233/234/235 - Renal and Urothelial Pathology, Cancer Flashcards
Which hereditary tumor syndrome is associated with upper tract urothelial cancer?
Lynch 2
Mutation in DNA mismatch repair genes
Which type of renal cell cancer will have “chicken wire vasculature”?

Clear cell carcinoma
List the 3 malignant types of renal cell carcinoma
Clear cell
Papillary
Chromophobe
Which type of cancer is most stronly associated with mutations in the VHL gene?
Clear cell RCC
Which structures constitute the urothelial system? (4)
- Kidney
- Ureter
- Bladder
- Proximal urethra
List 2 risk factors for developing urothelaial cancer
Smoking
Chronic inflammation
Inflammation can be due to toxins, cystitis, stones, schistosoma, etc
Posterior urethra
- Blood supply:
- Lymph drainage:
- Blood supply: Inferior vesical and middle rectal arteries
- Lymph drainage: Deep pelvic nodes
Anterior = internal pudendal artery, inguinal nodes
What is the classic symptom triad in patinets with tumors of the renal parenchyma?
Hematuria
Flank pain
Flank mass
All 3 present in only 10% of new RCC cases
What are 2 common presenting symptoms/signs of bladder tumors?
Gross hematuria
And/or irritative voiding symptoms
- Ureter/upper collecting system tumor: Flank pain, gross hematuria*
- Urethral: obstructive voiding symptoms, hematuria, papable mass*
What is the mainstay of treatment for localized renal cell cancer?
Surgery
Remove all or part of the kidney
- Legions are basically incurable if metastatic - refractory to chemo and radiation*
- New immune-modulation therapy is more promising*
How are kidney cancers staged?
(What is the system)
TNM staging
- Fuhrman calssification used for clear cell RCC*
- *Honestly I am between maybe 5 and infinity years away from the responsibility of staging cancer so cards on this will not be extensive sorryyy**
List 4 ways to prevent urothelial cancer
- Smoking cessation
- Fruits and veggies
- Less intake of fat and cholesterol
- Increase intake of non-chlorinated water
Antioxidants *may* be helpful, but not a ton of evidence to support
What landmarks help us determine the level of a renal vein/IVC tumor thrombus?
- Level 1:
- Level 2:
- Level 3:
- Level 4:
- Level 1: <2cm from RV ostium
- Level 2: >2cm, but below hepatic veins
- Level 3: In the intrahepatic IVC, but below hepatic veins
- Level 4: Above the hepatic veins
- Includes into the right atrium
What diagnostic studies comprise the gold standard work-up for hematuria? (4)
CT urogram (no contrast)
Cystoscpy
Digital rectal exam
PSA
New onset hematuria is concerning for bladder/urothelial cancer
Are environmental exposures more likley to contribute to renal cell carcinoma or urothelial cell carcinoma?
Urothelial
What is the key difference between a renal papillary adenoma and a papillary renal cell carcinoma?
Size
- Papillary adenomas are <1.5cm w/low nuclear grade
What is the most common type of bladder cancer?
Low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
<10% will be invasive, but likely to reccur
Which renal tumor has the lowest 5-year survival rate?
Sarcomatoid RCC

Anterior urethra
- Blood supply:
- Lymph drainage:
- Blood supply: Internal pudendal artery
- Lymph drainage: Inguinal lymph nodes
Posterior = inferior vesical and middle rectal arteries, drains into deep pelvic nodes
Schistosoma hematobium is a risk factor for what kind of cancer?
Squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder
List 2 risk factors for renal cell carcinoma
- Smoking
- Family history w/autosomal dominant genotype
A mutation in which gene is associated wtih hereditary papillary RCC?
MET oncogene on 7q31
What is the function of the VHL gene?
Degrades hypoxia-inducible factor alpha
Mutation results in increased angiogenesis
- Mutation -> Renal cell carcinoma more likely*
- Why anti-VEGF therapies may be helpful*
Which type of repro/GU cancer is most strongly associated with paraneoplastic syndromes?
What are the paraneoplastic syndromes?
Renal cell carcinoma
- Cachexia/weight loss
- Hepatic dysfunction
- Anemia
- Erythrocytosis
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypertension
- Caused by RCCs that secrete PTHrP, EPO, ACTH, and/or renin*
- Thank you @Alba!*
Which paraneoplastic condition associated with RCC may be caused by increased IL-6 production?
Stauffer’s syndrome
Is alcohol consumption a risk factor for renal cell carcinoma?
NO
What genomic abnormality is typical of most clear cell RCC?
Problem with VHL gene on 3p
Deletion, mutation, or hypermethylation
List 4 types of drugs that can be used to treat metastatic renal cancer
- Anti-VEGF drugs
- Stop tumor-associated angiogenesis
- Signal transduction inhibitors
- Tarket tyrosine kinase and mTOR pathways
- CTLA-4 inhibitors
- Checkpoint inhibitors
- PD-1, PDL-1
Metastatic renal disease is refractory to both chemotherapy and radiation
Which variant of urothelial carcinoma will show spindle cells?
Sarcomatoid - very aggressive!
In general, I think anything that has “sarcoma” in it is pretty bad?

