Socket = Acetabulum
- -
Pubic Symphysis
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
- -
Pubic Tubercle
- -
Obturator Foramen
Palpable anterior projection for muscle attachment
- -
Palpable attachment for Inguinal Ligament
- -
Large opening made of ischium and pubis, covered by Obturator membrane for muscle attachment
Ischial Tuberosity
Bony prominence on posterior part of ischium; “sit bones”
What ligaments prevent the sacrum from rotating due to weight transmitted down vertebral column?
Sacrotuberous and Sacrospinous ligaments
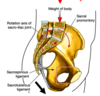
Where do muscles attach on the femur?
What area of the femur is subject to fractur?
Muscles attach to trochanters
- -
Neck - narrow region is subject to fracture
- -
Patella
Sesamoid bone, located in tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle
Patella can appear bipartite or tripartite
Can misinterpret as facture on x-ray
Palpable lower features of Tibia and Fibula
What do these form?
Palpable upper feature of the fibula?
Medial malleolus (tibia)
Lateral malleolus (fibula)
- -
Form joint for dorsiflexion, plantar flexion
- -
Head, important for Foot Drop (nerve damage)


What bones if the foot an arch?
Why is this important?
Talus sits above the Calcaneus
Arch gives spring-like
Great Saphenous Vein
Superficial vein that courses on whole medial side of lower extremity
Starts at dorsal venous arch of foot
Ascends anterior to Medial Malleolus
Small Saphenous Vein
Superficial vein that drains from lateral side of Dorsal Venous Arch, found on posterior side of Lateral Malleolus
Perforating Veins
How does fluid travel in these?
Connect Superficial Veins to Deep Veins; have valves
- -
Superficial to Deep (ONE WAY)
How is fluid pushed in veins of the lower extremities?
Valves prevent flow being pooled from gravity and muscles constricting push blood up


