3 - Scales, Chromatic, Modes, Pentatonic & More Flashcards
Use this deck to learn Scales (Major, minor, Chromatic, Modes, Pentatonic, Blues, Octatonic and Whole Tone), Tempo Terms, Simple Intervals, Rests, and Dynamic and Articulation Placement. Audio is included to supplement your learning. Master Your Musicianship Skills - Complete Lesson 3 of the matching Ultimate Music Theory Advanced Workbook to enhance your music theory training. UltimateMusicTheory.com
Name the Major scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

G flat Major scale
Supertonic

Name the Major scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

C flat Major scale
Submediant

Name the Major scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

A Major scale
Supertonic

Name the Major scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

C Major scale
Subdominant

Name the Major scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

A flat Major scale
Dominant

Name the Major scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

F Major scale
Submediant

Name the Major scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

D flat Major scale
Mediant

Name the Major scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

F sharp Major scale
Dominant

Name the Major scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

G Major scale
Mediant

Name the mode that begins on the Supertonic degree of a Major scale.
Dorian mode
Name the mode that begins on the Tonic degree of a Major scale.
Ionian mode
Name the mode that begins on the Subdominant degree of a Major scale.
Lydian mode
Name the mode that begins on the Submediant degree of a Major scale.
Aeolian mode
Name the mode that begins on the Leading note degree of a Major scale.
Locrian mode
Name the mode that begins on the Mediant degree of a Major scale.
Phrygian mode
Name the mode that begins on the Dominant degree of a Major scale.
Mixolydian mode
The Dorian mode begins on which Major scale degree?
Supertonic
The Lydian mode begins on which Major scale degree?
Subdominant
The Aeolian mode begins on which Major scale degree?
Submediant
The Phrygian mode begins on which Major scale degree?
Mediant
The Mixolydian mode begins on which Major scale degree?
Dominant
The Ionian mode begins on which Major scale degree?
Tonic
The Locrian mode begins on which Major scale degree?
Leading note
Name the mode.

Dorian mode starting on B flat

Name the mode.

Mixolydian mode starting on E flat

Name the mode.

Phrygian mode starting on C sharp

Name the mode.

Aeolian mode starting on F sharp

Name the mode.

Lydian mode starting on E flat

Name the mode.

Dorian mode starting on C sharp

Name the mode.

Mixolydian mode starting on F sharp

Name the mode.

Phrygian mode starting on E flat

Name the mode.

Aeolian mode starting on A flat

Name the mode.

Lydian mode starting on F

Name the mode.

Phrygian mode starting on B flat

Name the mode.

Lydian mode starting on C

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

b minor melodic scale
Tonic

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

e minor melodic scale
Leading note

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

g sharp minor harmonic scale
Submediant

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

e minor natural scale
Tonic

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

a flat minor natural or melodic scale
Subtonic

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

c sharp minor melodic scale
Leading note

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

a minor natural scale
Subdominant

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

c sharp minor natural or melodic scale
Submediant

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

g sharp minor natural or melodic scale
Subdominant

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

d minor melodic scale
Submediant

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

f minor harmonic scale
Mediant

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

a minor natural scale
Supertonic

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

d sharp minor natural or melodic scale
Subtonic

Name the minor scale. Identify the technical degree name of the first note.

f sharp minor natural or melodic scale
Subdominant

True or False. A chromatic scale will use 13 semitones (half steps) plus the upper Tonic for a total of 14 notes.
False. Standard Chromatic scale notation uses 12 semitones (half steps) plus the upper Tonic for a total of 13 notes.
True or False. A chromatic scale will be written using no letter name more than twice in a row.
TRUE
True or False. When writing a chromatic scale, the scale can begin and end on different notes.
False. A chromatic scale must begin and end on the same letter name and cannot be changed enharmonically.
Is the notation for this chromatic scale starting on E Correct or Incorrect?

Incorrect. The letter name G is used 3 times in a row.

Is the notation for this chromatic scale starting on G flat Correct or Incorrect?

Incorrect. The chromatic scale starts on G flat but ends on F sharp.

Is the notation for this chromatic scale starting on A sharp Correct or Incorrect?

Correct

Is the notation for this chromatic scale starting on G flat Correct or Incorrect?

