237/239 - Pathology of the Prostate, Prostate Cancer Flashcards
According to the AUA, who should be screened for prostate cancer?
What is the appropriate interval?
People of average risk 55-69 years old
People with increased risk 40-55 years old
Every 2+ years “may be preferred” over annual
(This is a shared-decision making process)
- Don’t screen <40 years or average risk 40-55 years
- Don’t screen 70+, unless life expectancy >10 years
How do we enhance the accuracy of PSA testing?
Do advanced imaging (MRI) after elevated PSA
Helps determine whether biopsy is needed, and increases accuracy
(we know what to aim for)
What is the most common type of prostate cancer?
Adenocarcinoma
What is the mainstay of therapy for patinets with metastatic, castrate-sensitive prostate cancer?
Androgen deprivation therapy
- Anti-androgens
- GnRH antagonist or continuous agonist
- Tesosterone synthesis inhibitor
- Surgical castration
Maybe add bone protective therapy or chermohormonal therapy
Which cell type will be notably absent from a prostate adenocarcinoma?
Basal cells

Where in the prostate do most prostate cancers arise?
Peripheral zone
(Close to the capsule)
List 4 non-adenocarcinoma types of prostate cancer
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Ductal adenocarcinoma
- Small cell carcinoma
- Primary urothelial carcinoma of the prostate
- Derived from urothelium of the prosatatic urethra
- This is technically not a type of prostate cancer
What are the management options for organ-confined prostate cancer?
- Prostatectomy (robot-assisted or orpen)
- External beam radiotherapy
- Brachytherapy
- Cryoablation
- High-intensity focused ultrasound
- MRI-guided laser ablation
Basically, do not need to do chemotherapy, may not need to take out the whole prostate
List 7 risk factors for prostate cancer
- Old age
- Family hx
- African American ethnicity
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Obesity
- Chronic inflammation - IBD
Prostate cancer= cancer most commonly associated with aging
What is the most common method of detection for prostate cancer?
Elevated serum PSA
How do we screen for prostate cancer?
PSA or digital rectal exam
PSA is not specific for prostate cancer
When prostate caner metastasizes to the bone, what changes will occur?
Increased osteoblastic activity
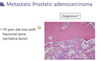
-> Thick trabecula
What is the most prevalent cancer diagnosis in men?
Prostate cancer
Is PSA a tumor marker?
No!
Will be elevated in prostate cancer
BUT can also be elevated in other conditions
Must confirm prostate cancer with tumor markers, pathologic microscipic features
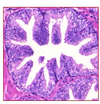
What are the histologic features of prostate adenocarcinoma?
Small glands with an infiltrating pattern
Cells will have prominent nucleoli
No basal cells - they have been lost :(
Staining for basal cells will be negative

AMACR is a tumor marker that will be positive in which cancer cells?
Prostate
AMACR is an enzyme involved in beta-oxidation of branched-chain fatty acids
What is the treatment for prostate cancer that is “interemediate risk” or higher?
Radical prostatectomy

What is the frequency of hereditary prostate cancer?
15%
What is the precursor lesion for prostate cancer?
High-grade prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia
A non-invasive neoplastic lesion, but we don’t call it carcinoma in situ
Name a transmembrane glycoprotein that is expressed in 95% of all prostate cancer specimens
PSMa
Irritable bowel disease is associated with increased risk of which GU cancer?
Prostate cancer
What system is used to grade prostate cancer?
Gleason score
I would recommend using sources outside of this deck if you want to get cozy with the Gleason grading system

Which prostate cancer patients are candidates for surveillence?
Older men with low volume tumors that are Gleason 6 or less and low PSA


