200/201/220/221 - Anatomy of Abdominal Wall, Pelvis, Perineum I, II, III Flashcards
How do the upper rectus sheath and the lower rectus sheath differ?
-
Upper sheath:
- All 3 aponeuroses envelop each rectus muscle
-
Lower sheath
- All 3 aponeuroses pass anterior to all the muscles
- The posterior sheath terminates abruptly at the arcuate line

The transversus abdominis contributes to the [layer of covering of the spermatic cord]
The transversus abdominis contributes to NONE of the layers covering the spermatic cord

The splanchnopleure gives rise to the [superficial/deep] body wall
The somatopleure gives rise to the [superficial/deep] body wall
The splanchnopleure gives rise to the deep body wall
The somatopleure gives rise to the superficial body wall
The [layer of the body wall] contributes to the internal spermatic fascia and deep inguinal ring
The Transversalis Fascia contributes to the internal spermatic fascia and deep inguinal ring

In females, the gubernaculum persists as which two structure?
Ovarian ligamnet
Round ligament of the uterus

What is contained in the superficial pouch?
(In general, not specific structures)
External genital organs
- Penis
- Clitoris (body and crura)

The [layer of the body wall] contributes to the cremaster muscle
The internal oblique muscle contributes to the cremaster muscle
Which muscle maintains constant muscle tone to bend the rectum and relaxes to allow defecation?
Puborectalis (aka pubo-rectal sling)
- Skeletal muscle => under somatic control*
- Most medial part of levator ani (=> most medial part of the pelvic diaphragm)*

Which structure marks the transition from internal to external anal sphincter?
Pectinate line
Where splanchnopleure meets somatopleure
This is the site of the cloacal membrane (vestigial)

What are the boundaries of the inguinal triangle?
- Lateral edge of the rectus
- Inferior epigastric artery
- Inguinal ligament

List the muscle sof the pelvic diaphragm (2 but kind of 3)
- Levator ani
- Pubococcygeous
- Iliococcygeus
- Ischiococcygeus

As the testes descends, each layer of the body wall except the _____ contributes to the covering of the spermatic cord
As the testes descends, each layer of the body wall except the transversus abdominus contributes to the covering of the spermatic cord

Between which landmarks is the largest diameter of the birth canal?
Transverse dimension of the pelvic brim
Above the pectinate line:
- Type of muscle:
- Innervation:
- Venous drainage:
- Lymph drainage:
Below the pectinate line:
- Type of muscle:
- Innervation:
- Venous drainage:
- Lymph drainage:
Above the pectinate line: endoderm
- Type of muscle: Smooth
- Innervation: Visceral, autonomic
- Pelvic splanchnics
- Venous drainage: Portal system
- Lymph drainage: With internal iliac vessels
Below the pectinate line: ectoderm
- Type of muscle: Skeletal (striated)
- Innervation: General sensory, somatomotor
- Pudendal nerve
- Venous drainage: Iliac/caval system
- Lymph drainage: Superficial inguinal nodes
A women with chronic, severe cramping of the uterus can get relief from severing or anesthetizing which of the following?
A. Pudendal nerve
B. Nerve roots in the sacral canal
C. Superior hypogastric plexus
D. Pelvic splanchnic nerves
C. Superior hypogastric plexus
Lumbar splanchnics provide sensory innervation to the uterine body and fundus

The transversalis fasciacontributes to the[layer of covering of the spermatic cord]
The transversalis fasciacontributes to theinternal spermatic fascia (and deep inguinal ring)

[direct/indirect] hernias are lateral to the inferior epigastric artery
Indirect hernias are lateral to the inferior epigastric artery

Which part of the pelvis marks the course of the pudendal nerve?
Ischial spine
Which part of the urethra constitutes the membranous urethra?
The part that passes through the UG diaphragm

A needle through the vagina can most easily sample peritoneal fluid from which location?
Rectouterine pouch

Which of the following is NOT part of the pelvic diaphragm?
- Iliococcygeus
- Pubococcygeus
- Coccygeus
- Obturator internus
- Puborectalis
d. Obturator internus
All others are part of the pelvic diaphragm
Where in the anal canal does the epithelium change from GI to skin?
Which type of epithelium is found in each place?
White line
GI = simple columnar
Skin = stratified squamous

Infection in which of the following locations might impair function of the external anal sphincter by interrupting its nerve supply?
A. Superficial perineal pouch
B. Ischioanal fossa
C. Deep perineal pouch
D. Rectouterine pouch
E. Pelvic peritoneal cavity
B. Ischioanal fossa
Inferior rectal branches of the pudendal nerve must traverse the ischioanal fosa to reach the external anal sphincter
- Rectouterine pouch and pelvic cavity have nothing to do with rectal innervation*
- Perineal pouch relates to the UG diaphragm*
How does fluid in the superficial perineal pouch drain?
Must flow in between superficial (scarpa’s) and deep investing fascia

