242/243 - Intro to CBC, Approach to Anemias, Anemia CBL Flashcards
RBC characteristic associated with autoimmune hemolysis
Spherocyte (Dark small RBC with no central pallor)

What is the next diagnostic step when RBC agglutination is found on a blood smear?
Warm up the sample, look again
(And probably run labs again to get accurate values for RBC count, MCV)
What could result in a falsely high RBC count? (2)
Marked leukocytosis (Leukocytosis = increased WBCs, so WBCs contribute more than expected)
Giant platelets (Platelets counted as RBCs)

Describe the RBC morphology in iron deficiency anemia
Microcytic, hypochromic anemia

What shape will RBCs be if there is excess RBC membrane relative to the its volume?
Target cells
- Macro target cells: liver disease*
- Micro target cells: Hemoglobinopathy (thalassemia, HbgE, HgbC)*

What is the finding indicated by the arrows?
What is the DDx? (3)

Spherocytes
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Burns
RBC characteristic associated with hereditary elliptocytosis
Ovalocyte (also called elliptocytes)
Hereditary elliptocytosis = caused by mutations in gene encoding for RBC membrane protein, usually assymptomatic
Ovalocytes also associated with B12/folate deficiency, iron deficiency, thalesemia, and myelofibrosis.

Are symptoms of orthostatic hypotension, headache, and tachycardia more likely with acute or chronic anemia?
Acute
No time for compensatory mechanisms to develop -> more symptoms
A patient with sickle cell disease has this finding: Howell-Jolly Body
What does it indicate?
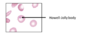
Splenic failure/Asplenia
Howell Jolly bodies have small remnants of DNA in the periphery of the cell –> means that the spleen isn’t functioning normally
List 4 clinical scenarios in which you would expect to see increased numbers of immature RBCs on a peripheral blood smear
- Newborns (<5 days old)
- Brisk hemolysis
- Myelodysplasia (hypercellularity and dysplasia of the bone marrow)
- Extramedullary hematopoiesis (occuring outside of the medulla of the bone b/c can’t occur normally in the bone)
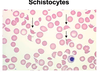
Intravascular hemolysis will cause red blood cells to be what shape?
Schistocytes
(red blood cell fragments)
What could result in a falsely low RBC count? (2)
RBC agglutination (Multiple RBCs counted as one)
Microcytosis (RBCs too small to be counted)
What does mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) measure?
The amount of hemoglobin in each RBC
Vs MCHC, which measures hemoglobin concentration in a given volume of packed RBCs
What does mean corpuscular Hb concentration (MCHC) measure?
Hemoglobin concentration in a given volume of packed RBCs
Vs. MCH, which measures amt of hemoglobin per RBC
List 3 CBC abnormalities present in sickle cell anemia
Reticulocytes are high
Leukocytosis (increased WBC)
RBCs will be normocytic, normochromic
Thank you @Tyler Jacobson and Emily Waples!
What could cause a falsely low platelet count? (3)
- Clotted sample (platelets are trapped in the blood clots)
- Platelet clumping (can’t be counted as individual platelets)
- Frequent giant platelets (giant platelets are counted as WBC or RBC b/c of their large size)
What does MCV measure?
Average red blood cell size (volume)
List 6 clinical scenarios that would cause RBCs to turn into “spur cells” (acanthocytes)
Acanthocytes = thorny, irregular cytoplasmic projections of varying length and width

- Liver disease
- Abetalipoproteinemia (deficiency in apolipoproteins due to MTTP gene mutation)
- Vitamin E deficiency
- Hypothyroidism
- Post-splenectomy
- Anorexia/Nutritional deficiency
What is the finding indicated by the arrows?
What is the DDx? (2)

Schistocytes
- Mechanical shear
- Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia (MAHA)
- microthrombi plug small vessels –> RBCs are sheared as they pass through the small blood vessels
- caused by:
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura (TTP)
- HELLP Syndrome
What could cause falsely high hemoglobin? (4)
Anything that increases turbidity of the sample:
Hyperlipidemia
Hyperbilirubinemia
High protein
Marked leukocytosis
Hemoglobin measured spectrophotometrically; anything that makes the sample cloudier = less light = interpreted as more hemoglobin
What does hematocrit (HCT) measure?
Volume of RBCs / blood volume
(Basically, the percentage of blood made up by the actual cells)
How will the hemoglobin/oxygen dissociation curve change as a result of anemia?
Right shift
- Via increased 2,3 bisphosphoglycerate (decreases affinity)
- Allows existing RBCs to offload more oxygen to tissues to try to meet oxygen demands
2,3 BPG is the same thing as 2,3 DPG bc why not ¯_(ツ)_/¯