In staging renal cell carcinoma:
What feature determines progression from T1 to T2?
What about T2 to T3?
T1 to T2 determined by size
T2 to T3 determined by invasion into adjacent structures/veins
How does does the presentation of urothelial cancer change with a mass in the ureter and upper collecting system vs. the urethra?
- Ureter/upper collecting system:
- Flank pain
- Gross hematuria
- May have clots, microhematuria, obstruction
- Urethra:
- Obstructive voiding sx
- Palpable mass
- Urethral discharge
- Hematuria
- Fistula
List 3 topical therapies that can be used to manage superficial bladder cancer
Mitiomycin
Thiotepa
BCG
What is the standard treament for tumors of the distal ureter?
Resection + ureteral re-implantation
Which type of urothelial cancer is assocaited with chronic irritation?
Squamous cell carcinoma
Risk factors include:
- Inflammation
- Cystitis
- Kidney stones
- Schistosoma
- Smoking
What is the natural course of a flat, urothelial carcinoma in situ?
Aggressive!
Can progress to invasive disease in weeks-months
Even CIS ill have high nuclear grade with +urine cytology
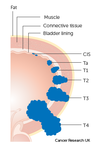
A stage T1 urothelial cancer may invade up to which layer of the bladder wall?
Lamina propria
- Will not touch the muscle*
- T2 will have invaded partway through the muscular layers*

What is the treatment for metastatic urothelial cancer?
Chemotherapy
MVAC or GC
- MVAC = Methotrexate + vinblasine + adriamycin + cysplatin
- GC = Gemcitabine + cisplastin
PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors may be helpful
Key: Metastatic urothelial cancers can be treated with chemo, metastatic renal cancers cannot
How does the managment of urethral cancer change if the tumor is in the anterior vs. posterior urethra?
- Anterior
- Ammenable to organ-preserving therapy
- Usually presents at an earlier stage
- Posterior
- Requires aggressive, multi-modality therapy
- Usually presents at a later stage
Both will require systemic chemo if locally advanced or metastatic
Which GU cancers are refractory to chemotherapy and radiation
What can bu used to treat them instead?
Metatsatic renal cell carcinoma
- Anti-VEGF
- Signal transduction inhibitors (Tyrosine kinase, MTOR)
- Anti-CTLA4 agents*
- Checkpoint inhibitors*
- Anti-PD1 or Anti-PDL1
Both are considered new-age immune modulators
Which type of renal ccell cancer will have vague, flocculent, pale cytoplasme rich in lysosomes?

Chromophobe renal cell carcioma
- Arises from collecting duct cells*
- Best prognosis of all malignant RCC*
What is the most common benign renal tumor?
Oncocytoma
Which UG cancer is more common in women than men?
Urethral urothelial carcinoma
I think this is the only one but not completely sure
Which malignant renal tumor is derived from the intercalated cells of the collecting duct?
Chromophobe RCC
What is the standard treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer?
Radial cystectomy
Often preceded by neoadjuvant MVAC or GC chemotherapy
- MVAC = Methotrexate, vinblastine, adriamycin**, cisplatin*
- GC = Gemcitabine + cysplatin*
Which cancer is the most lethal urologic cancer?
Kidney cancer
(RCC)
Will TURBT cure an invasive urothelial carcinoma?
No
- TURBT gets down to the muscular layer, but cant get through the muscle
- Invasive tumors penetrate the muscle by definition
- Gold standard to cure invasive urothelial tumors = radical cystectomy, can give neoadjuvant chemo beforehand (cisplatin)
From which cells do most urothelial carcinoma arise?
Transition cells
Most commonly in the bladder, but can affect other parts of the UG system
Transition cell carcioma = most common urothelial carcinoma
Can also have squamous and adeno
- The urothelium is made up of transition cells that line the bladder and UG lumen, plus some squamous celsl.*
- Cancer most common in the bladder b/c whatever toxins are in the lumen hang out there the longest*

Which chemotherapy agents constitute the MVAC regimen?
Methotrexate
Vinblastine
Adriamycin
Cisplatin

B - Hereditary Papillary RCC
A superficial baldder cancer becomes invasive when it invades which layer of the urothelium?
Tunica muscularis propria
List the 4 growth patterns exhibited by urothelial tumors of the bladder
Invasive
Noninvasive
Papillary
Flat
9q deletion and/or upregrulation of FGFR3 is most commonly associated with which type of cancer?
Non-muscle invasive blader cancer
What histologic finding is characteristic of malakoplakia?
Michaelis-gutman bodies
Small, laminated, calcified concretions

Which renal cell carcinomas arise from proximal convoluted tubule cells?
Clear cell RCC
Papilary RCC
Chromophobe comes from intercalated cells of the collecting duct