What kind of muscle is found in the external anal sphincter?
Striated (skeletal) muscle
Which structure related to the uterus corrensponds to the male gubernaculum?
Round ligament of the uterus

Which layer forms the deep inguinal ring? (Aka beginning of the inguinal canal)
Transversalis fascia
What is the best surgical approach for removing a kidney stone to minimize bleeding?
Midline
You will avoid the major veins and arteries, which open into the renal pelvis anteriorly and posteriorly (not midline)

The space between which two ligaments forms the lesser sciatic foramen?
Sacrospinus (from 1 to sacrum)
Sacrotuberous (from 2 to sacrum)

The ventral ramus of [spinal nerve] supplies the body wall at the level of the umbilicus
The ventral ramus of T10 supplies the body wall at the level of the umbilicus
The aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle forms, contributes to, or is otherwise related to all of the following EXCEPT:
- Superficial inguinal ring
- Conjoint tendon
- External spermatic fascia
- Sheath of the rectus abdominus muscle
- Inguinal ligament
b. Conjoint tendon
* Conjoint tendon is formed by the internal oblique and transversus abdominus*
List 3 bony structures that form the boundary of the perineum
Which muscles form the superior and lateral boundaries?
- Bony
- Pubic symphysis
- Ischeal tuberosity
- Coccyx
- Muscles
- Pelvic diaphram superiorly
- Obturator internus laterally

Incontinence due to dysfunction of the internal urethral sphincter would result from damage to which of the following?
- Pudendal nerve
- Pelvic splanchnic nerves
- Sacral sympathetic trunk
- Lumbar splanchnic nerves
d. Lumbar splanchnic nerves
- Internal urethral sphincter is under sympathetic control;
- Sympathetics for pelvic function come from lumbar sympathetics
- Pelvicsplancnnics areparasympathetic
Which muscle is labeled by #2?

Pubococcygeus
- Part of levator ani*
- Muscles 1-4 are all part of the pelvic diaphragm*

What is the deepest layer of the body wall in the abdomen?
Parietal peritoneum
Which of the following is NOT a branch of the internal iliac artery?
A. Ovarian artery
B. Inferior rectal artery
C. Obturator artery
D. Inferior gluteal artery
E. Uterine artery
A. Ovarian artery
Which artery is labled by #3?
What structures does it supply blood to?

Pudendal artery
External genitalia (penis and clitoris)
Lowest one exiting the greater sciatic foramen

The internal oblique contributes to the [layer of covering of the spermatic cord]
The internal oblique contributes to the cremaster muscle

The [layer of the body wall] contributes to the external spermatic fascia and superficial inguinal ring
The external oblique contributes to the external spermatic fascia and superficial inguinal ring

Which artery is labled by #4?

Obturator artery
Follows obturator nerve through the obturator canal

Which muscles become the conjoint tendon?
Internal oblique and transversus abdominus
The external obliquecontributes to the[layer of covering of the spermatic cord]
The external obliquecontributes to theexternal eprmatic fascia (and the superficial inquinal ring)

List 3 structures that are anchored to the perineal body (aka central tendon of the perineum)
- Pelvic diaphragm
- External anal sphincter
- Urogenital diaphragm
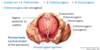
Which muscle is labeled by #4?

Ischiococcygeus
Part of the pelvic diaphragm but NOT part of levator ani

Which one of the following is in the deep perineal pouch?
A. Greater vestibular gland
B. Internal anal sphincter
C. Prostate gland
D. External urethral sphincter
E. Bulbospongiosus muscle
D. External urethral sphincter
Which structure guides the descent of the testes?
Gubernaculum
What structures are supplied by the uterine artery?
Vagina
Uterus
Ovary
Ovary alos gets supply from the ovarian artery

What are the attachments of levator ani? (3)
- Obturator internus + fascia
- Middle of pubis
- Ischial spine
Not the pelvic brim

What is the only part of body wall innervated by parasymathetics?
Penis / clitoris

Which part of the bladder is innervated by sympathetic nerves?
Trigone
- Stimulation -> holds pee in
- Parasympathetics innervate detrusor -> pushes pee out*

What is the primary structure cut in a midline episiotomy to enlarge the birth canal?
A. Anococcygeal ligament
B. Perineal body
C. Urogenital diaphragm
D. Cardinal ligaments
E. Pelvic diaphragm
B. Perineal body
Immediately posterior to the vagia, aterior ot the rectum
- Mediolateral cut would sever UG and pelic diaphragms*
- Anococcygeal ligament is posterior to the anus*
- Cardinal ligaments anchor the uterus on each side*
[direct/indirect] hernias are medial to the inferior epigastric artery
Direct hernias are medial to the inferior epigastric artery

Which muscle is labeled by #1?