RBC characteristic associated with myelofibrosis
Myelofibrosis = Myeloproliferative neoplasm leading to bone marrow insufficiency, extramedullary hematopoiesis, and splenomegaly.
Teardrop cell (dacryocytes)

What defines anemia?
Decreased number of circulating red blood cells

RBC characteristic associated with microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA)
Schistocytes

What is the morphology finding indicated by the arrows?
What is the DDx? (4)

Hypochromic, microcytic, increased RDW (size variation)
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Thalassemia
- Lead poisoning
- Anemia of chronic disease
What is the MOA of RBC agglutination?
IgM antibodies develop against RBCs
- One IgM antibody can bind 5 RBCs -> Clumping

RBC characteristic associated with G6PD deficiency
Bite cell

(G6PD causes Heinz body hemolysis, results in bite cells)
List 4 compensatory mechanisms for anemia
- Increased cardiac output
- Tachycardia
- Altered blood flow
- Maintain O2 delivery to most important organs
- Increased EPO
- Increased 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
- Causes RBC to have less affinity for O2
- -> Right shift, allows more O2 offloading to tissues per RBC

When is splenectomy indicated in sickle cell disease?
1 or more episodes of hyper-splenism (overactive spleen)
How do bite cells form?
- Heinz bodies (inclusion bodies which contain denatured Hb) form in cells suceptible to oxidative damage
- When the RBCs try to filter through the basement membrane, Heinz bodies get stuck
- The rest of the cell moves on, leaving a “bite” where the Heinz body got left behind

What does red cell distribution width (RDW) measure?
Degree of variation of RBC size
Lots of variation = high RDW
RBC characteristic associated with iron deficiency anemia
Hypochromic, microcytic
May see ovalocytes
Also associated with thalassemia

What could cause falsely high MCV? (3)
- RBC agglutination
- doublet erythrocytes are counted as one and larger clumps are not counted as RBCs at all –> decrease in red cell count and increase in MCV
- Osmotic abnormalities (Hyperglycemia, hypernatremia)
- in hyperglycemia, RBCs are transiently hypertonic –> swollen cells –> elevated MCV
- More young RBCs
MCV = volume of pack RBCs / red cell count
List 3 components of the initial laboratory evaluation for anemia
CBC
Reticulocyte count
Peripheral blood smear
What are reticulocytes?
slightly immature RBCs
- larger than mature RBCs and have no central pallor
- spend 3 days in bone marrow, then 1 day in peripheral circulation
What does reticulocyte count tell you about RBC production during anemia?
high reticulocyte count = adequate marrow response
low reticulocyte count = inadequate marrow response (aplastic anemia)
Explain physiologic pathway of increased RBC production via compensation for anemia.
- decreased RBCs
- low O2 sensed by renal proximal tubule
- incresed hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) production
- increased EPO production
- stimulation of erythropoetin
- increased RBC production
- increased O2 sensed by kidney
- negative feedback on EPO production
What are echinocytes (Burr cells) ?
abnormal cells that have smooth, rounded, and evenly spaced cytoplasmic projections (smaller than projections of acanthocytes)
seen in Vit E deficiency, hypothyroidism, post-splenectomy, liver disease, abetalipoproteinemia, and chronic kidney disease
can also be present on the slide just due to artifact
What is pernicious anemia?
autoimmune disease due to antibodies against intrinsic factor –> leads to Vit B12 deficiency
If RBC parameters are abnormal, what is the next step?
look at peripheral smear!
What are the components of blood, their order, and their percentage breakdown?
Plasma = 55%
WBC + platelet = very thin later btwn plasma and RBC
RBC = 45%
What is the rule of 3’s?
RBCs x 3 should equal hemglobin
hemoglobin x 3 should equal hematocrit
What is a “Rouleaux formation”?
RBCs that are on top of each other on blood smear that look like a stack of coins due to increased plasma proteins

What are the 4 types of microangiopathic hemolytic anemias?
-
Disseminated intravascular hemolysis (DIC)
- intravascular activation of the coagulation cascade leading to intravascular deposition of fibrin thrombi
-
thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
- pentad of symptoms: hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal failure, fever, neurologic symptom
- due to decreased ADAMTS13, which cleaves vWF ==> resuts in high molecular vWF
-
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)
- caused by e coli infection
- triad of symptoms: hemolytic anemia, acute renal failure, thrombocytopenia
- HELLP syndrome