Correct

Is the notation for this chromatic scale starting on E Correct or Incorrect?

Correct

Is the notation for this chromatic scale starting on A sharp Correct or Incorrect?

Incorrect. The upper Tonic A is used 3 times in a row.

True or False. An octatonic scale consists of 8 notes plus the upper Tonic (total of 9 notes).
TRUE
True or False. An octatonic scale is formed by using consecutive whole tones (whole steps).
False. An octatonic scale is formed by alternating whole tones (whole steps) and semitones (half steps).
True or False. In an octatonic scale, the Tonic note may be written as its enharmonic equivalent.
False. The Tonic note must remain the same and may not be written as its enharmonic equivalent.
True or False. An octatonic scale can start with a whole tone (whole step) OR a semitone (half step).
TRUE
Is the notation for this octatonic scale starting on C Correct or Incorrect?

Incorrect. A letter name cannot be used 3 times in a row. The Correct notation is

Is the notation for this octatonic scale starting on F Correct or Incorrect?

Correct

Is the notation for this octatonic scale starting on D flat Correct or Incorrect?

Incorrect. The lower and upper Tonic notes must be the same. The Correct notation is

Is the notation for this octatonic scale starting on F sharp Correct or Incorrect?

Correct

What is the distance between the first 2 notes of this octatonic scale starting on E flat?

whole tone (whole step)

What is the distance between the first 2 notes of this octatonic scale starting on E flat?

semitone (half step)

True or False. A whole tone scale consists of 6 notes plus the upper Tonic (total of 7 notes).
TRUE
True or False. A whole tone scale can be written using both sharps and flats.
False. A whole tone scale is written using sharps or flats (not both).
True or False. A whole tone scale can use different notes ascending and descending.
False. A whole tone scale uses the same notes ascending and descending.
True or False. A whole tone scale omits one letter name, creating one interval of a diminished 3rd.
TRUE
True or False. In a whole tone scale, the upper Tonic note may be written as its enharmonic equivalent.
False. The upper Tonic note must remain the same and may not be written as its enharmonic equivalent.
Is the notation for this whole tone scale starting on C Correct or Incorrect?

Incorrect. A whole tone scale cannot be written using sharps and flats. The Correct notation is

Is the notation for this whole tone scale starting on D flat Correct or Incorrect?

Correct

Is the notation for this whole tone scale starting on E flat Correct or Incorrect?

Incorrect. The lower and upper Tonic notes must be the same. The Correct notation is

Is the notation for this whole tone scale starting on F Correct or Incorrect?

Correct

Is the notation for this whole tone scale starting on F sharp Correct or Incorrect?

Correct

Identify the type of scale or mode.

Major scale (Ionian mode)

Identify the type of scale or mode.

natural minor scale (Aeolian mode)

Identify the type of scale or mode.

chromatic scale

Identify the type of scale or mode.

Dorian mode

Identify the type of scale or mode.

Major pentatonic scale

Identify the type of scale or mode.

Lydian mode

Identify the type of scale or mode.

blues scale

Identify the type of scale or mode.

whole tone scale

Identify the type of scale or mode.

minor pentatonic scale

Identify the type of scale or mode.

Locrian mode

Identify the type of scale or mode.

harmonic minor scale

Identify the type of scale or mode.

octatonic scale

Identify the type of scale or mode.

melodic minor scale

Identify the type of scale or mode.

Mixolydian mode

Identify the type of scale or mode.

chromatic scale

Identify the type of scale or mode.

Phrygian mode

Identify the type of scale or mode.

blues scale

Identify the type of scale or mode.