Puborectalis
- Part of levator ani*
- Muscles 1-4 are all part of the pelvic diaphragm*

What is the function of the pelvic diaphragm?
Supports abdominal viscera
Helps raise intra-abdominal pressure
- Made up of the levator ani + ischiococygeus*
- Levator ani = puborectalis + pubococcygeus + iliococcygeus*

The [structure] is the abrupt termination of the posterior rectus sheath
The arcuate line is the abrupt termination of the posterior rectus sheath
Below this line, the rectus abdominus lies directly on transversalis fascia

Which abdominal muscles can rotate the trunk ipsilaterally?
Internal oblique
Which 3 bones make up the innominate bone?
Ishium
Ilium
Pubis

Which structures are at risk during prostate surgery during each of the following approaches?
- Suprapubic
- Posterior
- Suprapubic
- Pelvic plexus of veins -> risk of bleeding
- Pelvic plexus of veins drains clitoris and penis
- Posterior
- Pelvic plexus of nerves (parasympathetics
- Can result in impotence - cannot maintain an erection
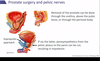
What is the difference in function between the ischiocavernosus vs. bulbospongiosus? (in the penis)
-
Ischiocavernosus
- Facilitates erection
- Contracts to constrict venous return, thus maintaining the erection
-
Bulbospongiosus
- Expells the last drops of urine during micturition
- Contracts during ejaculation
Which arteries and veins supply the penis and clitoris?
Artery = pudendal artery
Veins = Pelvic plexus of veins
Pelvic plexus of veins comes from below the pubic symphysis
*Does not follow the pudendal canal the way the artery does*
Which parts of the pelvis deliniate the narrowest diameter of the birth canal?
From one ishial spine to the other
Which artery is labled by #1?

Superior gluteal artery
(Highest one exiting the greater sciatic foramen)

Which muscle is labeled by #3?

Iliococcygeus

- Part of levator ani*
- Muscles 1-4 are all part of the pelvic diaphragm*
Which artery is mainly responsible for erection?
Deep artery of the penis
(in the middle of the corpus cavernosum on each side)

What ist he mesentary for the ovary?
Mesovarium

What is the function of the suspensory ligament of the ovary?
Connects the ovarian ligament to the abdominal wall
Carries blood vessels!

Which muscle surrounds the vestibular bulb and greater vestibular gland in the female anatomy?
What is its function?
Bulbospongiosus
- Expels last drops of urine during micturition
- Contracts during ejaculation
Same functions in male anatomy

List the contents of the UG diaphragm
(What is inside the superficial vs. deep pouch?)
- Deep pouch (aka superior)
- External urethral sphincter
- Deep transverse perinei
- Bulbourethral gland
- Superficial pouch (aka inferior, aka perineal membrane)
- External genital organs

The bulbospongiosus muscle surrounds what in the female?
A. Membranous urethra
B. Body of the clitoris
C. Labia minora
D. Cervix
E. Vestibule
E. Vestibule
Which 2 structures combine to form the ejaculatory duct?
Ampulla of ductus deferens + duct of seminal vesicle

Which artery is labled by #2?

Inferior gluteal artery

All of the following attach to the central tendon of the perineum (perineal body) EXCEPT?
A. External anal sphincter
B. Inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm
C. Obturator internus muscle
D. Deep transverse perineal muscle
E. Levator ani
C. Obturator internus muscle
Which two muscles are inside the UG diaphragm?
External urethral sphincter
Deep transverse perineal muscle
- Both skeletal muscles*
- In males, the bulbourethral gland is also within the UG diaphragm*
Which artery is labled by #5?

Superior vesicular artery
(umbilical artery in fetus)
Supplies bladder, ureter, seminal vesicle and ductus deferens

Which muscles make up the pelvic diaphragm?
- Levator ani
- Puborectalis + pubococcygus + iliococcygeus
- Ischiococcygeus (aka coccygeus)

What is the course of a direct inguinal hernia?
- Lateral to the deep inferior epigastric artery
- Through the deep in guinal ring
- Inside a persistent processus vaginalis
- Within the spermatic cord
- Under the conjoint tendon
e. Under the conjoint tendon

[direct/indirect] hernias project through the inquinal canal and deep ring
Indirect hernias project through the inquinal canal and deep ring