whole tone scale

True or False. An accent is written closest to the notehead and away from the stem.
TRUE
True or False. A staccato dot is written closest to the notehead and away from the stem.
TRUE
True or False. A tenuto is always written above the staff.
False. A tenuto is written closest to the notehead and away from the stem.
True or False. A Fermata is always written above a single staff.
TRUE
True or False. Dynamics are written below a single Bass Clef.
False. Dynamics are written above a single Bass Clef.
True or False. Dynamics are written above a single Alto Clef.
False. Dynamics are written below a single Alto Clef.
True or False. Dynamics are written below a single Tenor Clef.
TRUE
True or False. Dynamics are written below a single Treble Clef.
TRUE
Explain the Italian term adagio.
adagio - a slow tempo (slower than andante, but not as slow as largo)
Explain the Italian term larghetto.
larghetto - not as slow as largo
Explain the Italian term allegretto.
allegretto - fairly fast (a little slower than allegro)
Explain the Italian term largo.
largo - very slow
Explain the Italian term allegro.
allegro - fast
Explain the Italian term lento.
lento - slow
Explain the Italian term andante.
andante - moderately slow, at a walking pace
Explain the Italian term moderato.
moderato - at a moderate tempo
Explain the Italian term andantino.
andantino - a little faster than andante
Explain the Italian term presto.
presto - very fast
Explain the Italian term comodo.
comodo - at a comfortable, easy tempo
Explain the Italian term prestissimo.
prestissimo - as fast as possible
Explain the Italian term con moto.
con moto - with movement
Explain the Italian term stringendo.
stringendo - pressing, becoming faster
Explain the Italian term grave.
grave - slow and solemn
Explain the Italian term vivace.
vivace - lively, brisk
Name the Italian term meaning - a slow tempo (slower than andante, but not as slow as largo).
adagio
Name the Italian term meaning - not as slow as largo.
larghetto
Name the Italian term meaning - fairly fast (a little slower than allegro).
allegretto
Name the Italian term meaning - very slow.
largo
Name the Italian term meaning - fast.
allegro
Name the Italian term meaning - slow.
lento
Name the Italian term meaning - moderately slow, at a walking pace.
andante
Name the Italian term meaning - at a moderate tempo.
moderato
Name the Italian term meaning - a little faster than andante.
andantino
Name the Italian term meaning - very fast.
presto
Name the Italian term meaning - at a comfortable, easy tempo.
comodo
Name the Italian term meaning - as fast as possible.
prestissimo
Name the Italian term meaning - with movement.
con moto
Name the Italian term meaning - pressing, becoming faster.
stringendo
Name the Italian term meaning - slow and solemn.
grave
Name the Italian term meaning - lively, brisk.
vivace
Name the notes of the interval (lower note first). Name the interval.

C to D double flat
diminished 2

Name the notes of the interval (lower note first). Name the interval.

E flat to E natural
Augmented 1

Name the notes of the interval (lower note first). Name the interval.

F sharp to D natural
minor 6

Name the notes of the interval (lower note first). Name the interval.

B flat to F sharp
Augmented 5

Name the notes of the interval (lower note first). Name the interval.

B flat to C sharp
Augmented 2

Name the notes of the interval (lower note first). Name the interval.

A to G flat
diminished 7

Name the notes of the interval (lower note first). Name the interval.

C to C
Perfect 1

Name the notes of the interval (lower note first). Name the interval.

G flat to C natural
Augmented 4

Name the notes of the interval (lower note first). Name the interval.

B flat to E flat
Perfect 4

Name the missing rest.

thirty-second rest

Name the missing rest.

dotted eighth rest

Name the missing rest.

eighth rest

Name the missing rest.

thirty-second rest

Name the missing rest.

eighth rest

Name the missing rest.

dotted quarter rest

Name the missing rest.

sixteenth rest

Name the missing rest.

sixteenth rest

Name the missing rest.

sixteenth rest

Name the missing rest.

quarter rest

Name the missing rest.

thirty-second rest

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Alto Clef
Augmented 3

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Bass Clef
Perfect 1

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Alto Clef
minor 2

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Treble Clef
diminished 4

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Alto Clef
diminished 6

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Alto Clef
Perfect 4

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Tenor Clef
Augmented 3

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Alto Clef
Perfect 1

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Tenor Clef
Major 6

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Bass Clef
minor 2

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Alto Clef
minor 7
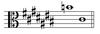
Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Tenor Clef
minor 7

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Treble Clef
Augmented 5

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Tenor Clef
diminished 3

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Treble Clef
Augmented 4

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Tenor Clef
Major 6

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Alto Clef
minor 3

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Bass Clef
minor 6

Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Treble Clef
Augmented 3
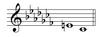
Identify the Clef. Name the interval.

Bass Clef
diminished 3



